在您的應用程式中使用多平台資源
當您已為專案設定好資源後,請建置專案以產生特殊的 Res 類別,該類別提供資源存取。若要重新產生 Res 類別及所有資源存取器,請再次建置專案或在 IDE 中重新匯入專案。
之後,您可以從程式碼或外部函式庫中使用產生的類別來存取已配置的多平台資源。
匯入產生的類別
若要使用已準備好的資源,請匯入產生的類別,例如:
import project.composeapp.generated.resources.Res
import project.composeapp.generated.resources.example_image這裡:
project是您的專案名稱composeapp是您放置資源目錄的模組Res是產生類別的預設名稱example_image是composeResources/drawable目錄中的影像檔案名稱(例如example_image.png)。
自訂存取器類別產生
您可以使用 Gradle 設定來自訂產生的 Res 類別,以符合您的需求。
在 build.gradle.kts 檔案的 compose.resources {} 區塊中,您可以指定多項設定,這些設定會影響專案 Res 類別的產生方式。 範例配置如下:
compose.resources {
publicResClass = false
packageOfResClass = "me.sample.library.resources"
generateResClass = auto
}- 將
publicResClass設定為true會使產生的Res類別為公開的。預設情況下,產生的類別為 internal。 packageOfResClass允許您將產生的Res類別指定給特定套件(以便在程式碼中存取,以及在最終成品中進行隔離)。預設情況下,Compose Multiplatform 會將{group name}.{module name}.generated.resources套件指定給該類別。- 將
generateResClass設定為always會使專案無條件地產生Res類別。當資源函式庫僅以傳遞方式可用時,這可能很有用。預設情況下,Compose Multiplatform 使用auto值來產生Res類別,僅當目前專案對資源函式庫具有明確的implementation或api依賴時才會產生。
資源使用
影像
您可以將 drawable 資源存取為簡單影像、點陣化影像或 XML 向量。 除了 Android 之外,所有平台都支援 SVG 影像。
若要將 drawable 資源存取為
Painter影像,請使用painterResource()函數:kotlin@Composable fun painterResource(resource: DrawableResource): Painter {...}painterResource()函數會取得資源路徑並傳回Painter值。此函數在所有目標上同步運作,唯網路目標除外。對於網路目標,它會在第一次重新組合時傳回空的Painter,並在隨後的重新組合中替換為載入的影像。painterResource()會載入BitmapPainter用於點陣化影像格式,例如.png、.jpg、.bmp、.webp,或載入VectorPainter用於 Android XML 向量 drawable 格式。- XML 向量 drawable 的格式與 Android 相同,唯不支援對 Android 資源的外部引用。
若要將 drawable 資源存取為
ImageBitmap點陣化影像,請使用imageResource()函數:kotlin@Composable fun imageResource(resource: DrawableResource): ImageBitmap {...}若要將 drawable 資源存取為
ImageVectorXML 向量,請使用vectorResource()函數:kotlin@Composable fun vectorResource(resource: DrawableResource): ImageVector {...}
以下是如何在 Compose Multiplatform 程式碼中存取影像的範例:
Image(
painter = painterResource(Res.drawable.my_image),
contentDescription = null
)圖示
您可以使用 Material Symbols 函式庫中的向量 Android XML 圖示:
開啟 Google Fonts Icons 圖庫,選擇一個圖示,前往 Android 頁籤,然後點擊 Download。
將下載的 XML 圖示檔案新增到您的多平台資源的
drawable目錄中。開啟 XML 圖示檔案並將
android:fillColor設定為#00000000。 移除任何其他用於顏色調整的 Android 特定屬性,例如android:tint。之前:
xml<vector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:width="24dp" android:height="24dp" android:viewportWidth="960" android:viewportHeight="960" android:tint="?attr/colorControlNormal"> <path android:fillColor="@android:color/white" android:pathData="..."/> </vector>之後:
