在应用中使用多平台资源
当你为项目设置了资源后,构建项目以生成特殊的 Res 类,该类提供对资源的访问。要重新生成 Res 类和所有资源访问器,请再次构建项目或在 IDE 中重新导入项目。
之后,你可以使用生成的类从代码或外部库访问已配置的多平台资源。
导入生成的类
要使用准备好的资源,请导入生成的类,例如:
import project.composeapp.generated.resources.Res
import project.composeapp.generated.resources.example_image此处:
project是你的项目名称composeapp是你放置资源目录的模块Res是生成类的默认名称example_image是composeResources/drawable目录中图片文件的名称(例如,example_image.png)。
自定义访问器类生成
你可以使用 Gradle 设置自定义生成的 Res 类以满足你的需求。
在 build.gradle.kts 文件的 compose.resources {} 代码块中,你可以指定影响项目 Res 类生成方式的多个设置。 一个配置示例类似这样:
compose.resources {
publicResClass = false
packageOfResClass = "me.sample.library.resources"
generateResClass = auto
}publicResClass设置为true会使生成的Res类变为公共(public)。默认情况下,生成的类是内部(internal)的。packageOfResClass允许你将生成的Res类分配给特定的包(以便在代码中访问,以及在最终 artifact 中隔离)。默认情况下,Compose Multiplatform 将{group name}.{module name}.generated.resources包分配给该类。generateResClass设置为always会使项目无条件地生成Res类。当资源库仅通过传递依赖(transitively)可用时,这可能很有用。默认情况下,Compose Multiplatform 使用auto值,仅当当前项目对资源库有显式的implementation或api依赖项时才生成Res类。
资源使用
图片
你可以将可绘制资源作为简单图片、栅格化图片或 XML 矢量图访问。 SVG 图片在所有平台都支持,Android 除外。
要将可绘制资源作为
Painter图片访问,请使用painterResource()函数:kotlin@Composable fun painterResource(resource: DrawableResource): Painter {...}painterResource()函数接受一个资源路径并返回一个Painter值。该函数在所有目标平台(web 除外)上同步工作。对于 web 目标平台,它在首次重组时返回一个空的Painter,该Painter会在后续重组时被加载的图片替换。painterResource()会为栅格化图片格式(例如.png、.jpg、.bmp、.webp)加载BitmapPainter,或为 Android XML 矢量可绘制格式加载VectorPainter。- XML 矢量可绘制文件与 Android 的格式相同,但它们不支持对 Android 资源的外部引用。
要将可绘制资源作为
ImageBitmap栅格化图片访问,请使用imageResource()函数:kotlin@Composable fun imageResource(resource: DrawableResource): ImageBitmap {...}要将可绘制资源作为
ImageVectorXML 矢量图访问,请使用vectorResource()函数:kotlin@Composable fun vectorResource(resource: DrawableResource): ImageVector {...}
以下是如何在 Compose Multiplatform 代码中访问图片的示例:
Image(
painter = painterResource(Res.drawable.my_image),
contentDescription = null
)图标
你可以使用 Material Symbols 库中的 Android XML 矢量图标:
打开 Google Fonts Icons 图库,选择一个图标,转到 Android 选项卡,然后点击 下载。
将下载的 XML 图标文件添加到你的多平台资源的
drawable目录中。打开 XML 图标文件,并将
android:fillColor设置为#000000。移除任何其他用于颜色调整的 Android 特有属性,例如android:tint。Before:
xml<vector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:width="24dp" android:height="24dp" android:viewportWidth="960" android:viewportHeight="960" android:tint="?attr/colorControlNormal"> <path android:fillColor="@android:color/white" android:pathData="..."/> </vector>After:
xml<vector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:width="24dp" android:height="24dp" android:viewportWidth="960" android:viewportHeight="960"> <path android:fillColor="#000000" android:pathData="..."/> </vector>构建项目以生成资源访问器,或让 Kotlin Multiplatform plugin 自动处理。
以下是如何在 Compose Multiplatform 代码中访问图标并使用 colorFilter 形参调整颜色的示例:
Image(
painter = painterResource(Res.drawable.ic_sample_icon),
contentDescription = "Sample icon",
modifier = Modifier.size(24.dp),
colorFilter = ColorFilter.tint(Color.Blue)
)字符串
将所有字符串资源存储在 composeResources/values 目录中的 XML 文件中。 每个文件中的每个项都会生成一个静态访问器。
关于如何为不同区域设置本地化字符串的更多信息,请参考字符串本地化指南。
简单字符串
要存储一个简单字符串,请向 XML 添加一个 <string> 元素:
<resources>
<string name="app_name">My awesome app</string>
<string name="title">Some title</string>
</resources>要将字符串资源作为 String 获取,请使用以下代码:
@Composable
fun stringResource(resource: StringResource): String {...}
@Composable
fun stringResource(resource: StringResource, vararg formatArgs: Any): String {...}例如:
Text(stringResource(Res.string.app_name))suspend fun getString(resource: StringResource): String
suspend fun getString(resource: StringResource, vararg formatArgs: Any): String例如:
coroutineScope.launch {
val appName = getString(Res.string.app_name)
}你可以在字符串资源中使用特殊符号:
– 换行符\t– 制表符\uXXXX– 特定 Unicode 字符
你无需像对于 Android 字符串那样转义特殊的 XML 字符,如 "@" 或 "?"。
字符串模板
目前,实参对字符串资源有基本支持。 创建模板时,使用 %<number> 格式将实参放置在字符串中,并包含 $d 或 $s 后缀以指示它是一个变量占位符而不是简单文本。 例如:
<resources>
<string name="str_template">Hello, %2$s! You have %1$d new messages.</string>
</resources>创建并导入字符串模板资源后,你可以在引用它时按正确顺序传递占位符的实参:
Text(stringResource(Res.string.str_template, 100, "User_name"))$s 和 $d 后缀之间没有区别,也不支持其他后缀。 你可以在资源字符串中放置 %1$s 占位符,并用它来显示一个小数,例如:
Text(stringResource(Res.string.str_template, "User_name", 100.1f))字符串数组
你可以将相关字符串分组到一个数组中,并自动将它们作为 List<String> 对象访问:
<resources>
<string name="app_name">My awesome app</string>
<string name="title">Some title</string>
<string-array name="str_arr">
<item>item \u2605</item>
<item>item \u2318</item>
<item>item \u00BD</item>
</string-array>
</resources>要获取对应的列表,请使用以下代码:
@Composable
fun stringArrayResource(resource: StringArrayResource): List<String> {...}例如:
val arr = stringArrayResource(Res.array.str_arr)
if (arr.isNotEmpty()) Text(arr[0])suspend fun getStringArray(resource: StringArrayResource): List<String>例如:
coroutineScope.launch {
val appName = getStringArray(Res.array.str_arr)
}复数
当你的 UI 显示某物的数量时,你可能希望支持相同事物的不同数量的语法一致性(一本_书_,多本_书_等),而无需在程序上创建不相关的字符串。
Compose Multiplatform 中的概念和基本实现与 Android 上的数量字符串相同。 有关在项目中复数用法的最佳实践和细微差别,请参见 Android 文档。
- 支持的变体有
zero、one、two、few、many和other。请注意,并非所有变体都考虑所有语言:例如,zero对于英语来说被忽略,因为它与除 1 以外的任何其他复数相同。请依赖语言专家了解该语言实际要求的区别。 - 通常可以通过使用数量中性的表述方式(例如“书籍:1”)来避免使用数量字符串。如果这不会恶化用户体验,
要定义一个复数,请将一个 <plurals> 元素添加到 composeResources/values 目录中的任何 .xml 文件中。 复数集合是一个简单资源,使用 name 属性引用(而不是 XML 文件的名称)。 因此,你可以将 plurals 资源与其他简单资源合并在一个 XML 文件中,放在一个 <resources> 元素下:
<resources>
<string name="app_name">My awesome app</string>
<string name="title">Some title</string>
<plurals name="new_message">
<item quantity="one">%1$d new message</item>
<item quantity="other">%1$d new messages</item>
</plurals>
</resources>要将复数作为 String 访问,请使用以下代码:
@Composable
fun pluralStringResource(resource: PluralStringResource, quantity: Int): String {...}
@Composable
fun pluralStringResource(resource: PluralStringResource, quantity: Int, vararg formatArgs: Any): String {...}例如:
Text(pluralStringResource(Res.plurals.new_message, 1, 1))suspend fun getPluralString(resource: PluralStringResource, quantity: Int): String
suspend fun getPluralString(resource: PluralStringResource, quantity: Int, vararg formatArgs: Any): String例如:
coroutineScope.launch {
val appName = getPluralString(Res.plurals.new_message, 1, 1)
}字体
将自定义字体存储在 composeResources/font 目录中,文件格式为 *.ttf 或 *.otf。
要将字体加载为 Font 类型,请使用 Font() 可组合函数:
@Composable
fun Font(
resource: FontResource,
weight: FontWeight = FontWeight.Normal,
style: FontStyle = FontStyle.Normal
): Font例如:
@Composable
private fun InterTypography(): Typography {
val interFont = FontFamily(
Font(Res.font.Inter_24pt_Regular, FontWeight.Normal),
Font(Res.font.Inter_24pt_SemiBold, FontWeight.Bold),
)
return with(MaterialTheme.typography) {
copy(
displayLarge = displayLarge.copy(fontFamily = interFont, fontWeight = FontWeight.Bold),
displayMedium = displayMedium.copy(fontFamily = interFont, fontWeight = FontWeight.Bold),
