与 SwiftUI 框架集成
Compose Multiplatform 可与 SwiftUI 框架互操作。 你可以将 Compose Multiplatform 嵌入到 SwiftUI 应用程序中,也可以将原生 SwiftUI 组件嵌入到 Compose Multiplatform UI 中。本页提供了在 SwiftUI 中使用 Compose Multiplatform 以及在 Compose Multiplatform 应用中嵌入 SwiftUI 的示例。
关于 UIKit 互操作性,请参见 与 UIKit 框架集成 一文。
在 SwiftUI 应用程序中使用 Compose Multiplatform
要在 SwiftUI 应用程序中使用 Compose Multiplatform,请创建一个 Kotlin 函数 MainViewController(),该函数返回 UIKit 中的 UIViewController 并包含 Compose Multiplatform 代码:
fun MainViewController(): UIViewController =
ComposeUIViewController {
Box(Modifier.fillMaxSize(), contentAlignment = Alignment.Center) {
Text("This is Compose code", fontSize = 20.sp)
}
}ComposeUIViewController() 是一个 Compose Multiplatform 库函数,它接受一个可组合函数作为 content 实参。 以这种方式传递的函数可以调用其他可组合函数,例如 Text()。
可组合函数是带有
@Composable注解的函数。
接下来,你需要一个在 SwiftUI 中表示 Compose Multiplatform 的结构。 创建以下结构,它将一个 UIViewController 实例转换为 SwiftUI 视图:
struct ComposeViewController: UIViewControllerRepresentable {
func makeUIViewController(context: Context) -> UIViewController {
return Main_iosKt.MainViewController()
}
func updateUIViewController(_ uiViewController: UIViewController, context: Context) {
}
}现在你可以在其他 SwiftUI 代码中使用 ComposeView 结构了。
Main_iosKt.MainViewController 是一个生成的名字。关于从 Swift 访问 Kotlin 代码的更多信息,请参见 与 Swift/Objective-C 的互操作性 页面。
最终,你的应用程序应该看起来像这样:
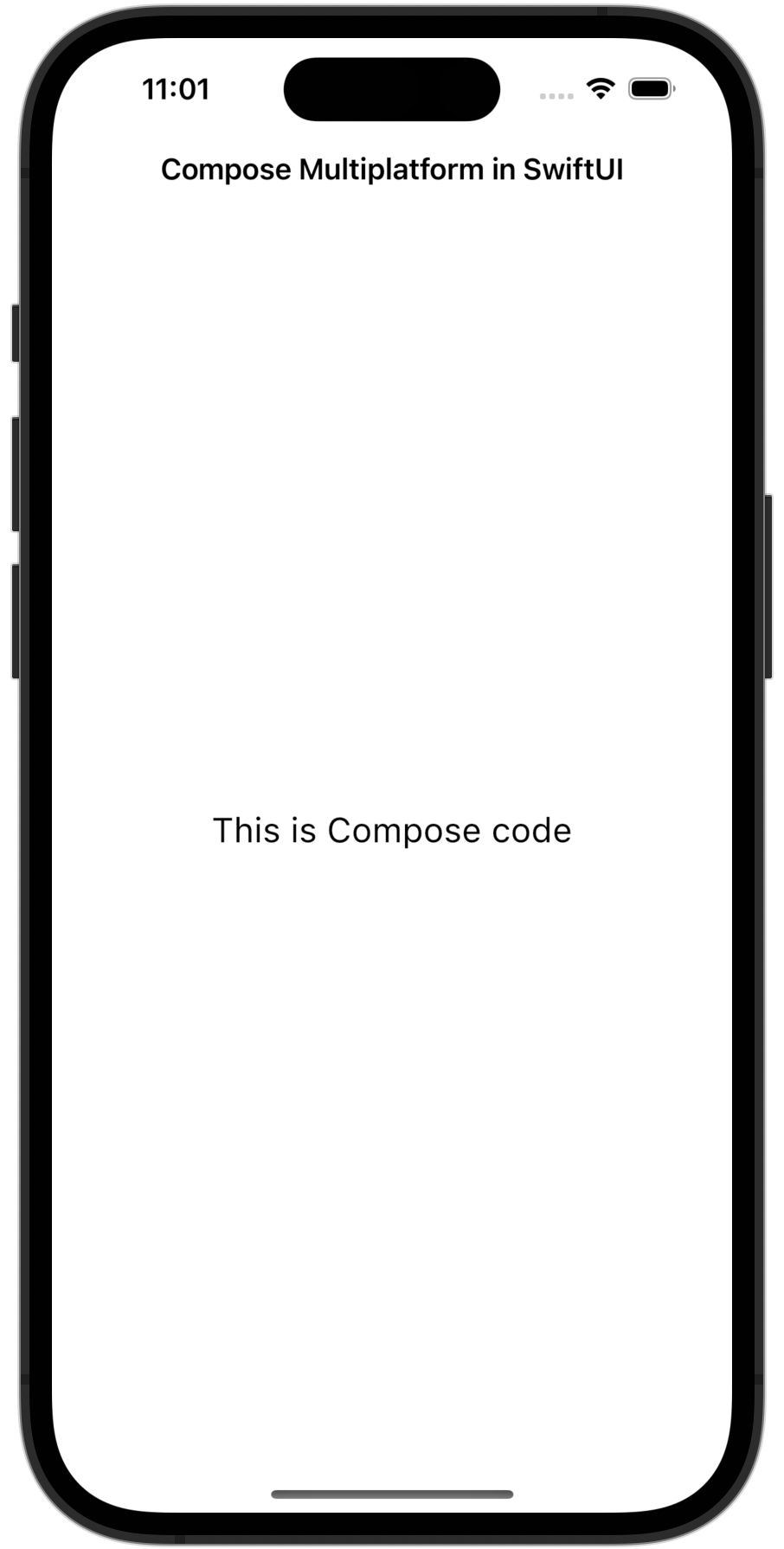
你可以在任何 SwiftUI 视图层级结构中使用此 ComposeView,并从 SwiftUI 代码内部控制其大小。
如果你想将 Compose Multiplatform 嵌入到现有应用程序中,请在所有使用 SwiftUI 的地方使用 ComposeView 结构。 关于示例,请参见我们的 示例项目。
在 Compose Multiplatform 中使用 SwiftUI
要在 Compose Multiplatform 中使用 SwiftUI,请将你的 Swift 代码添加到一个中间的 UIViewController 中。 目前,你无法直接在 Kotlin 中编写 SwiftUI 结构。相反,你必须在 Swift 中编写它们,并将它们传递给 Kotlin 函数。
首先,为你的入口点函数添加一个实参,以创建 ComposeUIViewController 组件:
@OptIn(ExperimentalForeignApi::class)
fun ComposeEntryPointWithUIViewController(
createUIViewController: () -> UIViewController
): UIViewController =
ComposeUIViewController {
Column(
Modifier
.fillMaxSize()
.windowInsetsPadding(WindowInsets.systemBars),
horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally
) {
Text("How to use SwiftUI inside Compose Multiplatform")
UIKitViewController(
factory = createUIViewController,
