SwiftUI 프레임워크와의 통합
Compose Multiplatform은 SwiftUI 프레임워크와 상호 운용 가능합니다. SwiftUI 애플리케이션 내부에 Compose Multiplatform을 포함할 수 있으며, 네이티브 SwiftUI 컴포넌트를 Compose Multiplatform UI 내부에 포함할 수도 있습니다. 이 페이지에서는 SwiftUI 내에서 Compose Multiplatform을 사용하는 예제와 Compose Multiplatform 앱 내부에 SwiftUI를 포함하는 예제를 모두 제공합니다.
UIKit 상호 운용성에 대해 자세히 알아보려면 UIKit 프레임워크와의 통합 문서를 참조하십시오.
SwiftUI 애플리케이션 내에서 Compose Multiplatform 사용
SwiftUI 애플리케이션 내에서 Compose Multiplatform을 사용하려면, UIKit의 UIViewController를 반환하고 Compose Multiplatform 코드를 포함하는 Kotlin 함수 MainViewController()를 생성합니다.
fun MainViewController(): UIViewController =
ComposeUIViewController {
Box(Modifier.fillMaxSize(), contentAlignment = Alignment.Center) {
Text("This is Compose code", fontSize = 20.sp)
}
}ComposeUIViewController()는 composable 함수를 content 인수로 받는 Compose Multiplatform 라이브러리 함수입니다. 이 방식으로 전달된 함수는 Text()와 같은 다른 composable 함수를 호출할 수 있습니다.
컴포저블 함수는
@Composable어노테이션이 있는 함수입니다.
다음으로, SwiftUI에서 Compose Multiplatform을 나타내는 구조체가 필요합니다. UIViewController 인스턴스를 SwiftUI 뷰로 변환하는 다음 구조체를 생성합니다.
struct ComposeViewController: UIViewControllerRepresentable {
func makeUIViewController(context: Context) -> UIViewController {
return Main_iosKt.MainViewController()
}
func updateUIViewController(_ uiViewController: UIViewController, context: Context) {
}
}이제 다른 SwiftUI 코드에서 ComposeView 구조체를 사용할 수 있습니다.
Main_iosKt.MainViewController는 생성된 이름입니다. Swift에서 Kotlin 코드에 액세스하는 방법에 대한 자세한 내용은 Swift/Objective-C와의 상호 운용성 페이지에서 확인할 수 있습니다.
결과적으로 애플리케이션은 다음과 같아야 합니다.
