自訂策略圖
策略圖是 Koog 框架中代理工作流程的骨幹。它們定義了代理如何處理輸入、與工具互動以及生成輸出。策略圖由節點和邊緣連接而成,執行流程則由條件決定。
建立策略圖可讓您根據特定需求調整代理的行為,無論您是建立一個簡單的聊天機器人、一個複雜的資料處理管道,還是介於兩者之間的任何事物。
策略圖架構
從高層次來看,策略圖包含以下組件:
- 策略 (Strategy):圖的頂層容器,使用
strategy函數建立,並透過泛型參數指定輸入和輸出類型。 - 子圖 (Subgraphs):圖的區段,可以有自己的工具集和上下文。
- 節點 (Nodes):工作流程中的個別操作或轉換。
- 邊緣 (Edges):定義轉換條件和轉換的節點之間的連接。
策略圖始於一個名為 nodeStart 的特殊節點,並終止於 nodeFinish。這些節點之間的路徑由圖中指定的邊緣和條件決定。
策略圖組件
節點 (Nodes)
節點是策略圖的構成要素。每個節點都代表一個特定的操作。
Koog 框架提供了預定義的節點,也允許您使用 node 函數建立自訂節點。
邊緣 (Edges)
邊緣連接節點並定義策略圖中的操作流程。邊緣使用 edge 函數和 forwardTo 中綴函數建立:
edge(sourceNode forwardTo targetNode)條件 (Conditions)
條件決定何時遵循策略圖中的特定邊緣。條件有幾種類型,以下是一些常見的類型:
| 條件類型 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| onCondition | 一種通用條件,接受一個返回布林值的 Lambda 表達式。 |
| onToolCall | 當 LLM 呼叫工具時匹配的條件。 |
| onAssistantMessage | 當 LLM 以訊息回應時匹配的條件。 |
| onMultipleToolCalls | 當 LLM 呼叫多個工具時匹配的條件。 |
| onToolNotCalled | 當 LLM 未呼叫工具時匹配的條件。 |
您可以使用 transformed 函數在將輸出傳遞給目標節點之前對其進行轉換:
edge(sourceNode forwardTo targetNode
onCondition { input -> input.length > 10 }
transformed { input -> input.uppercase() }
)子圖 (Subgraphs)
子圖是策略圖的區段,它們擁有自己的工具集和上下文。策略圖可以包含多個子圖。每個子圖都使用 subgraph 函數定義:
val strategy = strategy<Input, Output>("strategy-name") {
val firstSubgraph by subgraph<FirstInput, FirstOutput>("first") {
// Define nodes and edges for this subgraph
}
val secondSubgraph by subgraph<SecondInput, SecondOutput>("second") {
// Define nodes and edges for this subgraph
}
}子圖可以使用工具註冊表中的任何工具。但是,您可以指定此註冊表中可用於子圖的工具子集,並將其作為參數傳遞給 subgraph 函數:
val strategy = strategy<Input, Output>("strategy-name") {
val firstSubgraph by subgraph<FirstInput, FirstOutput>(
name = "first",
tools = listOf(someTool)
) {
// Define nodes and edges for this subgraph
}
// Define other subgraphs
}基本策略圖建立
基本策略圖的操作如下:
- 將輸入傳送給 LLM。
- 如果 LLM 以訊息回應,則結束流程。
- 如果 LLM 呼叫工具,則執行工具。
- 將工具結果傳回給 LLM。
- 如果 LLM 以訊息回應,則結束流程。
- 如果 LLM 呼叫另一個工具,則執行工具,並從步驟 4 重複流程。
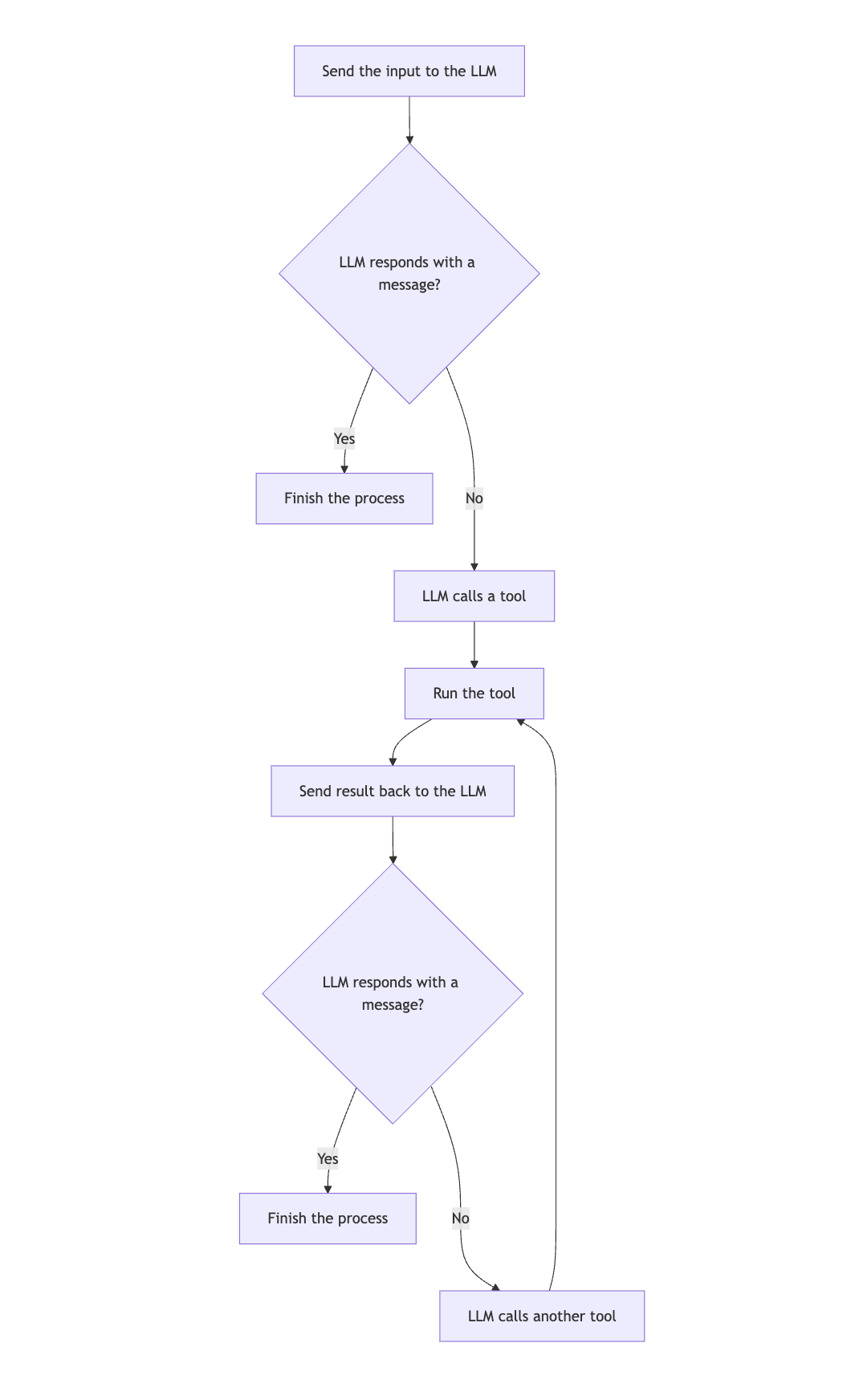
以下是一個基本策略圖的範例:
val myStrategy = strategy<String, String>("my-strategy") {
val nodeCallLLM by nodeLLMRequest()
val executeToolCall by nodeExecuteTool()
val sendToolResult by nodeLLMSendToolResult()
edge(nodeStart forwardTo nodeCallLLM)