modifier = Modifier.size(300.dp).border(2.dp, Color.Blue),
)
}
}在你的 Swift 代码中,将 createUIViewController 传递给你的入口点函数。 你可以使用 UIHostingController 实例来包装 SwiftUI 视图:
Main_iosKt.ComposeEntryPointWithUIViewController(createUIViewController: { () -> UIViewController in
let swiftUIView = VStack {
Text("SwiftUI in Compose Multiplatform")
}
return UIHostingController(rootView: swiftUIView)
})最终,你的应用程序应该看起来像这样:

你可以在 示例项目 中探索此示例代码。
地图视图
你可以在 Compose Multiplatform 中使用 SwiftUI 的 Map 组件来实现地图视图。 这使得你的应用程序能够显示完全交互式的 SwiftUI 地图。
对于相同的 Kotlin 入口点函数,在 Swift 中,使用 UIHostingController 传递包装 Map 视图的 UIViewController:
import SwiftUI
import MapKit
Main_iosKt.ComposeEntryPointWithUIViewController(createUIViewController: {
let region = Binding.constant(
MKCoordinateRegion(
center: CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: 37.7749, longitude: -122.4194),
span: MKCoordinateSpan(latitudeDelta: 0.05, longitudeDelta: 0.05)
)
)
let mapView = Map(coordinateRegion: region)
return UIHostingController(rootView: mapView)
})现在,让我们来看一个高级示例。此代码向 SwiftUI 地图添加了一个自定义标注,并允许你从 Swift 更新视图状态:
import SwiftUI
import MapKit
struct AnnotatedMapView: View {
// Manages map region state
@State private var region = MKCoordinateRegion(
center: CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: 51.5074, longitude: -0.1278),
span: MKCoordinateSpan(latitudeDelta: 0.1, longitudeDelta: 0.1)
)
// Displays a map with a custom annotation
var body: some View {
Map(coordinateRegion: $region, annotationItems: [Landmark.example]) { landmark in
MapMarker(coordinate: landmark.coordinate, tint: .blue)
}
}
}
struct Landmark: Identifiable {
let id = UUID()
let name: String
let coordinate: CLLocationCoordinate2D
static let example = Landmark(
name: "Big Ben",
coordinate: CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: 51.5007, longitude: -0.1246)
)
}然后,你可以将这个带标注的地图包装在 UIHostingController 中,并将其传递给你的 Compose Multiplatform 代码:
Main_iosKt.ComposeEntryPointWithUIViewController(createUIViewController: {
return UIHostingController(rootView: AnnotatedMapView())
})AnnotatedMapView 执行以下任务:
- 定义了一个 SwiftUI
Map视图,并将其嵌入到一个名为AnnotatedMapView的自定义视图中。 - 使用