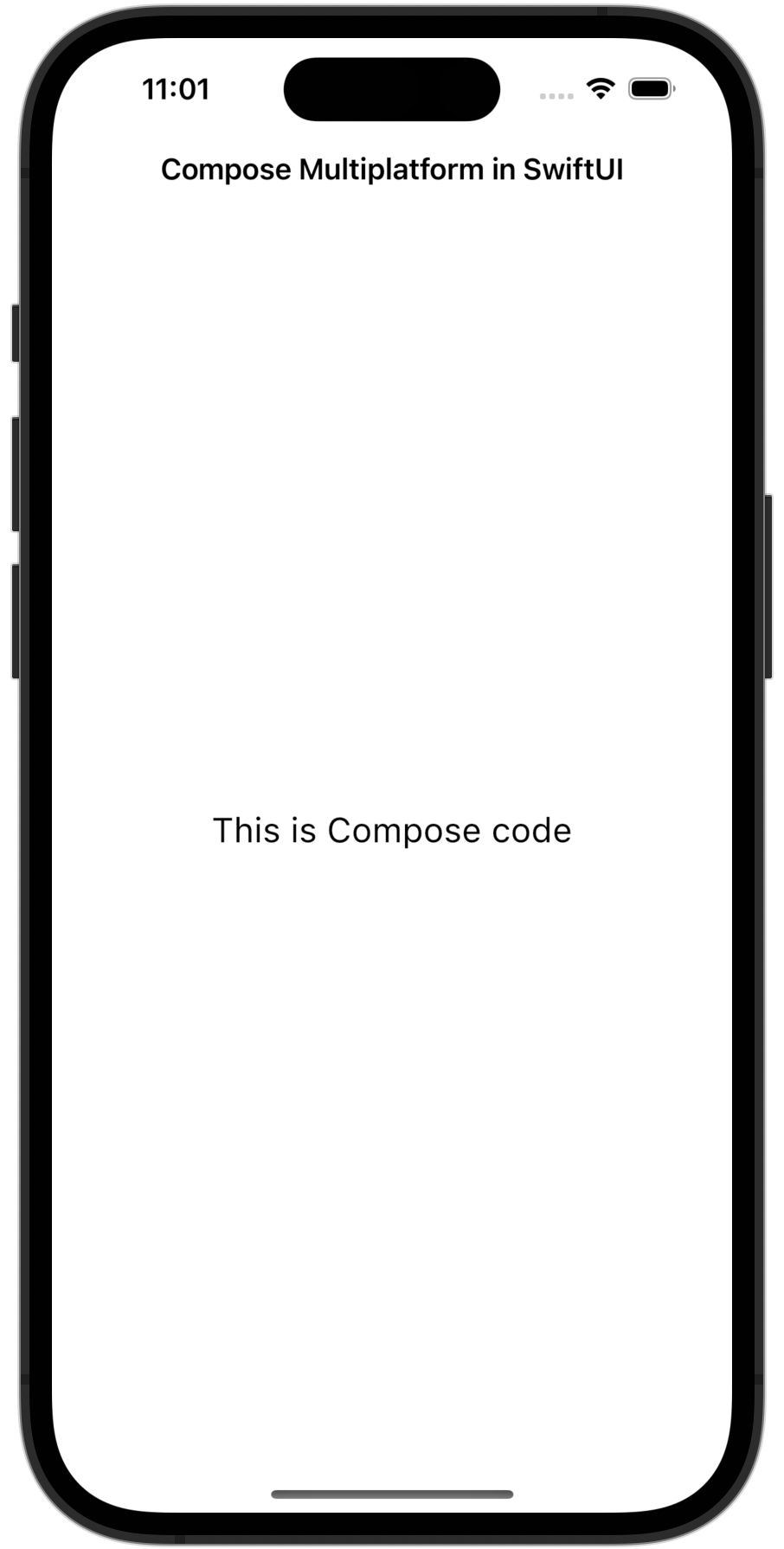
이 ComposeView를 모든 SwiftUI 뷰 계층 구조에서 사용할 수 있으며, SwiftUI 코드 내에서 해당 크기를 제어할 수 있습니다.
기존 애플리케이션에 Compose Multiplatform을 포함하려면 SwiftUI가 사용되는 모든 곳에서 ComposeView 구조체를 사용하십시오. 예제는 샘플 프로젝트를 참조하십시오.
Compose Multiplatform 내에서 SwiftUI 사용
Compose Multiplatform 내에서 SwiftUI를 사용하려면, 중간 UIViewController에 Swift 코드를 추가하십시오. 현재는 Kotlin에서 SwiftUI 구조체를 직접 작성할 수 없습니다. 대신 Swift로 작성하여 Kotlin 함수로 전달해야 합니다.
시작하려면 ComposeUIViewController 컴포넌트를 생성하기 위해 진입점 함수에 인수를 추가합니다.
@OptIn(ExperimentalForeignApi::class)
fun ComposeEntryPointWithUIViewController(
createUIViewController: () -> UIViewController
): UIViewController =
ComposeUIViewController {
Column(
Modifier
.fillMaxSize()
.windowInsetsPadding(WindowInsets.systemBars),
horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally
) {
Text("How to use SwiftUI inside Compose Multiplatform")
UIKitViewController(
factory = createUIViewController,
modifier = Modifier.size(300.dp).border(2.dp, Color.Blue),
)
}
}Swift 코드에서 createUIViewController를 진입점 함수에 전달합니다. UIHostingController 인스턴스를 사용하여 SwiftUI 뷰를 래핑할 수 있습니다.
Main_iosKt.ComposeEntryPointWithUIViewController(createUIViewController: { () -> UIViewController in
let swiftUIView = VStack {
Text("SwiftUI in Compose Multiplatform")
}
return UIHostingController(rootView: swiftUIView)
})결과적으로 애플리케이션은 다음과 같아야 합니다.

이 예제의 코드는 샘플 프로젝트에서 살펴볼 수 있습니다.
맵 뷰
SwiftUI의 Map 컴포넌트를 사용하여 Compose Multiplatform에서 맵 뷰를 구현할 수 있습니다. 이를 통해 애플리케이션에서 완전한 대화형 SwiftUI 맵을 표시할 수 있습니다.
