在 iOS 和 Android 之間分享更多邏輯
本教學課程使用 IntelliJ IDEA,但您也可以在 Android Studio 中跟隨操作 – 兩個 IDE 都共享相同的核心功能和 Kotlin 多平台支援。
這是使用共享邏輯和原生 UI 建立 Kotlin 多平台應用程式教學課程的第四部分。在繼續之前,請確保您已完成先前的步驟。
既然您已經使用外部依賴項實現了通用邏輯,您就可以開始添加更複雜的邏輯。網路請求和資料序列化是使用 Kotlin 多平台共享程式碼的最受歡迎用例。了解如何在您的第一個應用程式中實現這些功能,以便在完成此入門旅程後,您可以在未來的專案中使用它們。
更新後的應用程式將透過網路從 SpaceX API 檢索資料,並顯示 SpaceX 火箭上次成功發射的日期。
您可以在我們的 GitHub 儲存庫的兩個分支中找到專案的最終狀態,它們具有不同的協程解決方案:
新增更多依賴項
您需要在專案中新增以下多平台函式庫:
kotlinx.coroutines,用於異步程式碼的協程,這允許同時操作。kotlinx.serialization,用於將 JSON 響應反序列化為實體類別的物件,這些物件用於處理網路操作。- Ktor,一個用於建立 HTTP 客戶端以透過網路檢索資料的框架。
kotlinx.coroutines
若要將 kotlinx.coroutines 加入到您的專案,請在通用原始碼集中指定一個依賴項。為此,請將以下行新增到 shared/build.gradle.kts 檔案中:
kotlin {
// ...
sourceSets {
commonMain.dependencies {
// ...
implementation("org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-coroutines-core:1.10.2")
}
}
}多平台 Gradle 外掛程式會自動將依賴項添加到 kotlinx.coroutines 的平台特定(iOS 和 Android)部分。
kotlinx.serialization
若要使用 kotlinx.serialization 函式庫,請設定相應的 Gradle 外掛程式。為此,請將以下行新增到 shared/build.gradle.kts 檔案開頭的現有 plugins {} 區塊中:
plugins {
// ...
kotlin("plugin.serialization") version "2.2.21"
}Ktor
您需要將核心依賴項(ktor-client-core)新增到共享模組的通用原始碼集。 您還需要新增支援依賴項:
- 新增
ContentNegotiation功能(ktor-client-content-negotiation),它允許以特定格式序列化和反序列化內容。 - 新增
ktor-serialization-kotlinx-json依賴項,以指示 Ktor 使用 JSON 格式並將kotlinx.serialization作為序列化函式庫。Ktor 將預期 JSON 資料並在接收響應時將其反序列化為資料類別。 - 透過在平台原始碼集中新增相應的 artifact 依賴項(
ktor-client-android、ktor-client-darwin)來提供平台引擎。
kotlin {
// ...
val ktorVersion = "3.3.1"
sourceSets {
commonMain.dependencies {
// ...
implementation("io.ktor:ktor-client-core:$ktorVersion")
implementation("io.ktor:ktor-client-content-negotiation:$ktorVersion")
implementation("io.ktor:ktor-serialization-kotlinx-json:$ktorVersion")
}
androidMain.dependencies {
implementation("io.ktor:ktor-client-android:$ktorVersion")
}
iosMain.dependencies {
implementation("io.ktor:ktor-client-darwin:$ktorVersion")
}
}
}點擊同步 Gradle 變更按鈕以同步 Gradle 檔案。
建立 API 請求
您將需要 SpaceX API 來檢索資料,您將使用單一方法從 v4/launches 端點獲取所有發射列表。
新增資料模型
在 shared/src/commonMain/.../greetingkmp 目錄中,建立一個新的 RocketLaunch.kt 檔案,並新增一個資料類別,該類別儲存來自 SpaceX API 的資料:
import kotlinx.serialization.SerialName
import kotlinx.serialization.Serializable
@Serializable
data class RocketLaunch (
@SerialName("flight_number")
val flightNumber: Int,
@SerialName("name")
val missionName: String,
@SerialName("date_utc")
val launchDateUTC: String,
@SerialName("success")
val launchSuccess: Boolean?,
)RocketLaunch類別標記了@Serializable註解,以便kotlinx.serialization外掛程式可以自動為其生成預設序列化器。@SerialName註解允許您重新定義欄位名稱,從而可以在資料類別中宣告更具可讀性的屬性。
連接 HTTP 客戶端
在
shared/src/commonMain/.../greetingkmp目錄中,建立一個新的RocketComponent類別。新增
httpClient屬性,以透過 HTTP GET 請求檢索火箭發射資訊:kotlinimport io.ktor.client.HttpClient import io.ktor.client.plugins.contentnegotiation.ContentNegotiation import io.ktor.serialization.kotlinx.json.json import kotlinx.serialization.json.Json class RocketComponent { private val httpClient = HttpClient { install(ContentNegotiation) { json(Json { prettyPrint = true isLenient = true ignoreUnknownKeys = true }) } } }- ContentNegotiation Ktor 外掛程式 和 JSON 序列化器會反序列化 GET 請求的結果。