edge(nodeCallLLM forwardTo nodeFinish onAssistantMessage { true })
edge(nodeCallLLM forwardTo executeToolCall onToolCall { true })
edge(executeToolCall forwardTo sendToolResult)
edge(sendToolResult forwardTo nodeFinish onAssistantMessage { true })
edge(sendToolResult forwardTo executeToolCall onToolCall { true })
}可視化策略圖
在 JVM 上,您可以為策略圖產生 Mermaid 狀態圖。
對於上一個範例中建立的圖,您可以執行:
val mermaidDiagram: String = myStrategy.asMermaidDiagram()
println(mermaidDiagram)輸出將是:
---
title: my-strategy
---
stateDiagram
state "nodeCallLLM" as nodeCallLLM
state "executeToolCall" as executeToolCall
state "sendToolResult" as sendToolResult
[*] --> nodeCallLLM
nodeCallLLM --> [*] : transformed
nodeCallLLM --> executeToolCall : onCondition
executeToolCall --> sendToolResult
sendToolResult --> [*] : transformed
sendToolResult --> executeToolCall : onCondition進階策略技巧
歷史壓縮 (History compression)
對於長時間執行的對話,歷史可能會變得很大並消耗大量 token。要了解如何壓縮歷史,請參閱 歷史壓縮。
並行工具執行 (Parallel tool execution)
對於需要並行執行多個工具的工作流程,您可以使用 nodeExecuteMultipleTools 節點:
val executeMultipleTools by nodeExecuteMultipleTools()
val processMultipleResults by nodeLLMSendMultipleToolResults()
edge(someNode forwardTo executeMultipleTools)
edge(executeMultipleTools forwardTo processMultipleResults)您還可以使用 toParallelToolCallsRaw 擴充函數來串流資料:
parseMarkdownStreamToBooks(markdownStream).toParallelToolCallsRaw(BookTool::class).collect()要了解更多,請參閱 工具。
並行節點執行 (Parallel node execution)
並行節點執行可讓您同時執行多個節點,從而提高效能並實現複雜的工作流程。
若要啟動並行節點執行,請使用 parallel 方法:
val calc by parallel<String, Int>(
nodeCalcTokens, nodeCalcSymbols, nodeCalcWords,
) {
selectByMax { it }
}上面的程式碼建立了一個名為 calc 的節點,它會並行執行 nodeCalcTokens、nodeCalcSymbols 和 nodeCalcWords 節點,並將結果作為 AsyncParallelResult 的實例返回。
有關並行節點執行以及詳細參考的更多資訊,請參閱 並行節點執行。
條件分支 (Conditional branching)
對於需要根據特定條件採取不同路徑的複雜工作流程,您可以使用條件分支:
val branchA by node<String, String> { input ->
// Logic for branch A
"Branch A: $input"
}
val branchB by node<String, String> { input ->
// Logic for branch B
"Branch B: $input"
}
edge(
(someNode forwardTo branchA)
onCondition { input -> input.contains("A") }
)
edge(
(someNode forwardTo branchB)
onCondition { input -> input.contains("B") }
)最佳實踐
當您建立自訂策略圖時,請遵循以下最佳實踐:
- 保持簡單。從簡單的圖開始,然後根據需要增加複雜度。
- 為您的節點和邊緣提供描述性名稱,以使圖更容易理解。