동일한 Kotlin 진입점 함수의 경우, Swift에서 UIHostingController를 사용하여 Map 뷰를 래핑하는 UIViewController를 전달합니다.
import SwiftUI
import MapKit
Main_iosKt.ComposeEntryPointWithUIViewController(createUIViewController: {
let region = Binding.constant(
MKCoordinateRegion(
center: CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: 37.7749, longitude: -122.4194),
span: MKCoordinateSpan(latitudeDelta: 0.05, longitudeDelta: 0.05)
)
)
let mapView = Map(coordinateRegion: region)
return UIHostingController(rootView: mapView)
})이제 고급 예제를 살펴보겠습니다. 이 코드는 SwiftUI 맵에 사용자 정의 어노테이션을 추가하고 Swift에서 뷰 상태를 업데이트할 수 있도록 합니다.
import SwiftUI
import MapKit
struct AnnotatedMapView: View {
// Manages map region state
@State private var region = MKCoordinateRegion(
center: CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: 51.5074, longitude: -0.1278),
span: MKCoordinateSpan(latitudeDelta: 0.1, longitudeDelta: 0.1)
)
// Displays a map with a custom annotation
var body: some View {
Map(coordinateRegion: $region, annotationItems: [Landmark.example]) { landmark in
MapMarker(coordinate: landmark.coordinate, tint: .blue)
}
}
}
struct Landmark: Identifiable {
let id = UUID()
let name: String
let coordinate: CLLocationCoordinate2D
static let example = Landmark(
name: "Big Ben",
coordinate: CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: 51.5007, longitude: -0.1246)
)
}그런 다음 이 어노테이션이 추가된 맵을 UIHostingController로 래핑하고 Compose Multiplatform 코드로 전달할 수 있습니다.
Main_iosKt.ComposeEntryPointWithUIViewController(createUIViewController: {
return UIHostingController(rootView: AnnotatedMapView())
})AnnotatedMapView는 다음 작업을 수행합니다.
- SwiftUI
Map뷰를 정의하고AnnotatedMapView라는 사용자 정의 뷰 내부에 포함합니다. @State및MKCoordinateRegion을 사용하여 맵 위치 지정에 대한 내부 상태를 관리하여 Compose Multiplatform이 대화형이며 상태를 인식하는 맵을 표시할 수 있도록 합니다.- SwiftUI의 어노테이션에 필요한
Identifiable을 준수하는 정적Landmark모델을 사용하여 맵에MapMarker를 표시합니다. annotationItems를 사용하여 맵에 사용자 정의 마커를 선언적으로 배치합니다.- SwiftUI 컴포넌트를
UIHostingController내부에 래핑하며, 이는UIViewController로 Compose Multiplatform에 전달됩니다.
카메라 뷰
SwiftUI 및 UIKit의 UIImagePickerController를 SwiftUI 호환 컴포넌트로 래핑하여 Compose Multiplatform에서 카메라 뷰를 구현할 수 있습니다. 이를 통해 애플리케이션에서 시스템 카메라를 실행하고 사진을 촬영할 수 있습니다.
동일한 Kotlin 진입점 함수의 경우, Swift에서 UIImagePickerController를 사용하여 기본 CameraView를 정의하고 UIHostingController를 사용하여 포함합니다.
Main_iosKt.ComposeEntryPointWithUIViewController(createUIViewController: {
return UIHostingController(rootView: CameraView { image in
// Handle captured image here
})
})이를 작동시키려면 CameraView를 다음과 같이 정의합니다.
import SwiftUI
import UIKit
struct CameraView: UIViewControllerRepresentable {
let imageHandler: (UIImage) -> Void
@Environment(\.presentationMode) private var presentationMode
init(imageHandler: @escaping (UIImage) -> Void) {
self.imageHandler = imageHandler
}
func makeCoordinator() -> Coordinator {
Coordinator(self)
}
func makeUIViewController(context: Context) -> UIImagePickerController {
let picker = UIImagePickerController()
picker.sourceType = .camera
picker.delegate = context.coordinator
return picker
}
func updateUIViewController(_ uiViewController: UIImagePickerController, context: Context) {}
class Coordinator: NSObject, UINavigationControllerDelegate, UIImagePickerControllerDelegate {
let parent: CameraView
init(_ parent: CameraView) {
self.parent = parent
}
func imagePickerController(_ picker: UIImagePickerController,
didFinishPickingMediaWithInfo info: [UIImagePickerController.InfoKey : Any]) {
if let image = info[.originalImage] as? UIImage {
parent.imageHandler(image)
}
parent.presentationMode.wrappedValue.dismiss()
}
func imagePickerControllerDidCancel(_ picker: UIImagePickerController) {
parent.presentationMode.wrappedValue.dismiss()
}
}
}이제 고급 예제를 살펴보겠습니다. 이 코드는 카메라 뷰를 표시하고 촬영된 이미지의 썸네일을 동일한 SwiftUI 뷰에 표시합니다.
import SwiftUI
import UIKit
struct CameraPreview: View {
// Controls the camera sheet visibility
@State private var showCamera = false
// Stores the captured image
@State private var capturedImage: UIImage?
var body: some View {
VStack {
if let image = capturedImage {
// Displays the captured image
Image(uiImage: image)
.resizable()
.scaledToFit()
.frame(height: 200)
} else {
// Shows placeholder text when no image is captured
Text("No image captured")
}
// Adds a button to open the camera
Button("Open Camera") {
showCamera = true
}
// Presents CameraView as a modal sheet
.sheet(isPresented: $showCamera) {
CameraView { image in
capturedImage = image
}
}
}
}
}CameraPreview 뷰는 다음 작업을 수행합니다.