@State和MKCoordinateRegion管理地图定位的内部状态,使 Compose Multiplatform 能够显示交互式、状态感知型地图。 - 使用一个符合
Identifiable协议的静态Landmark模型在地图上显示MapMarker,Identifiable是 SwiftUI 中标注所需的协议。 - 使用
annotationItems声明式地在地图上放置自定义标记。 - 将 SwiftUI 组件包装在
UIHostingController中,然后将其作为UIViewController传递给 Compose Multiplatform。
相机视图
你可以在 Compose Multiplatform 中使用 SwiftUI 和 UIKit 的 UIImagePickerController 来实现相机视图,将其包装在一个 SwiftUI 兼容组件中。 这使得你的应用程序能够启动系统相机并拍摄照片。
对于相同的 Kotlin 入口点函数,在 Swift 中,使用 UIImagePickerController 定义一个基本的 CameraView 并使用 UIHostingController 嵌入它:
Main_iosKt.ComposeEntryPointWithUIViewController(createUIViewController: {
return UIHostingController(rootView: CameraView { image in
// Handle captured image here
})
})要使其工作,请按如下方式定义 CameraView:
import SwiftUI
import UIKit
struct CameraView: UIViewControllerRepresentable {
let imageHandler: (UIImage) -> Void
@Environment(\.presentationMode) private var presentationMode
init(imageHandler: @escaping (UIImage) -> Void) {
self.imageHandler = imageHandler
}
func makeCoordinator() -> Coordinator {
Coordinator(self)
}
func makeUIViewController(context: Context) -> UIImagePickerController {
let picker = UIImagePickerController()
picker.sourceType = .camera
picker.delegate = context.coordinator
return picker
}
func updateUIViewController(_ uiViewController: UIImagePickerController, context: Context) {}
class Coordinator: NSObject, UINavigationControllerDelegate, UIImagePickerControllerDelegate {
let parent: CameraView
init(_ parent: CameraView) {
self.parent = parent
}
func imagePickerController(_ picker: UIImagePickerController,
didFinishPickingMediaWithInfo info: [UIImagePickerController.InfoKey : Any]) {
if let image = info[.originalImage] as? UIImage {
parent.imageHandler(image)
}
parent.presentationMode.wrappedValue.dismiss()
}
func imagePickerControllerDidCancel(_ picker: UIImagePickerController) {
parent.presentationMode.wrappedValue.dismiss()
}
}
}现在,让我们来看一个高级示例。此代码呈现一个相机视图,并在同一 SwiftUI 视图中显示捕获图像的缩略图:
import SwiftUI
import UIKit
struct CameraPreview: View {
// Controls the camera sheet visibility
@State private var showCamera = false
// Stores the captured image
@State private var capturedImage: UIImage?