- 這裡的 JSON 序列化器配置為使用
prettyPrint屬性以更具可讀性的方式列印 JSON。它在讀取格式錯誤的 JSON 時使用isLenient更具彈性,並且使用ignoreUnknownKeys忽略未在火箭發射模型中宣告的鍵。
將
getDateOfLastSuccessfulLaunch()暫停函式新增到RocketComponent:kotlinclass RocketComponent { // ... private suspend fun getDateOfLastSuccessfulLaunch(): String { } }呼叫
httpClient.get()函式以檢索有關火箭發射的資訊:kotlinimport io.ktor.client.request.get import io.ktor.client.call.body class RocketComponent { // ... private suspend fun getDateOfLastSuccessfulLaunch(): String { val rockets: List<RocketLaunch> = httpClient.get("https://api.spacexdata.com/v4/launches").body() } }httpClient.get()也是一個暫停函式,因為它需要異步地透過網路檢索資料而不會阻塞執行緒。- 暫停函式只能從協程或其他暫停函式中呼叫。這就是為什麼
getDateOfLastSuccessfulLaunch()被標記為suspend關鍵字。網路請求在 HTTP 客戶端的執行緒池中執行。
再次更新函式以在列表中找到最後一次成功發射:
kotlinclass RocketComponent { // ... private suspend fun getDateOfLastSuccessfulLaunch(): String { val rockets: List<RocketLaunch> = httpClient.get("https://api.spacexdata.com/v4/launches").body() val lastSuccessLaunch = rockets.last { it.launchSuccess == true } } }火箭發射列表按日期從最舊到最新排序。
將發射日期從 UTC 轉換為您的本地日期並格式化輸出:
kotlinimport kotlinx.datetime.TimeZone import kotlinx.datetime.toLocalDateTime import kotlin.time.ExperimentalTime import kotlin.time.Instant class RocketComponent { // ... @OptIn(ExperimentalTime::class) private suspend fun getDateOfLastSuccessfulLaunch(): String { val rockets: List<RocketLaunch> = httpClient.get("https://api.spacexdata.com/v4/launches").body() val lastSuccessLaunch = rockets.last { it.launchSuccess == true } val date = Instant.parse(lastSuccessLaunch.launchDateUTC) .toLocalDateTime(TimeZone.currentSystemDefault()) return "${date.month} ${date.day}, ${date.year}" } }日期將採用「MMMM DD, YYYY」格式,例如 OCTOBER 5, 2022。
新增另一個暫停函式
launchPhrase(),它將使用getDateOfLastSuccessfulLaunch()函式建立一條訊息:kotlinclass RocketComponent { // ... suspend fun launchPhrase(): String = try { "The last successful launch was on ${getDateOfLastSuccessfulLaunch()} 🚀" } catch (e: Exception) { println("Exception during getting the date of the last successful launch $e") "Error occurred" } }
建立 Flow
您可以使用 Flow 而不是暫停函式。它們發出一系列值,而不是暫停函式返回的單個值。
在
shared/src/commonMain/kotlin目錄中開啟Greeting.kt檔案。為
Greeting類別新增rocketComponent屬性。該屬性將儲存包含最後一次成功發射日期的訊息:kotlinprivate val rocketComponent = RocketComponent()將
greet()函式更改為返回一個Flow:kotlinimport kotlinx.coroutines.delay import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.Flow import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.flow import kotlin.time.Duration.Companion.seconds class Greeting { // ... fun greet(): Flow<String> = flow { emit(if (Random.nextBoolean()) "Hi!" else "Hello!") delay(1.seconds) emit("Guess what this is! > ${platform.name.reversed()}") delay(1.seconds) emit(daysPhrase()) emit(rocketComponent.launchPhrase()) } }- 這裡使用
flow()構建器函式建立Flow,它包裝了所有語句。 Flow以一秒的延遲發出字串,每個發出之間間隔一秒。最後一個元素僅在網路響應返回後才發出,因此確切的延遲取決於您的網路。
- 這裡使用
新增網際網路存取權限
若要存取網際網路,Android 應用程式需要適當的權限。由於所有網路請求都來自共享模組,因此將網際網路存取權限新增到其資訊清單中是合理的。
使用存取權限更新您的 composeApp/src/androidMain/AndroidManifest.xml 檔案:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/>
...
