预定义代理策略
为简化代理实现,Koog 提供了预定义的代理策略,以应对常见的代理用例。 以下是可用的预定义策略:
Chat 代理策略
Chat 代理策略旨在执行聊天交互过程。 它协调不同阶段、节点和工具之间的交互,以处理用户输入、执行工具并以类似聊天的方式提供响应。
概览
Chat 代理策略实现了以下代理模式:
- 接收用户输入
- 使用 LLM 处理输入
- 调用工具或提供直接响应
- 处理工具结果并继续对话
- 如果 LLM 尝试使用纯文本而非工具进行响应,则提供反馈
这种方法创建了一个会话式界面,代理可以在其中使用工具来满足用户请求。
设置与依赖项
Koog 中 Chat 代理策略的实现是通过 chatAgentStrategy 函数完成的。为了在代理代码中使该函数可用,请添加以下依赖项导入:
ai.koog.agents.ext.agent.chatAgentStrategy要使用此策略,请按照以下模式创建 AI 代理:
val chatAgent = AIAgent(
promptExecutor = promptExecutor,
toolRegistry = toolRegistry,
llmModel = model,
// Set chatAgentStrategy as the agent strategy
strategy = chatAgentStrategy()
)何时使用 Chat 代理策略
Chat 代理策略特别适用于:
- 构建需要使用工具的会话代理
- 创建可以根据用户请求执行操作的助手
- 实现需要访问外部系统或数据的聊天机器人
- 希望强制使用工具而非纯文本响应的场景
示例
下面是一个 AI 代理的代码示例,它实现了预定义的 Chat 代理策略 (chatAgentStrategy) 以及代理可能使用的工具:
val chatAgent = AIAgent(
promptExecutor = promptExecutor,
llmModel = model,
// Use chatAgentStrategy as the agent strategy
strategy = chatAgentStrategy(),
// Add tools the agent can use
toolRegistry = ToolRegistry {
tool(searchTool)
tool(weatherTool)
}
)
suspend fun main() {
// Run the agent with a user query
val result = chatAgent.run("What's the weather like today and should I bring an umbrella?")
}ReAct 策略
ReAct(推理与行动)策略是一种 AI 代理策略,它在推理和执行阶段之间交替进行,以动态处理任务并从大型语言模型(LLM)请求输出。
概览
ReAct 策略实现了以下代理模式:
- 推理当前状态并规划下一步
- 根据推理采取行动
- 观察这些行动的结果
- 重复循环
这种方法结合了推理(逐步思考问题)和行动(执行工具以收集信息或执行操作)的优势。
流程图
下面是 ReAct 策略的流程图:
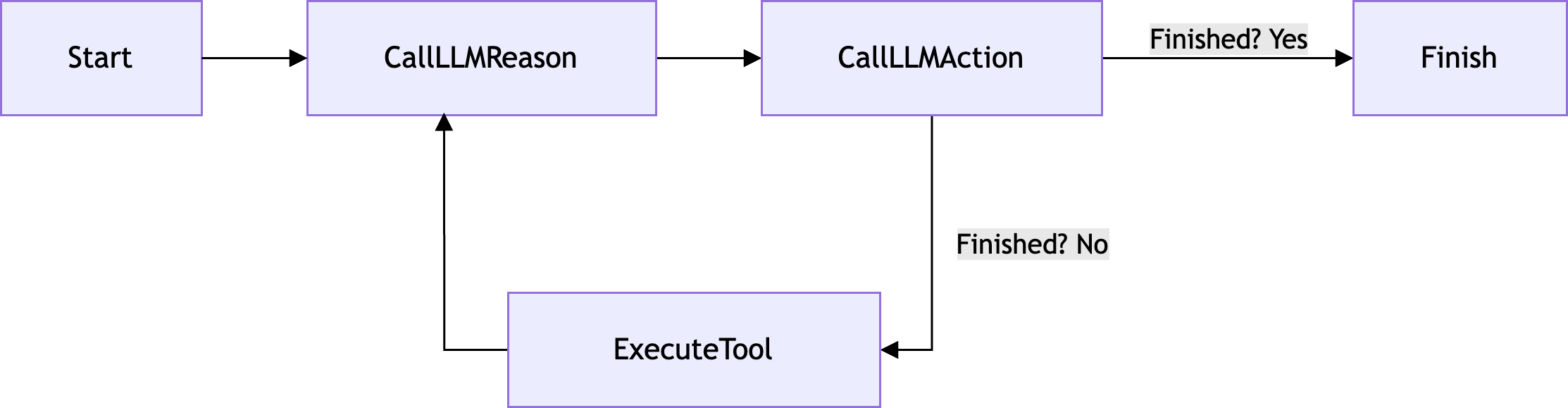
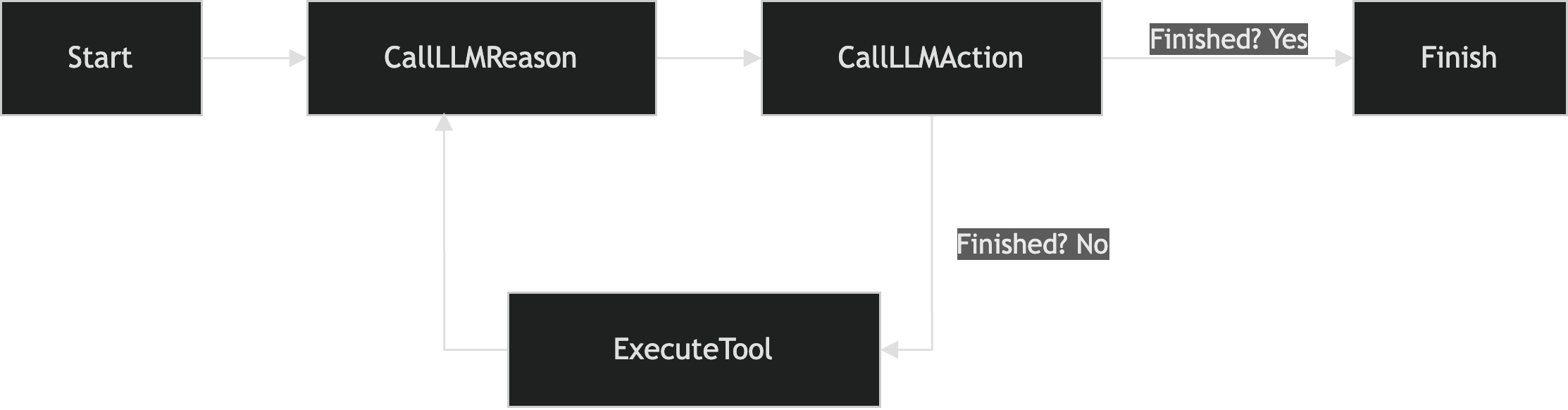
设置与依赖项
Koog 中 ReAct 策略的实现是通过 reActStrategy 函数完成的。为了在代理代码中使该函数可用,请添加以下依赖项导入:
ai.koog.agents.ext.agent.reActStrategy要使用此策略,请按照以下模式创建 AI 代理:
val reActAgent = AIAgent(
promptExecutor = promptExecutor,
toolRegistry = toolRegistry,
llmModel = model,
// Set reActStrategy as the agent strategy
strategy = reActStrategy(
// Set optional parameter values
reasoningInterval = 1,
name = "react_agent"
)
)形参
reActStrategy 函数接受以下形参:
| 形参 | 类型 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