xml<vector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:width="24dp" android:height="24dp" android:viewportWidth="960" android:viewportHeight="960"> <path android:fillColor="#00000000" android:pathData="..."/> </vector>建置專案以產生資源存取器,或讓 Kotlin Multiplatform 外掛程式自動處理。
以下是如何在 Compose Multiplatform 程式碼中,使用 colorFilter 參數存取圖示並調整顏色的範例:
Image(
painter = painterResource(Res.drawable.ic_sample_icon),
contentDescription = "Sample icon",
modifier = Modifier.size(24.dp),
colorFilter = ColorFilter.tint(Color.Blue)
)字串
將所有字串資源儲存在 composeResources/values 目錄中的 XML 檔案。 每個檔案中的每個項目都會產生一個靜態存取器。
有關如何為不同地區設定字串本地化的更多資訊,請參閱字串本地化指南。
簡單字串
若要儲存簡單字串,請將 <string> 元素新增至您的 XML:
<resources>
<string name="app_name">My awesome app</string>
<string name="title">Some title</string>
</resources>若要將字串資源作為 String 取得,請使用以下程式碼:
@Composable
fun stringResource(resource: StringResource): String {...}
@Composable
fun stringResource(resource: StringResource, vararg formatArgs: Any): String {...}例如:
Text(stringResource(Res.string.app_name))suspend fun getString(resource: StringResource): String
suspend fun getString(resource: StringResource, vararg formatArgs: Any): String例如:
coroutineScope.launch {
val appName = getString(Res.string.app_name)
}您可以在字串資源中使用特殊符號:
– 用於新行\t– 用於 tab 符號\uXXXX– 用於特定 Unicode 字元
您無需像針對 Android 字串那樣,逸脫特殊 XML 字元如 "@" 或 "?"。
字串範本
目前,參數對字串資源有基本支援。 建立範本時,使用 %<number> 格式將參數放置在字串內,並包含 $d 或 $s 後綴,以指示其為變數佔位符而非簡單文字。 例如:
<resources>
<string name="str_template">Hello, %2$s! You have %1$d new messages.</string>
</resources>建立並匯入字串範本資源後,您可以在傳遞佔位符參數時按正確順序引用它:
Text(stringResource(Res.string.str_template, 100, "User_name"))$s 和 $d 後綴之間沒有區別,也不支援其他後綴。 您可以將 %1$s 佔位符放入資源字串中,並使用它來顯示小數,例如:
Text(stringResource(Res.string.str_template, "User_name", 100.1f))字串陣列
您可以將相關字串分組為陣列,並自動將其作為 List<String> 物件存取:
<resources>
<string name="app_name">My awesome app</string>
<string name="title">Some title</string>
<string-array name="str_arr">
<item>item \u2605</item>
<item>item \u2318</item>
<item>item \u00BD</item>
</string-array>
</resources>若要取得對應的列表,請使用以下程式碼:
@Composable
fun stringArrayResource(resource: StringArrayResource): List<String> {...}例如:
val arr = stringArrayResource(Res.array.str_arr)
if (arr.isNotEmpty()) Text(arr[0])suspend fun getStringArray(resource: StringArrayResource): List<String>例如:
coroutineScope.launch {
val appName = getStringArray(Res.array.str_arr)
}複數
當您的 UI 顯示某物的數量時,您可能希望在不建立程式上不相關的字串的情況下,支援相同事物的不同數量之間的語法一致性(例如,一本_書_,多本_書_等)。
Compose Multiplatform 中的概念和基本實作與 Android 上的數量字串相同。 請參閱 Android 文件,以了解在專案中使用複數的最佳實踐和細微差異。
- 支援的變體有
zero、one、two、few、many和other。請注意,並非所有語言都考慮所有變體:例如,英語中會忽略zero,因為它與除 1 之外的任何其他複數相同。請依賴語言專家來了解該語言實際堅持的區別。 - 通常可以透過使用數量中性的表達方式來避免數量字串,例如「書本:1」。如果這不會惡化使用者體驗,