</manifest>您已經透過將 greet() 函式的返回類型更改為 Flow 來更新了共享模組的 API。現在您需要更新專案的原生部分,以便它們可以正確處理呼叫 greet() 函式的結果。
更新原生 Android UI
由於共享模組和 Android 應用程式都用 Kotlin 編寫,因此從 Android 使用共享程式碼非常簡單。
引入視圖模型
現在應用程式變得更複雜了,是時候向名為 MainActivity 的 Android activity 引入一個視圖模型了。它呼叫實現 UI 的 App() 函式。視圖模型將管理來自 activity 的資料,並且在 activity 經歷生命週期更改時不會消失。
在
composeApp/src/androidMain/.../greetingkmp目錄中,建立一個新的MainViewModelKotlin 類別:kotlinimport androidx.lifecycle.ViewModel class MainViewModel : ViewModel() { // ... }此類別擴展了 Android 的
ViewModel類別,這確保了關於生命週期和配置更改的正確行為。建立一個 StateFlow 類型的
greetingList值及其支援屬性:kotlinimport kotlinx.coroutines.flow.MutableStateFlow import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.StateFlow class MainViewModel : ViewModel() { private val _greetingList = MutableStateFlow<List<String>>(listOf()) val greetingList: StateFlow<List<String>> get() = _greetingList }- 這裡的
StateFlow擴展了Flow介面,但它只有一個單一值或狀態。 - 私有支援屬性
_greetingList確保只有此類別的客戶端才能存取唯讀的greetingList屬性。
- 這裡的
在視圖模型的
init函式中,從Greeting().greet()Flow 中收集所有字串:kotlinimport androidx.lifecycle.viewModelScope import kotlinx.coroutines.launch class MainViewModel : ViewModel() { private val _greetingList = MutableStateFlow<List<String>>(listOf()) val greetingList: StateFlow<List<String>> get() = _greetingList init { viewModelScope.launch { Greeting().greet().collect { phrase -> //... } } } }由於
collect()函式是暫停的,因此launch協程在視圖模型的範圍內使用。這表示 launch 協程只會在視圖模型生命週期的正確階段執行。在
collecttrailing lambda 內部,更新_greetingList的值,將收集到的phrase附加到list中的片語列表:kotlinimport kotlinx.coroutines.flow.update class MainViewModel : ViewModel() { //... init { viewModelScope.launch { Greeting().greet().collect { phrase -> _greetingList.update { list -> list + phrase } } } } }update()函式將自動更新值。