displaySmall = displaySmall.copy(fontFamily = interFont, fontWeight = FontWeight.Bold),
headlineLarge = headlineLarge.copy(fontFamily = interFont, fontWeight = FontWeight.Bold),
headlineMedium = headlineMedium.copy(fontFamily = interFont, fontWeight = FontWeight.Bold),
headlineSmall = headlineSmall.copy(fontFamily = interFont, fontWeight = FontWeight.Bold),
titleLarge = titleLarge.copy(fontFamily = interFont, fontWeight = FontWeight.Bold),
titleMedium = titleMedium.copy(fontFamily = interFont, fontWeight = FontWeight.Bold),
titleSmall = titleSmall.copy(fontFamily = interFont, fontWeight = FontWeight.Bold),
labelLarge = labelLarge.copy(fontFamily = interFont, fontWeight = FontWeight.Normal),
labelMedium = labelMedium.copy(fontFamily = interFont, fontWeight = FontWeight.Normal),
labelSmall = labelSmall.copy(fontFamily = interFont, fontWeight = FontWeight.Normal),
bodyLarge = bodyLarge.copy(fontFamily = interFont, fontWeight = FontWeight.Normal),
bodyMedium = bodyMedium.copy(fontFamily = interFont, fontWeight = FontWeight.Normal),
bodySmall = bodySmall.copy(fontFamily = interFont, fontWeight = FontWeight.Normal),
)
}
}{initial-collapse-state="collapsed" collapsible="true" collapsed-title="@Composable private fun InterTypography(): Typography
当
Font是可组合项时,请确保其依赖组件(例如TextStyle和Typography)也是可组合项。
为了在 web 目标平台支持表情符号或阿拉伯语脚本等特殊字符,你需要将相应的字体添加到资源中,并预加载回退字体。
原始文件
要将任意原始文件加载为字节数组,请使用 Res.readBytes(path) 函数:
suspend fun readBytes(path: String): ByteArray你可以将原始文件放在 composeResources/files 目录中,并在其中创建任何层级。
例如,要访问原始文件,请使用以下代码:
var bytes by remember {
mutableStateOf(ByteArray(0))
}
LaunchedEffect(Unit) {
bytes = Res.readBytes("files/myDir/someFile.bin")
}
Text(bytes.decodeToString())coroutineScope.launch {
val bytes = Res.readBytes("files/myDir/someFile.bin")
}将字节数组转换为图片
如果你正在读取的文件是位图(JPEG、PNG、BMP、WEBP)或 XML 矢量图片,你可以使用以下函数将其转换为适合 Image() 可组合项的 ImageBitmap 或 ImageVector 对象。
如原始文件部分所示访问原始文件,然后将结果传递给可组合项:
// bytes = Res.readBytes("files/example.png")
Image(bytes.decodeToImageBitmap(), null)
// bytes = Res.readBytes("files/example.xml")
Image(bytes.decodeToImageVector(LocalDensity.current), null)除了 Android 之外,在所有平台你还可以将 SVG 文件转换为 Painter 对象:
// bytes = Res.readBytes("files/example.svg")
Image(bytes.decodeToSvgPainter(LocalDensity.current), null)资源和字符串 ID 的生成 map
为了方便访问,Compose Multiplatform 还将资源与字符串 ID 映射。你可以通过使用文件名作为键来访问它们:
val Res.allDrawableResources: Map<String, DrawableResource>
val Res.allStringResources: Map<String, StringResource>
val Res.allStringArrayResources: Map<String, StringArrayResource>
val Res.allPluralStringResources: Map<String, PluralStringResource>
val Res.allFontResources: Map<String, FontResource>将映射的资源传递给可组合项的示例:
Image(painterResource(Res.allDrawableResources["compose_multiplatform"]!!), null)Compose Multiplatform 资源作为 Android assets
从 Compose Multiplatform 1.7.0 开始,所有多平台资源都打包到 Android assets 中。 这使 Android Studio 能够为 Android 源代码集中的 Compose Multiplatform 可组合项生成预览。
Android Studio 预览仅适用于 Android 源代码集中的可组合项。 它们还需要最新版本的 AGP 之一:8.5.2、8.6.0-rc01 或 8.7.0-alpha04。
将 Multiplatform 资源用作 Android assets 也使得从 WebView 和媒体播放器组件在 Android 上直接访问成为可能,因为资源可以通过简单的路径访问,例如 Res.getUri("files/index.html")。
一个 Android 可组合项显示资源 HTML 页面,其中包含指向资源图片的链接的示例:
// androidMain/kotlin/com/example/webview/App.kt
@OptIn(ExperimentalResourceApi::class)
@Composable
@Preview
fun App() {
MaterialTheme {
val uri = Res.getUri("files/webview/index.html")
// Adding a WebView inside AndroidView with layout as full screen.