若要定義複數,請將 <plurals> 元素新增至 composeResources/values 目錄中的任何 .xml 檔案。 plurals 集合是使用 name 屬性(而非 XML 檔案名稱)引用的簡單資源。 因此,您可以在一個 XML 檔案中,在一個 <resources> 元素下,將 plurals 資源與其他簡單資源結合:
<resources>
<string name="app_name">My awesome app</string>
<string name="title">Some title</string>
<plurals name="new_message">
<item quantity="one">%1$d new message</item>
<item quantity="other">%1$d new messages</item>
</plurals>
</resources>若要將複數作為 String 存取,請使用以下程式碼:
@Composable
fun pluralStringResource(resource: PluralStringResource, quantity: Int): String {...}
@Composable
fun pluralStringResource(resource: PluralStringResource, quantity: Int, vararg formatArgs: Any): String {...}例如:
Text(pluralStringResource(Res.plurals.new_message, 1, 1))suspend fun getPluralString(resource: PluralStringResource, quantity: Int): String
suspend fun getPluralString(resource: PluralStringResource, quantity: Int, vararg formatArgs: Any): String例如:
coroutineScope.launch {
val appName = getPluralString(Res.plurals.new_message, 1, 1)
}字型
將自訂字型儲存在 composeResources/font 目錄中,作為 *.ttf 或 *.otf 檔案。
若要將字型載入為 Font 類型,請使用 Font() 可組合函數:
@Composable
fun Font(
resource: FontResource,
weight: FontWeight = FontWeight.Normal,
style: FontStyle = FontStyle.Normal
): Font例如:
@Composable
private fun InterTypography(): Typography {
val interFont = FontFamily(
Font(Res.font.Inter_24pt_Regular, FontWeight.Normal),
Font(Res.font.Inter_24pt_SemiBold, FontWeight.Bold),
)
return with(MaterialTheme.typography) {
copy(
displayLarge = displayLarge.copy(fontFamily = interFont, fontWeight = FontWeight.Bold),
displayMedium = displayMedium.copy(fontFamily = interFont, fontWeight = FontWeight.Bold),
displaySmall = displaySmall.copy(fontFamily = interFont, fontWeight = FontWeight.Bold),
headlineLarge = headlineLarge.copy(fontFamily = interFont, fontWeight = FontWeight.Bold),
headlineMedium = headlineMedium.copy(fontFamily = interFont, fontWeight = FontWeight.Bold),
headlineSmall = headlineSmall.copy(fontFamily = interFont, fontWeight = FontWeight.Bold),
titleLarge = titleLarge.copy(fontFamily = interFont, fontWeight = FontWeight.Bold),
titleMedium = titleMedium.copy(fontFamily = interFont, fontWeight = FontWeight.Bold),
titleSmall = titleSmall.copy(fontFamily = interFont, fontWeight = FontWeight.Bold),
labelLarge = labelLarge.copy(fontFamily = interFont, fontWeight = FontWeight.Normal),
labelMedium = labelMedium.copy(fontFamily = interFont, fontWeight = FontWeight.Normal),
labelSmall = labelSmall.copy(fontFamily = interFont, fontWeight = FontWeight.Normal),