使用視圖模型的 Flow
在
composeApp/src/androidMain/kotlin中,開啟App.kt檔案並更新它,替換先前的實現:kotlinimport androidx.lifecycle.compose.collectAsStateWithLifecycle import androidx.compose.runtime.getValue import androidx.lifecycle.viewmodel.compose.viewModel @Composable @Preview fun App(mainViewModel: MainViewModel = viewModel()) { MaterialTheme { val greetings by mainViewModel.greetingList.collectAsStateWithLifecycle() Column( modifier = Modifier .safeContentPadding() .fillMaxSize(), verticalArrangement = Arrangement.spacedBy(8.dp), ) { greetings.forEach { greeting -> Text(greeting) HorizontalDivider() } } } }collectAsStateWithLifecycle()函式呼叫greetingList,以從 ViewModel 的 Flow 中收集值,並以認知生命週期的方式將其表示為可組合狀態。- 當建立新的 Flow 時,組合狀態將會改變,並顯示一個可滾動的
Column,其中包含垂直排列並由分隔線分隔的問候片語。
要查看結果,請重新執行您的 composeApp 配置:
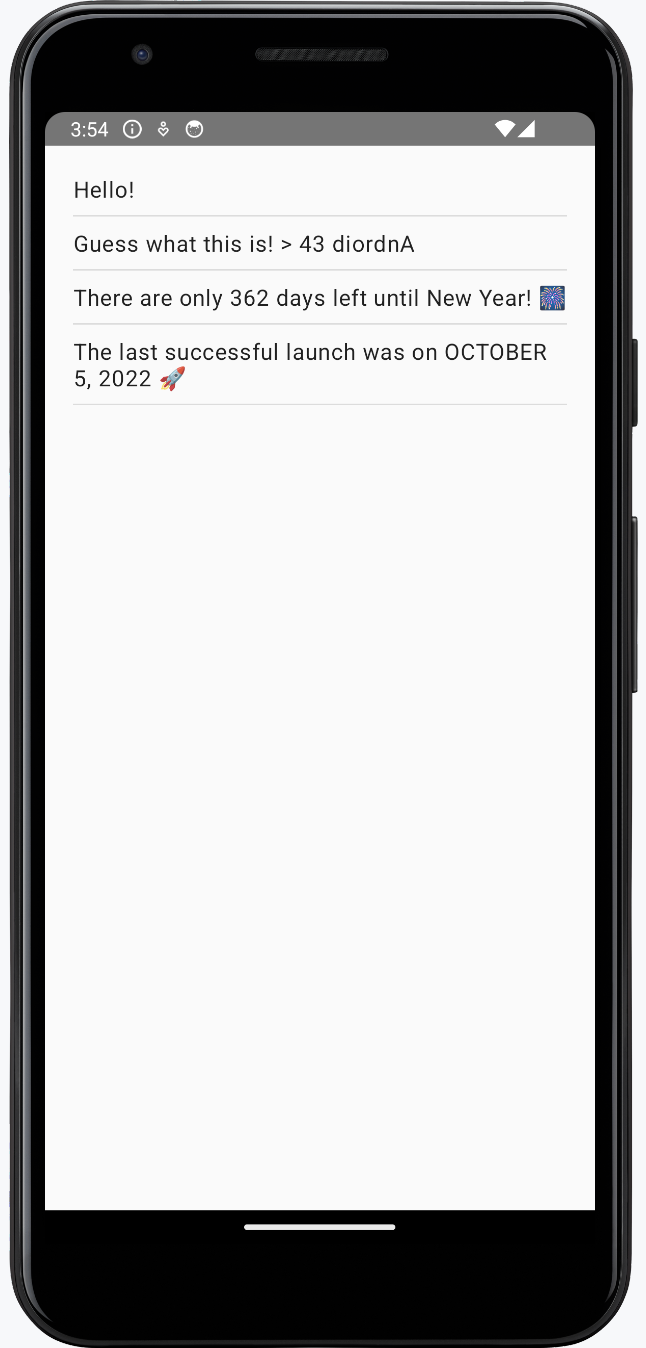
更新原生 iOS UI
對於專案的 iOS 部分,您將再次利用 模型-視圖-視圖模型 (Model–view–viewmodel) 模式將 UI 連接到包含所有業務邏輯的共享模組。
該模組已在 ContentView.swift 檔案中透過 import Shared 宣告導入。
引入 ViewModel
在 iosApp/ContentView.swift 中,為 ContentView 建立一個 ViewModel 類別,它將為其準備和管理資料。在 task() 呼叫中呼叫 startObserving() 函式以支援並發:
import SwiftUI
import Shared
struct ContentView: View {
@ObservedObject private(set) var viewModel: ViewModel
var body: some View {
ListView(phrases: viewModel.greetings)
.task { await self.viewModel.startObserving() }
}
}
extension ContentView {
@MainActor
class ViewModel: ObservableObject {
@Published var greetings: Array<String> = []
func startObserving() {
// ...