var body: some View {
VStack {
if let image = capturedImage {
// Displays the captured image
Image(uiImage: image)
.resizable()
.scaledToFit()
.frame(height: 200)
} else {
// Shows placeholder text when no image is captured
Text("No image captured")
}
// Adds a button to open the camera
Button("Open Camera") {
showCamera = true
}
// Presents CameraView as a modal sheet
.sheet(isPresented: $showCamera) {
CameraView { image in
capturedImage = image
}
}
}
}
}CameraPreview 视图执行以下任务:
- 当用户轻触按钮时,在模态
.sheet中呈现CameraView。 - 使用
@State属性包装器来存储和显示捕获的图像。 - 嵌入 SwiftUI 的原生
Image视图来预览照片。 - 复用与之前相同的基于
UIViewControllerRepresentable的CameraView,但将其更深入地集成到 SwiftUI 状态系统。
要在真机上测试,你需要将
NSCameraUsageDescription键添加到你的应用Info.plist文件中。否则,应用将在运行时崩溃。
Web 视图
你可以在 Compose Multiplatform 中使用 SwiftUI 实现 Web 视图,方法是使用 UIViewRepresentable 包装 UIKit 的 WKWebView 组件。 这允许你以完整的原生渲染方式显示嵌入式 Web 内容。
对于相同的 Kotlin 入口点函数,在 Swift 中,使用 UIHostingController 定义一个基本的嵌入式 WebView:
Main_iosKt.ComposeEntryPointWithUIViewController(createUIViewController: {
let url = URL(string: "https://www.jetbrains.com")!
return UIHostingController(rootView: WebView(url: url))
})现在,让我们来看一个高级示例。此代码为 Web 视图添加了导航跟踪和加载状态显示:
import SwiftUI
import UIKit
import WebKit
struct AdvancedWebView: UIViewRepresentable {
let url: URL
@Binding var isLoading: Bool
@Binding var currentURL: String
// Creates WKWebView with navigation delegate
func makeUIView(context: Context) -> WKWebView {
let webView = WKWebView()
webView.navigationDelegate = context.coordinator
webView.load(URLRequest(url: url))
return webView
}
func updateUIView(_ uiView: WKWebView, context: Context) {}
// Creates coordinator to handle web navigation events
func makeCoordinator() -> Coordinator {
Coordinator(isLoading: $isLoading, currentURL: $currentURL)
}
class Coordinator: NSObject, WKNavigationDelegate {
@Binding var isLoading: Bool
@Binding var currentURL: String
init(isLoading: Binding<Bool>, currentURL: Binding<String>) {
_isLoading = isLoading
_currentURL = currentURL
}
func webView(_ webView: WKWebView, didStartProvisionalNavigation navigation: WKNavigation?) {
isLoading = true
}
// Updates URL and indicates loading has completed
func webView(_ webView: WKWebView, didFinish navigation: WKNavigation?) {
isLoading = false
currentURL = webView.url?.absoluteString ?? ""
}
}
}在 SwiftUI 视图中按如下方式使用它:
struct WebViewContainer: View {
// Tracks loading state of web view
@State private var isLoading = false
// Tracks current URL displayed
@State private var currentURL = ""
var body: some View {
VStack {
// Displays loading indicator while loading
if isLoading {
ProgressView()
}
// Shows current URL
Text("URL: \(currentURL)")
.font(.caption)
.lineLimit(1)
.truncationMode(.middle)
// Embeds the advanced web view
AdvancedWebView(
url: URL(string: "https://www.jetbrains.com")!,
isLoading: $isLoading,
currentURL: $currentURL
)
}
}
}AdvancedWebView 和 WebViewContainer 执行以下任务:
- 创建一个带有自定义导航委托的
WKWebView,以跟踪加载进度和 URL 更改。 - 使用 SwiftUI 的
@State绑定来动态更新 UI,以响应导航事件。 - 在页面加载时显示
ProgressView加载指示器。 - 使用
Text组件在视图顶部显示当前 URL。 - 使用
UIHostingController将此组件集成到你的 Compose UI 中。
下一步
你还可以探索 Compose Multiplatform 与 UIKit 框架集成 的方式。