bodyLarge = bodyLarge.copy(fontFamily = interFont, fontWeight = FontWeight.Normal),
bodyMedium = bodyMedium.copy(fontFamily = interFont, fontWeight = FontWeight.Normal),
bodySmall = bodySmall.copy(fontFamily = interFont, fontWeight = FontWeight.Normal),
)
}
}{initial-collapse-state="collapsed" collapsible="true" collapsed-title="@Composable private fun InterTypography(): Typography
當
Font是可組合項時,請確保其依賴的組件,例如TextStyle和Typography,也是可組合項。
若要在網路目標中支援如表情符號或阿拉伯文腳本等特殊字元,您需要將相應的字型新增至資源,並預載入後備字型。
原始檔案
若要將任何原始檔案載入為位元組陣列,請使用 Res.readBytes(path) 函數:
suspend fun readBytes(path: String): ByteArray您可以將原始檔案放置在 composeResources/files 目錄中,並在其內部建立任何層級結構。
例如,若要存取原始檔案,請使用以下程式碼:
var bytes by remember {
mutableStateOf(ByteArray(0))
}
LaunchedEffect(Unit) {
bytes = Res.readBytes("files/myDir/someFile.bin")
}
Text(bytes.decodeToString())coroutineScope.launch {
val bytes = Res.readBytes("files/myDir/someFile.bin")
}將位元組陣列轉換為影像
如果您正在讀取的檔案是點陣圖 (JPEG, PNG, BMP, WEBP) 或 XML 向量影像,您可以使用以下函數將它們轉換為適用於 Image() 可組合項的 ImageBitmap 或 ImageVector 物件。
依照原始檔案部分所示存取原始檔案,然後將結果傳遞給可組合項:
// bytes = Res.readBytes("files/example.png")
Image(bytes.decodeToImageBitmap(), null)
// bytes = Res.readBytes("files/example.xml")
Image(bytes.decodeToImageVector(LocalDensity.current), null)除了 Android 之外,在所有平台上,您還可以將 SVG 檔案轉換為 Painter 物件:
// bytes = Res.readBytes("files/example.svg")
Image(bytes.decodeToSvgPainter(LocalDensity.current), null)資源和字串 ID 的產生映射
為了便於存取,Compose Multiplatform 也會將資源與字串 ID 進行映射。您可以使用檔案名稱作為鍵來存取它們:
val Res.allDrawableResources: Map<String, DrawableResource>
val Res.allStringResources: Map<String, StringResource>
val Res.allStringArrayResources: Map<String, StringArrayResource>
val Res.allPluralStringResources: Map<String, PluralStringResource>
val Res.allFontResources: Map<String, FontResource>將映射資源傳遞給可組合項的範例:
Image(painterResource(Res.allDrawableResources["compose_multiplatform"]!!), null)Compose Multiplatform 資源作為 Android 資產
從 Compose Multiplatform 1.7.0 開始,所有多平台資源都打包到 Android 資產中。 這使得 Android Studio 能夠為 Android 原始碼集中的 Compose Multiplatform 可組合項產生預覽。
Android Studio 預覽僅適用於 Android 原始碼集中的可組合項。 它們還需要最新版本的 AGP:8.5.2、8.6.0-rc01 或 8.7.0-alpha04。
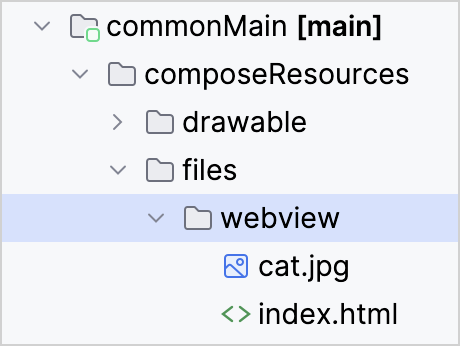
將多平台資源用作 Android 資產也使得可以直接從 Android 上的 WebView 和媒體播放器組件進行存取,因為資源可以透過簡單的路徑到達,例如 Res.getUri("files/index.html")。
Android 可組合項顯示資源 HTML 頁面並連結至資源影像的範例:
// androidMain/kotlin/com/example/webview/App.kt
@OptIn(ExperimentalResourceApi::class)
@Composable
@Preview
fun App() {
MaterialTheme {
val uri = Res.getUri("files/webview/index.html")
// Adding a WebView inside AndroidView with layout as full screen.