}
}
}
struct ListView: View {
let phrases: Array<String>
var body: some View {
List(phrases, id: \.self) {
Text($0)
}
}
}ViewModel被宣告為ContentView的擴展,因為它們緊密相關。ViewModel有一個greetings屬性,它是一個String片語的陣列。SwiftUI 將 ViewModel(ContentView.ViewModel)與視圖(ContentView)連接起來。ContentView.ViewModel被宣告為ObservableObject。@Published包裝器用於greetings屬性。@ObservedObject屬性包裝器用於訂閱 ViewModel。
當此屬性更改時,此 ViewModel 將發出訊號。現在您需要實現 startObserving() 函式來消費 Flow。
選擇函式庫以從 iOS 消費 Flow
在本教學課程中,您可以使用 SKIE 和 KMP-NativeCoroutines 函式庫來幫助您在 iOS 中使用 Flow。兩者都是開源解決方案,支援 Flow 的取消和泛型,而 Kotlin/Native 編譯器目前不提供這些功能:
- SKIE 函式庫擴展了 Kotlin 編譯器生成的 Objective-C API:SKIE 將 Flow 轉換為等效於 Swift 的
AsyncSequence。SKIE 直接支援 Swift 的async/await,沒有執行緒限制,並具有自動雙向取消功能(Combine 和 RxSwift 需要適配器)。SKIE 還提供其他功能,可從 Kotlin 生成 Swift 友善的 API,包括將各種 Kotlin 類型橋接到 Swift 等效類型。它也不需要在 iOS 專案中添加額外的依賴項。 - KMP-NativeCoroutines 函式庫透過生成必要的包裝器來幫助您從 iOS 消費暫停函式和 Flow。KMP-NativeCoroutines 支援 Swift 的
async/await功能以及 Combine 和 RxSwift。使用 KMP-NativeCoroutines 需要在 iOS 專案中添加 SPM 或 CocoaPod 依賴項。
選項 1. 配置 KMP-NativeCoroutines
我們建議使用函式庫的最新版本。 請查看 KMP-NativeCoroutines 儲存庫 以了解是否有更新版本的外掛程式可用。
在專案的根
build.gradle.kts檔案中(不是shared/build.gradle.kts檔案),將 KSP (Kotlin Symbol Processor) 和 KMP-NativeCoroutines 外掛程式新增到plugins {}區塊中:kotlinplugins { // ... id("com.google.devtools.ksp").version("2.2.10-2.0.2").apply(false) id("com.rickclephas.kmp.nativecoroutines").version("1.0.0-ALPHA-45").apply(false) }在