reasoningInterval | Int | 1 | 指定推理步骤的间隔。必须大于 0。 |
name | String | re_act | 策略的名称。 |
用例示例
下面是一个 ReAct 策略如何与一个简单银行代理协同工作的示例:
1. 用户输入
用户发送初始提示。例如,这可以是一个问题,如 How much did I spend last month?。
2. 推理
代理通过用户输入和推理提示执行初始推理。推理过程可能如下所示:
I need to follow these steps:
1. Get all transactions from last month
2. Filter out deposits (positive amounts)
3. Calculate total spending3. 行动与执行,阶段 1
基于代理在上一步中定义的行动项,它运行一个工具来获取上个月的所有交易。
在这种情况下,要运行的工具是 get_transactions,以及定义的 startDate 和 endDate 实参,它们与获取上个月所有交易的请求相匹配:
{tool: "get_transactions", args: {startDate: "2025-05-19", endDate: "2025-06-18"}}该工具返回的结果可能如下所示:
[
{date: "2025-05-25", amount: -100.00, description: "Grocery Store"},
{date: "2025-05-31", amount: +1000.00, description: "Salary Deposit"},
{date: "2025-06-10", amount: -500.00, description: "Rent Payment"},
{date: "2025-06-13", amount: -200.00, description: "Utilities"}
]4. 推理
凭借工具返回的结果,代理再次执行推理,以确定其流程中的下一步:
I have the transactions. Now I need to:
1. Remove the salary deposit of +1000.00
2. Sum up the remaining transactions5. 行动与执行,阶段 2
基于之前的推理步骤,代理调用 calculate_sum 工具,该工具对作为工具实参提供的金额进行求和。由于推理还得出从交易中移除正金额的行动点,因此作为工具实参提供的金额仅为负数:
{tool: "calculate_sum", args: {amounts: [-100.00, -500.00, -200.00]}}该工具返回最终结果:
-800.006. 最终响应
代理返回最终响应(助手消息),其中包含计算出的总和:
You spent $800.00 last month on groceries, rent, and utilities.何时使用 ReAct 策略
ReAct 策略特别适用于:
- 需要多步推理的复杂任务
- 代理需要在提供最终答案之前收集信息的场景
- 从分解为更小步骤中受益的问题
- 需要分析性思维和工具使用的任务
示例
下面是一个 AI 代理的代码示例,它实现了预定义的 ReAct 策略 (reActStrategy) 以及代理可能使用的工具:
val bankingAgent = AIAgent(
promptExecutor = promptExecutor,
llmModel = model,
// Use reActStrategy as the agent strategy
strategy = reActStrategy(
reasoningInterval = 1,
name = "banking_agent"
),
// Add tools the agent can use
toolRegistry = ToolRegistry {
tool(getTransactions)
tool(calculateSum)
}
)
suspend fun main() {
// Run the agent with a user query
val result = bankingAgent.run("How much did I spend last month?")
}