AndroidView(factory = {
WebView(it).apply {
layoutParams = ViewGroup.LayoutParams(
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT,
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT
)
}
}, update = {
it.loadUrl(uri)
})
}
}此範例適用於這個簡單的 HTML 檔案:
<html>
<header>
<title>
Cat Resource
</title>
</header>
<body>
<img src="cat.jpg">
</body>
</html>此範例中的兩個資源檔案都位於 commonMain 原始碼集:
網路目標的資源預載入
諸如字型和影像之類的網路資源會使用 fetch API 進行非同步載入。在初始載入期間或網路連線較慢時,資源擷取可能會導致視覺故障,例如 FOUT 或顯示佔位符而不是影像。
此問題的典型範例是當 Text() 組件包含自訂字型的文字時,但包含所需字形的字型仍在載入中。在這種情況下,使用者可能會暫時看到預設字型的文字,甚至看到空框和問號而不是字元。同樣地,對於影像或 drawable,使用者可能會觀察到一個空白或黑色方框之類的佔位符,直到資源完全載入。
為防止視覺故障,您可以使用內建瀏覽器功能進行資源預載入、Compose Multiplatform 預載入 API,或兩者結合使用。
使用瀏覽器功能預載入資源
在現代瀏覽器中,您可以使用帶有 rel="preload" 屬性的 <link> 標籤來預載入資源。 此屬性會指示瀏覽器在應用程式啟動之前優先下載和快取字型和影像等資源,確保這些資源能夠提早可用。
例如,若要啟用瀏覽器內字型預載入:
- 建置您的應用程式網路發佈版:
./gradlew :composeApp:wasmJsBrowserDistribution- 在產生的
dist目錄中找到所需的資源並儲存路徑。 - 開啟
wasmJsMain/resources/index.html檔案並在<head>元素內新增一個<link>標籤。 - 將
href屬性設定為資源路徑:
<link rel="preload" href="./composeResources/username.composeapp.generated.resources/font/FiraMono-Regular.ttf" as="fetch" type="font/ttf" crossorigin/>使用 Compose Multiplatform 預載入 API 預載入資源
即使您已在瀏覽器中預載入資源,它們仍會以原始位元組形式快取,這些位元組仍需要轉換為適合呈現的格式,例如 FontResource 和 DrawableResource。當應用程式第一次請求資源時,轉換是異步完成的,這可能會再次導致閃爍。為了進一步最佳化體驗,Compose Multiplatform 資源擁有自己的內部快取,用於資源的更高層次表示,這也可以預載入。
Compose Multiplatform 1.8.0 引入了一個實驗性 API,用於在網路目標上預載入字型和影像資源:preloadFont()、preloadImageBitmap() 和 preloadImageVector()。
此外,如果您需要表情符號等特殊字元,您可以設定與預設捆綁選項不同的後備字型。 若要指定後備字型,請使用 FontFamily.Resolver.preload() 方法。
以下範例示範如何使用預載入和後備字型:
import androidx.compose.foundation.background
import androidx.compose.foundation.clickable
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Box
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.fillMaxSize
import androidx.compose.material3.CircularProgressIndicator
import androidx.compose.runtime.*
import androidx.compose.ui.*
import androidx.compose.ui.graphics.Color
import androidx.compose.ui.platform.LocalFontFamilyResolver
import androidx.compose.ui.text.font.FontFamily
import androidx.compose.ui.text.font.FontStyle
import androidx.compose.ui.text.font.FontWeight
import androidx.compose.ui.window.CanvasBasedWindow
import components.resources.demo.shared.generated.resources.*
import components.resources.demo.shared.generated.resources.NotoColorEmoji
import components.resources.demo.shared.generated.resources.Res
import components.resources.demo.shared.generated.resources.Workbench_Regular
import components.resources.demo.shared.generated.resources.font_awesome
import org.jetbrains.compose.resources.ExperimentalResourceApi
import org.jetbrains.compose.resources.configureWebResources
import org.jetbrains.compose.resources.demo.shared.UseResources
import org.jetbrains.compose.resources.preloadFont
@OptIn(ExperimentalComposeUiApi::class, ExperimentalResourceApi::class, InternalComposeUiApi::class)