shared/build.gradle.kts檔案中,新增 KMP-NativeCoroutines 外掛程式:kotlinplugins { // ... id("com.google.devtools.ksp") id("com.rickclephas.kmp.nativecoroutines") }同樣在
shared/build.gradle.kts檔案中,選擇加入實驗性的@ObjCName註解:kotlinkotlin { // ... sourceSets{ all { languageSettings { optIn("kotlin.experimental.ExperimentalObjCName") optIn("kotlin.time.ExperimentalTime") } } // ... } }點擊同步 Gradle 變更按鈕以同步 Gradle 檔案。
使用 KMP-NativeCoroutines 標記 Flow
在
shared/src/commonMain/kotlin目錄中開啟Greeting.kt檔案。將
@NativeCoroutines註解添加到greet()函式。這將確保外掛程式生成正確的程式碼以支援 iOS 上的正確 Flow 處理:kotlinimport com.rickclephas.kmp.nativecoroutines.NativeCoroutines class Greeting { // ... @NativeCoroutines fun greet(): Flow<String> = flow { // ... } }
在 Xcode 中使用 SPM 導入函式庫
前往 File | Open Project in Xcode。
在 Xcode 中,右鍵單擊左側選單中的
iosApp專案,然後選擇 Add Package Dependencies。在搜尋欄中,輸入套件名稱:
nonehttps://github.com/rickclephas/KMP-NativeCoroutines.git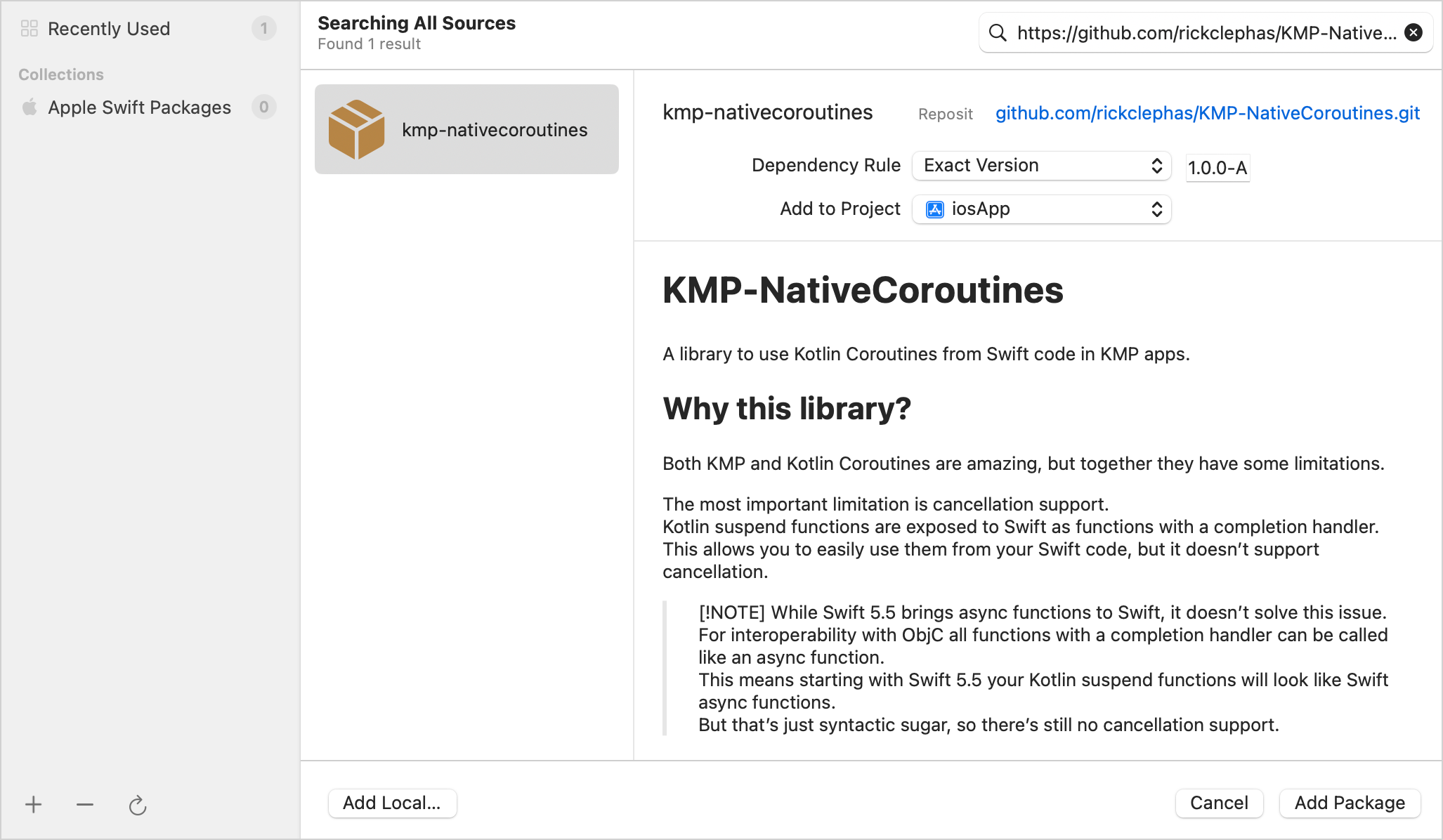
在Dependency Rule 下拉選單中,選擇 Exact Version 項目,並在相鄰欄位中輸入
1.0.0-ALPHA-45版本。點擊Add Package 按鈕:Xcode 將從 GitHub 獲取套件並開啟另一個視窗以選擇套件產品。
如圖所示,將「KMPNativeCoroutinesAsync」和「KMPNativeCoroutinesCore」新增到您的應用程式,然後點擊Add Package:
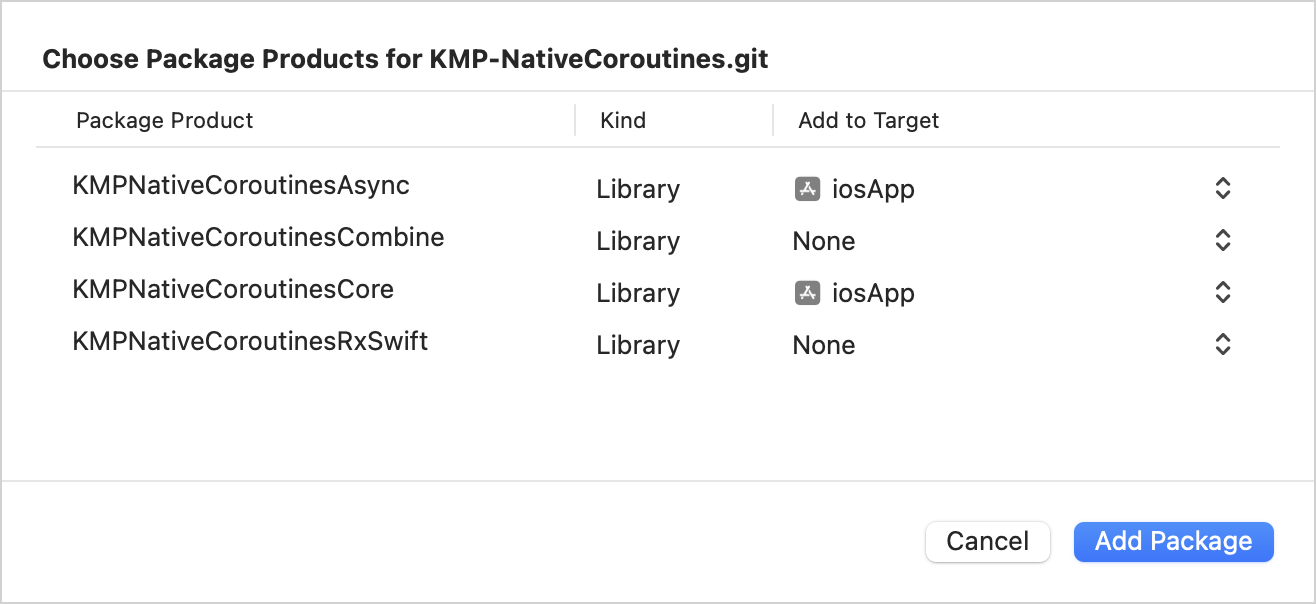
這應該會安裝 KMP-NativeCoroutines 套件中與 async/await 機制協同工作所需的組件。