AndroidView(factory = {
WebView(it).apply {
layoutParams = ViewGroup.LayoutParams(
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT,
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT
)
}
}, update = {
it.loadUrl(uri)
})
}
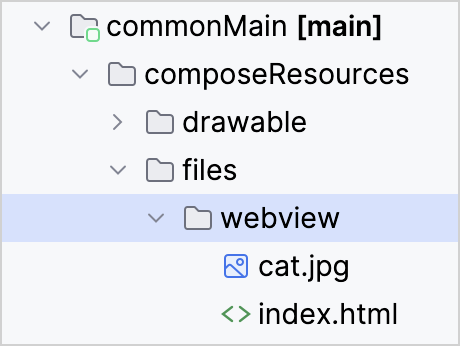
}该示例适用于这个简单的 HTML 文件:
<html>
<header>
<title>
Cat Resource
</title>
</header>
<body>
<img src="cat.jpg">
</body>
</html>此示例中的两个资源文件都位于 commonMain 源代码集中:
web 目标平台的资源预加载
字体和图片等 web 资源使用 fetch API 异步加载。在初始加载期间或网络连接较慢时,资源获取可能导致视觉故障,例如 FOUT 或显示占位符而不是图片。
此问题的一个典型示例是,当 Text() 组件包含自定义字体中的文本时,但包含必要字形的字体仍在加载。在这种情况下,用户可能会暂时看到默认字体中的文本,甚至看到空框和问号而不是字符。同样,对于图片或可绘制文件,用户可能会看到空白或黑框等占位符,直到资源完全加载。
为了防止视觉故障,你可以使用内置浏览器资源预加载功能、Compose Multiplatform 预加载 API,或两者的结合。
使用浏览器功能预加载资源
在现代浏览器中,你可以使用带有 rel="preload" 属性的 <link> 标签预加载资源。 此属性指示浏览器在应用程序启动之前优先下载和缓存字体和图片等资源,确保这些资源及早可用。
例如,要在浏览器中启用字体预加载:
- 构建应用程序的 web 分发:
./gradlew :composeApp:wasmJsBrowserDistribution- 在生成的
dist目录中找到所需资源并保存路径。 - 打开
wasmJsMain/resources/index.html文件,并在<head>元素内添加一个<link>标签。 - 将
href属性设置为资源路径:
<link rel="preload" href="./composeResources/username.composeapp.generated.resources/font/FiraMono-Regular.ttf" as="fetch" type="font/ttf" crossorigin/>使用 Compose Multiplatform 预加载 API
即使你已经在浏览器中预加载了资源,它们仍然作为原始字节缓存,需要转换为适合渲染的格式,例如 FontResource 和 DrawableResource。当应用程序首次请求资源时,转换是异步进行的,这可能再次导致闪烁。为了进一步优化体验,Compose Multiplatform 资源有自己的内部缓存,用于存储资源的高级表示,这些表示也可以预加载。
Compose Multiplatform 1.8.0 引入了一个实验性的 API,用于在 web 目标平台预加载字体和图片资源:preloadFont()、preloadImageBitmap() 和 preloadImageVector()。
此外,如果你需要表情符号等特殊字符,可以设置不同于默认捆绑选项的回退字体。 要指定回退字体,请使用 FontFamily.Resolver.preload() 方法。
以下示例演示了如何使用预加载和回退字体:
import androidx.compose.foundation.background
import androidx.compose.foundation.clickable
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Box
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.fillMaxSize
import androidx.compose.material3.CircularProgressIndicator
import androidx.compose.runtime.*
import androidx.compose.ui.*
import androidx.compose.ui.graphics.Color
import androidx.compose.ui.platform.LocalFontFamilyResolver
import androidx.compose.ui.text.font.FontFamily
import androidx.compose.ui.text.font.FontStyle
import androidx.compose.ui.text.font.FontWeight
import androidx.compose.ui.window.CanvasBasedWindow
import components.resources.demo.shared.generated.resources.*
import components.resources.demo.shared.generated.resources.NotoColorEmoji
import components.resources.demo.shared.generated.resources.Res
import components.resources.demo.shared.generated.resources.Workbench_Regular
import components.resources.demo.shared.generated.resources.font_awesome
import org.jetbrains.compose.resources.ExperimentalResourceApi
import org.jetbrains.compose.resources.configureWebResources
import org.jetbrains.compose.resources.demo.shared.UseResources
import org.jetbrains.compose.resources.preloadFont
@OptIn(ExperimentalComposeUiApi::class, ExperimentalResourceApi::class, InternalComposeUiApi::class)
fun main() {
configureWebResources {
