최상위 창 관리
데스크톱용 Compose Multiplatform은 창 관리를 위한 다양한 기능을 제공합니다. 창을 트레이에 숨기거나, 드래그 가능하게 만들거나, 크기를 조정하거나, 위치를 변경하는 등 다양한 작업을 할 수 있습니다.
창 열기 및 닫기
Window() 함수를 사용하여 일반 창을 만들 수 있습니다. 이를 컴포저블 스코프에 넣으려면 application 진입점에서 Window()를 사용합니다.
import androidx.compose.ui.window.Window
import androidx.compose.ui.window.application
fun main() = application {
Window(onCloseRequest = ::exitApplication) {
// Content of the window
}
}컴포저블 함수인 Window()를 사용하면 선언적으로 속성을 변경할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, 하나의 제목으로 창을 열고 나중에 제목을 변경할 수 있습니다.
import androidx.compose.material.Button
import androidx.compose.material.Text
import androidx.compose.runtime.getValue
import androidx.compose.runtime.mutableStateOf
import androidx.compose.runtime.remember
import androidx.compose.runtime.setValue
import androidx.compose.ui.window.Window
import androidx.compose.ui.window.application
fun main() = application {
var fileName by remember { mutableStateOf("Untitled") }
Window(onCloseRequest = ::exitApplication, title = "$fileName - Editor") {
Button(onClick = { fileName = "note.txt" }) {
Text("Save")
}
}
}
조건 추가