- 사용자가 버튼을 탭하면
CameraView를 모달.sheet로 표시합니다. @State프로퍼티 래퍼를 사용하여 촬영된 이미지를 저장하고 표시합니다.- 사진을 미리 보기 위해 SwiftUI의 네이티브
Image뷰를 포함합니다. - 이전과 동일한
UIViewControllerRepresentable기반CameraView를 재사용하지만, SwiftUI 상태 시스템에 더 깊이 통합합니다.
실제 장치에서 테스트하려면 앱의
Info.plist파일에NSCameraUsageDescription키를 추가해야 합니다. 이 키가 없으면 런타임에 앱이 충돌합니다.
웹 뷰
UIKit의 WKWebView 컴포넌트를 UIViewRepresentable로 래핑하여 SwiftUI를 사용하여 Compose Multiplatform에서 웹 뷰를 구현할 수 있습니다. 이를 통해 완전한 네이티브 렌더링으로 임베디드 웹 콘텐츠를 표시할 수 있습니다.
동일한 Kotlin 진입점 함수의 경우, Swift에서 UIHostingController를 사용하여 포함된 기본 WebView를 정의합니다.
Main_iosKt.ComposeEntryPointWithUIViewController(createUIViewController: {
let url = URL(string: "https://www.jetbrains.com")!
return UIHostingController(rootView: WebView(url: url))
})이제 고급 예제를 살펴보겠습니다. 이 코드는 웹 뷰에 내비게이션 추적 및 로딩 상태 표시 기능을 추가합니다.
import SwiftUI
import UIKit
import WebKit
struct AdvancedWebView: UIViewRepresentable {
let url: URL
@Binding var isLoading: Bool
@Binding var currentURL: String
// Creates WKWebView with navigation delegate
func makeUIView(context: Context) -> WKWebView {
let webView = WKWebView()
webView.navigationDelegate = context.coordinator
webView.load(URLRequest(url: url))
return webView
}
func updateUIView(_ uiView: WKWebView, context: Context) {}
// Creates coordinator to handle web navigation events
func makeCoordinator() -> Coordinator {
Coordinator(isLoading: $isLoading, currentURL: $currentURL)
}
class Coordinator: NSObject, WKNavigationDelegate {
@Binding var isLoading: Bool
@Binding var currentURL: String
init(isLoading: Binding<Bool>, currentURL: Binding<String>) {
_isLoading = isLoading
_currentURL = currentURL
}
func webView(_ webView: WKWebView, didStartProvisionalNavigation navigation: WKNavigation?) {
isLoading = true
}
// Updates URL and indicates loading has completed
func webView(_ webView: WKWebView, didFinish navigation: WKNavigation?) {
isLoading = false
currentURL = webView.url?.absoluteString ?? ""
}
}
}다음과 같이 SwiftUI 뷰에서 사용합니다.
struct WebViewContainer: View {
// Tracks loading state of web view
@State private var isLoading = false
// Tracks current URL displayed
@State private var currentURL = ""
var body: some View {
VStack {
// Displays loading indicator while loading
if isLoading {
ProgressView()
}
// Shows current URL
Text("URL: \(currentURL)")
.font(.caption)
.lineLimit(1)
.truncationMode(.middle)
// Embeds the advanced web view
AdvancedWebView(
url: URL(string: "https://www.jetbrains.com")!,
isLoading: $isLoading,
currentURL: $currentURL
)
}
}
}AdvancedWebView 및 WebViewContainer는 다음 작업을 수행합니다.
- 로딩 진행 상황 및 URL 변경 사항을 추적하기 위해 사용자 정의 내비게이션 델리게이트와 함께
WKWebView를 생성합니다. - 내비게이션 이벤트에 따라 UI를 동적으로 업데이트하기 위해 SwiftUI의
@State바인딩을 사용합니다. - 페이지가 로딩되는 동안
ProgressView스피너를 표시합니다. Text컴포넌트를 사용하여 뷰 상단에 현재 URL을 표시합니다.UIHostingController를 사용하여 이 컴포넌트를 Compose UI에 통합합니다.
다음 단계
Compose Multiplatform이 UIKit 프레임워크와 통합되는 방식도 살펴볼 수 있습니다.