fun main() {
configureWebResources {
// Overrides the resource location
resourcePathMapping { path -> "./$path" }
}
CanvasBasedWindow("Resources + K/Wasm") {
val font1 by preloadFont(Res.font.Workbench_Regular)
val font2 by preloadFont(Res.font.font_awesome, FontWeight.Normal, FontStyle.Normal)
val emojiFont = preloadFont(Res.font.NotoColorEmoji).value
var fontsFallbackInitialized by remember { mutableStateOf(false) }
// Uses the preloaded resource for the app's content
UseResources()
if (font1 != null && font2 != null && emojiFont != null && fontsFallbackInitialized) {
println("Fonts are ready")
} else {
// Displays the progress indicator to address a FOUT or the app being temporarily non-functional during loading
Box(modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize().background(Color.White.copy(alpha = 0.8f)).clickable { }) {
CircularProgressIndicator(modifier = Modifier.align(Alignment.Center))
}
println("Fonts are not ready yet")
}
val fontFamilyResolver = LocalFontFamilyResolver.current
LaunchedEffect(fontFamilyResolver, emojiFont) {
if (emojiFont != null) {
// Preloads a fallback font with emojis to render missing glyphs that are not supported by the bundled font
fontFamilyResolver.preload(FontFamily(listOf(emojiFont)))
fontsFallbackInitialized = true
}
}
}
}與其他函式庫和資源互動
從外部函式庫存取多平台資源
如果您想使用專案中包含的其他函式庫來處理多平台資源,您可以將平台特定的檔案路徑傳遞給這些其他 API。 若要取得平台特定路徑,請使用資源的專案路徑呼叫 Res.getUri() 函數:
val uri = Res.getUri("files/my_video.mp4")現在 uri 變數包含檔案的絕對路徑,任何外部函式庫都可以使用該路徑以適合其方式存取檔案。
對於 Android 特定用途,多平台資源也打包為 Android 資產。
遠端檔案
在資源函式庫的上下文中,只有作為應用程式一部分的檔案才被視為資源。
您可以使用專業函式庫透過其 URL 從網際網路載入遠端檔案:
使用 Java 資源
儘管您可以在 Compose Multiplatform 中使用 Java 資源,但它們無法受益於框架提供的擴展功能:產生的存取器、多模組支援、本地化等等。 考慮完全轉換到多平台資源函式庫以釋放該潛力。
隨著 Compose Multiplatform 1.7.0 的發佈,compose.ui 套件中可用的資源 API 已被棄用。 如果您仍然需要使用 Java 資源,請將以下實作複製到您的專案中,以確保您的程式碼在升級到 Compose Multiplatform 1.7.0 或更高版本後仍然有效:
@Composable
internal fun painterResource(
resourcePath: String
): Painter = when (resourcePath.substringAfterLast(".")) {
"svg" -> rememberSvgResource(resourcePath)
"xml" -> rememberVectorXmlResource(resourcePath)
else -> rememberBitmapResource(resourcePath)
}
@Composable
internal fun rememberBitmapResource(path: String): Painter {
return remember(path) { BitmapPainter(readResourceBytes(path).decodeToImageBitmap()) }
}
@Composable
internal fun rememberVectorXmlResource(path: String): Painter {
val density = LocalDensity.current
val imageVector = remember(density, path) { readResourceBytes(path).decodeToImageVector(density) }
return rememberVectorPainter(imageVector)
}
@Composable
internal fun rememberSvgResource(path: String): Painter {
val density = LocalDensity.current
return remember(density, path) { readResourceBytes(path).decodeToSvgPainter(density) }
}
private object ResourceLoader
private fun readResourceBytes(resourcePath: String) =
ResourceLoader.javaClass.classLoader.getResourceAsStream(resourcePath).readAllBytes()