- 處理所有可能的路徑和邊緣情況。
- 使用各種輸入測試您的圖,以確保其行為符合預期。
- 記錄您的圖的目的和行為,以供將來參考。
- 使用預定義的策略或常見模式作為起點。
- 對於長時間執行的對話,請使用歷史壓縮以減少 token 使用量。
- 使用子圖來組織您的圖並管理工具存取。
使用範例
語氣分析策略 (Tone analysis strategy)
語氣分析策略是包含歷史壓縮的基於工具策略的一個好範例:
fun toneStrategy(name: String, toolRegistry: ToolRegistry): AIAgentGraphStrategy<String, String> {
return strategy(name) {
val nodeSendInput by nodeLLMRequest()
val nodeExecuteTool by nodeExecuteTool()
val nodeSendToolResult by nodeLLMSendToolResult()
val nodeCompressHistory by nodeLLMCompressHistory<ReceivedToolResult>()
// Define the flow of the agent
edge(nodeStart forwardTo nodeSendInput)
// If the LLM responds with a message, finish
edge(
(nodeSendInput forwardTo nodeFinish)
onAssistantMessage { true }
)
// If the LLM calls a tool, execute it
edge(
(nodeSendInput forwardTo nodeExecuteTool)
onToolCall { true }
)
// If the history gets too large, compress it
edge(
(nodeExecuteTool forwardTo nodeCompressHistory)
onCondition { _ -> llm.readSession { prompt.messages.size > 100 } }
)
edge(nodeCompressHistory forwardTo nodeSendToolResult)
// Otherwise, send the tool result directly
edge(
(nodeExecuteTool forwardTo nodeSendToolResult)
onCondition { _ -> llm.readSession { prompt.messages.size <= 100 } }
)
// If the LLM calls another tool, execute it
edge(
(nodeSendToolResult forwardTo nodeExecuteTool)
onToolCall { true }
)
// If the LLM responds with a message, finish
edge(
(nodeSendToolResult forwardTo nodeFinish)
onAssistantMessage { true }
)
}
}此策略執行以下操作:
- 將輸入傳送給 LLM。
- 如果 LLM 以訊息回應,策略結束流程。
- 如果 LLM 呼叫工具,策略執行工具。
- 如果歷史過大(超過 100 條訊息),策略在傳送工具結果之前壓縮歷史。
- 否則,策略直接傳送工具結果。
- 如果 LLM 呼叫另一個工具,策略執行它。
- 如果 LLM 以訊息回應,策略結束流程。
故障排除
建立自訂策略圖時,您可能會遇到一些常見問題。以下是一些故障排除提示:
圖未能到達結束節點
如果您的圖未到達結束節點,請檢查以下內容:
- 從起始節點的所有路徑最終都通向結束節點。
- 您的條件沒有過於嚴格,導致邊緣無法遵循。
- 圖中沒有沒有退出條件的循環。
工具呼叫未運行
如果工具呼叫未運行,請檢查以下內容:
- 工具已在工具註冊表中正確註冊。
- 從 LLM 節點到工具執行節點的邊緣具有正確的條件 (
onToolCall { true })。
歷史過大
如果您的歷史過大並消耗了太多 token,請考慮以下內容:
- 添加歷史壓縮節點。
- 使用條件檢查歷史大小,並在歷史過大時壓縮它。
- 使用更積極的壓縮策略(例如,
FromLastNMessages帶有較小的 N 值)。
圖行為異常
如果您的圖採用了意外的分支,請檢查以下內容:
- 您的條件定義是否正確。
- 條件是否按預期順序評估(邊緣按其定義順序檢查)。
- 您沒有意外地用更一般的條件覆蓋了特定條件。
出現效能問題
如果您的圖出現效能問題,請考慮以下內容:
- 透過移除不必要的節點和邊緣來簡化圖。
- 對於獨立操作,使用並行工具執行。
- 壓縮歷史。
- 使用更高效的節點和操作。