使用 KMP-NativeCoroutines 函式庫消費 Flow
在
iosApp/ContentView.swift中,更新startObserving()函式以使用 KMP-NativeCoroutines 的asyncSequence()函式來消費Greeting().greet()函式的 Flow:Swiftfunc startObserving() async { do { let sequence = asyncSequence(for: Greeting().greet()) for try await phrase in sequence { self.greetings.append(phrase) } } catch { print("Failed with error: \(error)") } }這裡使用迴圈和
await機制來迭代 Flow,並在 Flow 每次發出值時更新greetings屬性。確保
ViewModel標記了@MainActor註解。該註解確保ViewModel中的所有異步操作都在主執行緒上運行,以符合 Kotlin/Native 的要求:Swift// ... import KMPNativeCoroutinesAsync import KMPNativeCoroutinesCore // ... extension ContentView { @MainActor class ViewModel: ObservableObject { @Published var greetings: Array<String> = [] func startObserving() async { do { let sequence = asyncSequence(for: Greeting().greet()) for try await phrase in sequence { self.greetings.append(phrase) } } catch { print("Failed with error: \(error)") } } } }
選項 2. 配置 SKIE
若要設定函式庫,請在 shared/build.gradle.kts 中指定 SKIE 外掛程式,然後點擊同步 Gradle 變更按鈕。
plugins {
id("co.touchlab.skie") version "0.10.6"
}目前 SKIE 的 0.10.6 版本不支援最新的 Kotlin。 若要使用它,請在
gradle/libs.versions.toml檔案中將您的 Kotlin 版本降級到 2.2.10。
使用 SKIE 消費 Flow
您將使用迴圈和 await 機制來迭代 Greeting().greet() Flow,並在 Flow 每次發出值時更新 greetings 屬性。
確保 ViewModel 標記了 @MainActor 註解。 該註解確保 ViewModel 中的所有異步操作都在主執行緒上運行,以符合 Kotlin/Native 的要求:
// ...