// Overrides the resource location
resourcePathMapping { path -> "./$path" }
}
CanvasBasedWindow("Resources + K/Wasm") {
val font1 by preloadFont(Res.font.Workbench_Regular)
val font2 by preloadFont(Res.font.font_awesome, FontWeight.Normal, FontStyle.Normal)
val emojiFont = preloadFont(Res.font.NotoColorEmoji).value
var fontsFallbackInitialized by remember { mutableStateOf(false) }
// Uses the preloaded resource for the app's content
UseResources()
if (font1 != null && font2 != null && emojiFont != null && fontsFallbackInitialized) {
println("Fonts are ready") // 字体已准备就绪
} else {
// Displays the progress indicator to address a FOUT or the app being temporarily non-functional during loading
// 显示进度指示器以解决 FOUT 或应用程序在加载期间暂时无法运行的问题
Box(modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize().background(Color.White.copy(alpha = 0.8f)).clickable { }) {
CircularProgressIndicator(modifier = Modifier.align(Alignment.Center))
}
println("Fonts are not ready yet") // 字体尚未准备就绪
}
val fontFamilyResolver = LocalFontFamilyResolver.current
LaunchedEffect(fontFamilyResolver, emojiFont) {
if (emojiFont != null) {
// Preloads a fallback font with emojis to render missing glyphs that are not supported by the bundled font
// 预加载带有表情符号的回退字体,以渲染捆绑字体不支持的缺失字形
fontFamilyResolver.preload(FontFamily(listOf(emojiFont)))
fontsFallbackInitialized = true
}
}
}
}与其他库和资源的交互
从外部库访问多平台资源
如果你想使用项目中包含的其他库处理多平台资源,可以将平台特有的文件路径传递给这些其他 API。 要获取平台特有的路径,请使用项目的资源路径调用 Res.getUri() 函数:
val uri = Res.getUri("files/my_video.mp4")现在 uri 变量包含文件的绝对路径,任何外部库都可以使用该路径以适合自己的方式访问该文件。
对于 Android 特有的用途,多平台资源也会打包为 Android assets。
远程文件
在资源库的上下文(context)中,只有作为应用程序一部分的文件才被视为资源。
你可以使用专门的库通过 URL 从互联网加载远程文件:
使用 Java 资源
虽然你可以将 Java 资源与 Compose Multiplatform 一起使用,但它们无法受益于框架提供的扩展特性:生成的访问器、多模块支持、本地化等。 考虑完全过渡到多平台资源库以释放该潜力。
随着 Compose Multiplatform 1.7.0 的发布,compose.ui 包中可用的资源 API 已被弃用。 如果你仍然需要使用 Java 资源,请将以下实现复制到你的项目,以确保在升级到 Compose Multiplatform 1.7.0 或更高版本后代码正常工作:
@Composable
internal fun painterResource(
resourcePath: String
): Painter = when (resourcePath.substringAfterLast(".")) {
"svg" -> rememberSvgResource(resourcePath)
"xml" -> rememberVectorXmlResource(resourcePath)
else -> rememberBitmapResource(resourcePath)
}
@Composable
internal fun rememberBitmapResource(path: String): Painter {
return remember(path) { BitmapPainter(readResourceBytes(path).decodeToImageBitmap()) }
}
@Composable
internal fun rememberVectorXmlResource(path: String): Painter {
val density = LocalDensity.current
val imageVector = remember(density, path) { readResourceBytes(path).decodeToImageVector(density) }
return rememberVectorPainter(imageVector)
}
@Composable
internal fun rememberSvgResource(path: String): Painter {
val density = LocalDensity.current
return remember(density, path) { readResourceBytes(path).decodeToSvgPainter(density) }
}
private object ResourceLoader
private fun readResourceBytes(resourcePath: String) =
ResourceLoader.javaClass.classLoader.getResourceAsStream(resourcePath).readAllBytes()