extension ContentView {
@MainActor
class ViewModel: ObservableObject {
@Published var greetings: [String] = []
func startObserving() async {
for await phrase in Greeting().greet() {
self.greetings.append(phrase)
}
}
}
}消費 ViewModel 並運行 iOS 應用程式
在 iosApp/iOSApp.swift 中,更新應用程式的進入點:
@main
struct iOSApp: App {
var body: some Scene {
WindowGroup {
ContentView(viewModel: ContentView.ViewModel())
}
}
}從 IntelliJ IDEA 運行 iosApp 配置,以確保您的應用程式邏輯已同步:
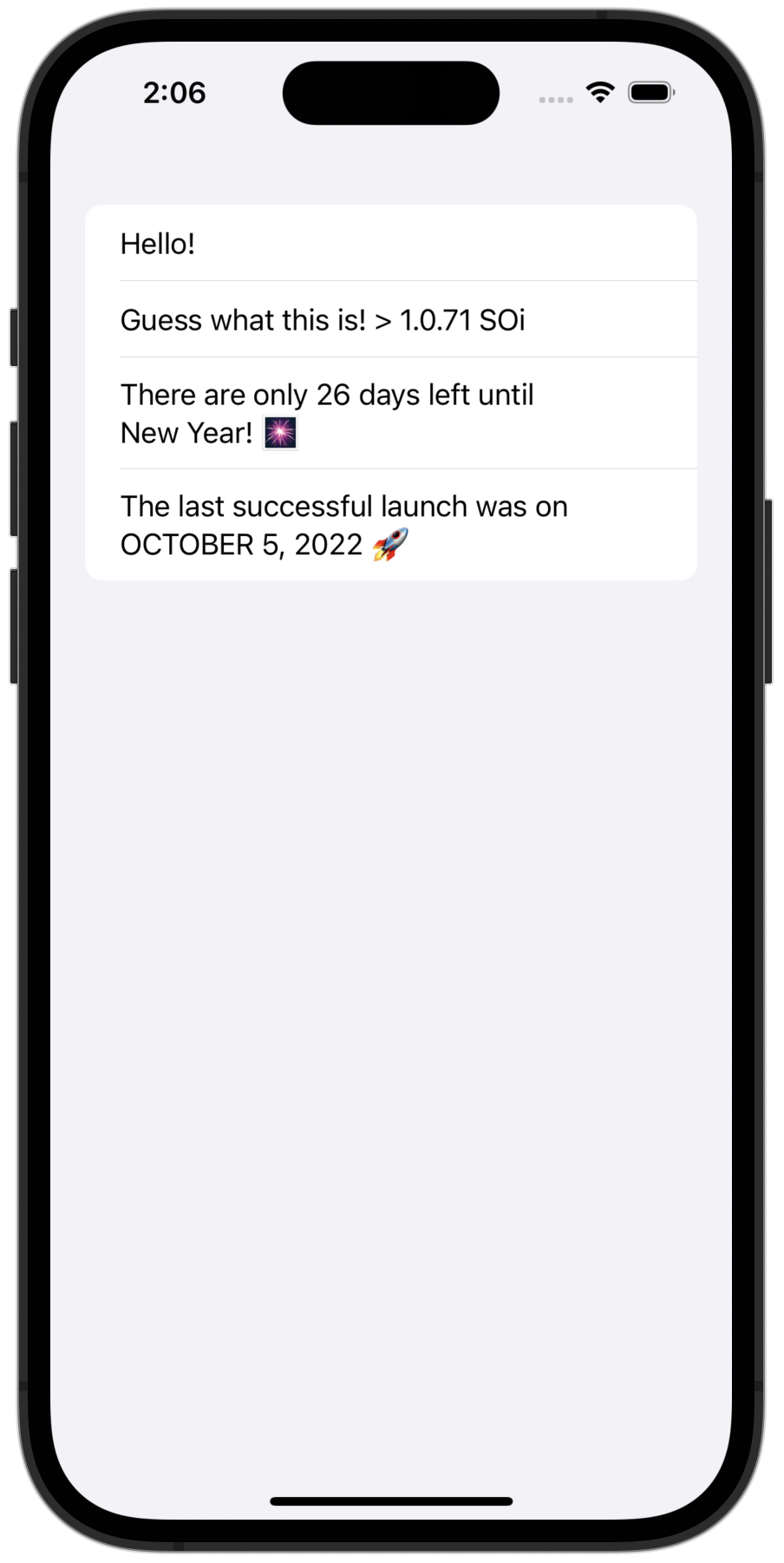
您可以在我們的 GitHub 儲存庫的兩個分支中找到專案的最終狀態,它們具有不同的協程解決方案:
下一步
在本教學課程的最後一部分,您將總結您的專案並了解接下來的步驟。
另請參閱
- 探索暫停函式的組合的各種方法。
- 了解更多關於與 Objective-C 框架和函式庫的互操作性。
- 完成關於網路和資料儲存的本教學課程。
取得協助
- Kotlin Slack。取得邀請並加入 #multiplatform 頻道。
- Kotlin 問題追蹤器。回報新問題。