간단한 if 조건을 사용하여 창을 열고 닫을 수도 있습니다. 다음 코드 예제에서는 작업 완료 후 애플리케이션 창이 자동으로 닫힙니다.
import androidx.compose.material.Text
import androidx.compose.runtime.LaunchedEffect
import androidx.compose.runtime.getValue
import androidx.compose.runtime.mutableStateOf
import androidx.compose.runtime.remember
import androidx.compose.runtime.setValue
import androidx.compose.ui.window.Window
import androidx.compose.ui.window.application
import kotlinx.coroutines.delay
fun main() = application {
var isPerformingTask by remember { mutableStateOf(true) }
LaunchedEffect(Unit) {
// Do some heavy lifting
delay(2000)
isPerformingTask = false
}
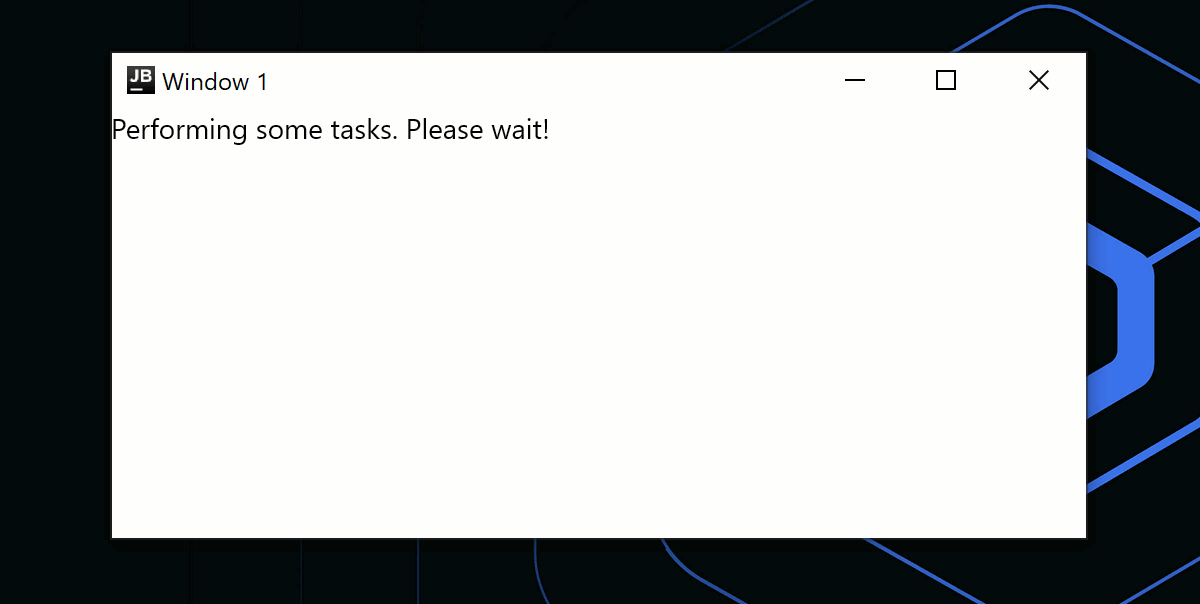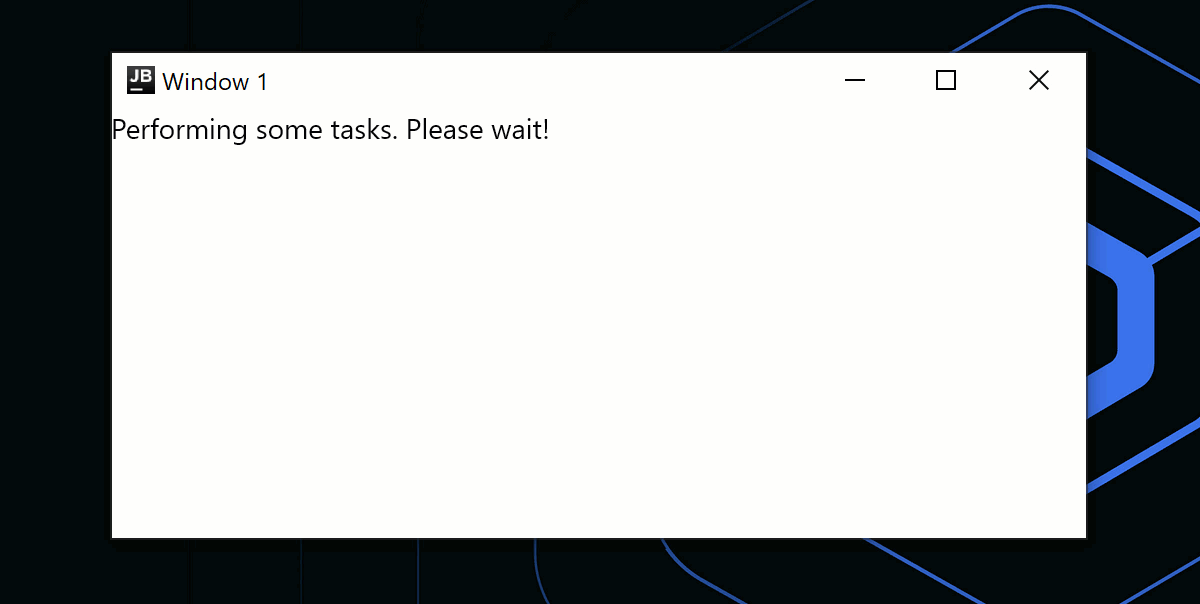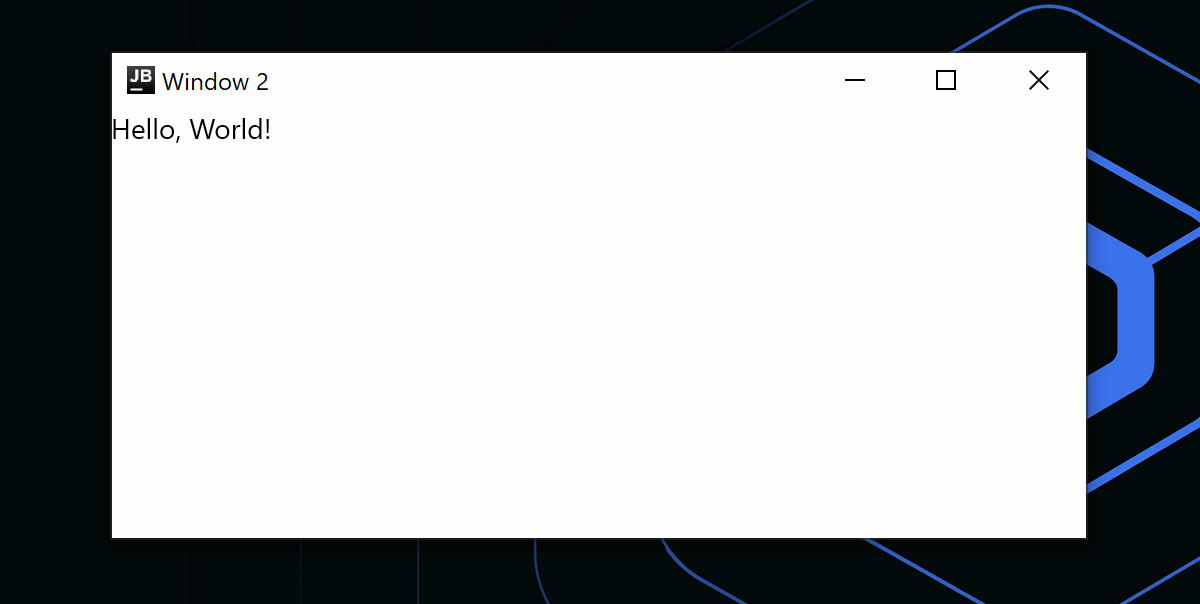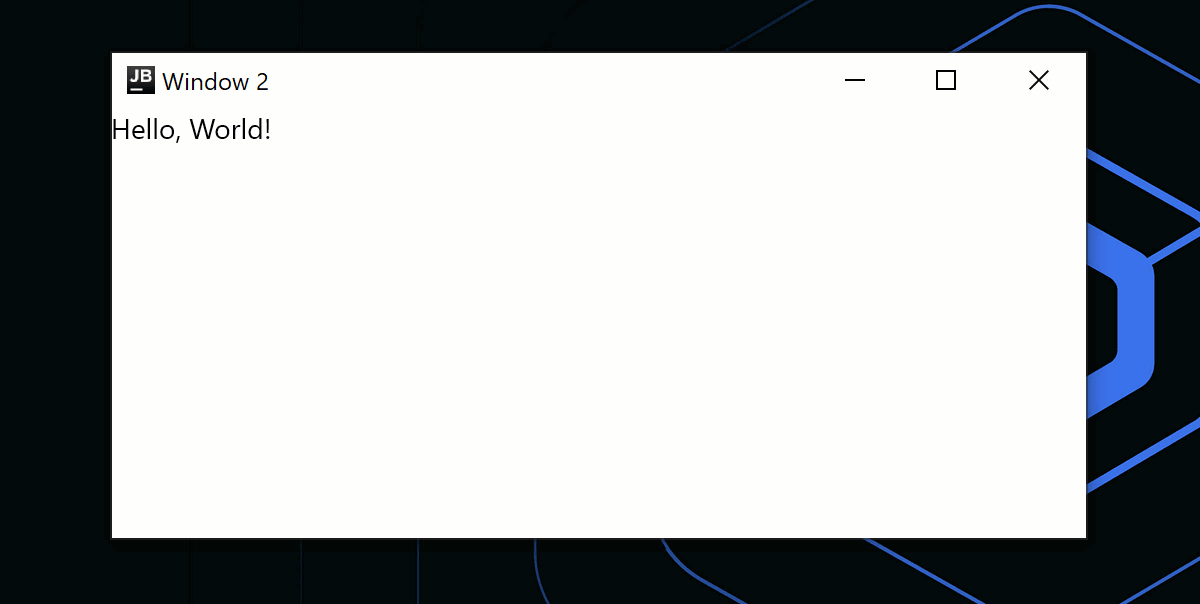
if (isPerformingTask) {
Window(
onCloseRequest = ::exitApplication,
title = "Window 1"
)
{
Text("Performing some tasks. Please wait!")
}
} else {
Window(
onCloseRequest = ::exitApplication,
title = "Window 2"
) {
Text("Hello, World!")
}
}
}
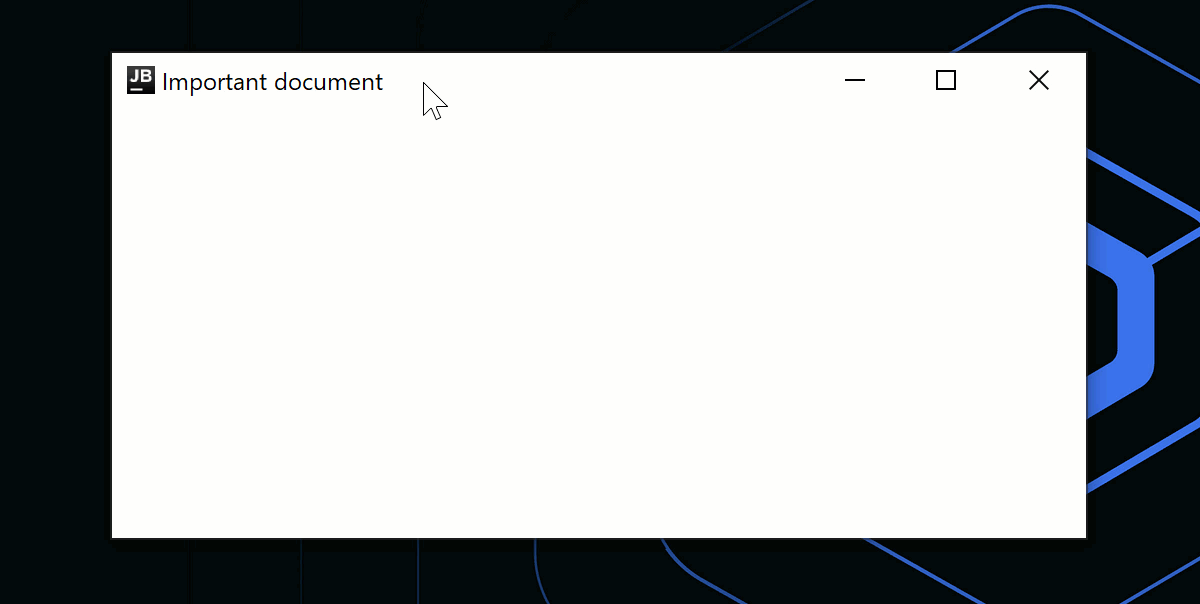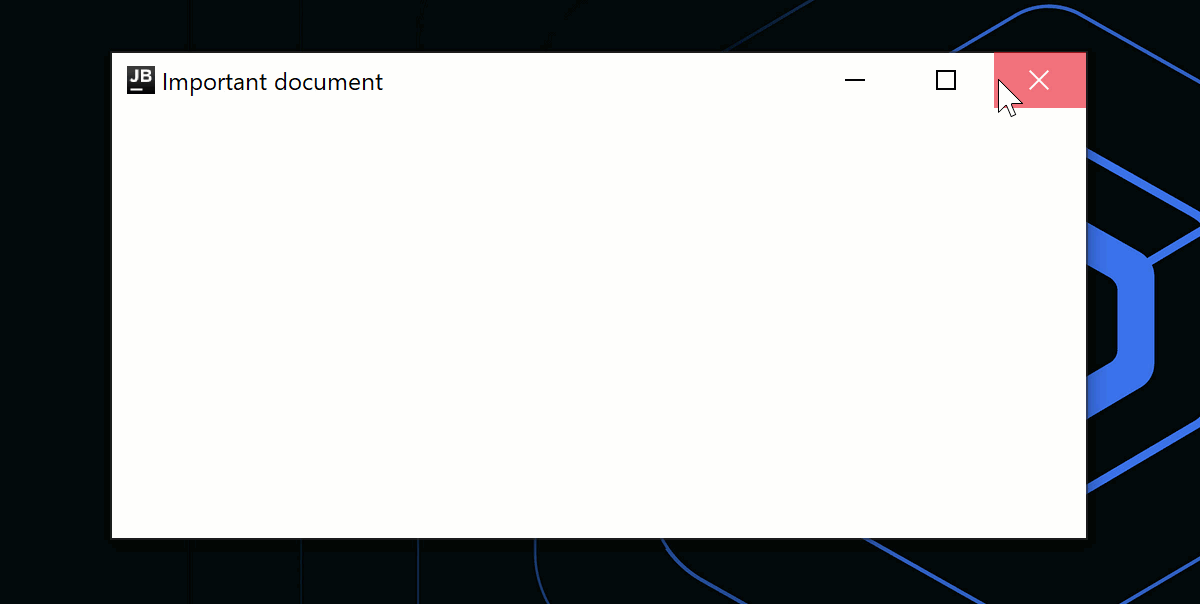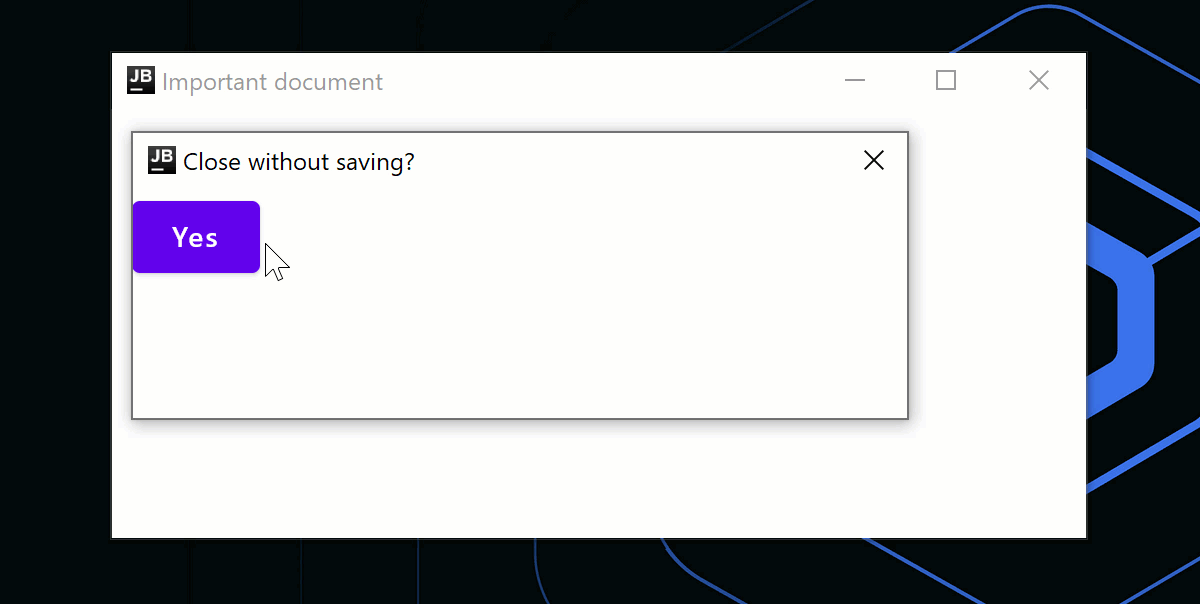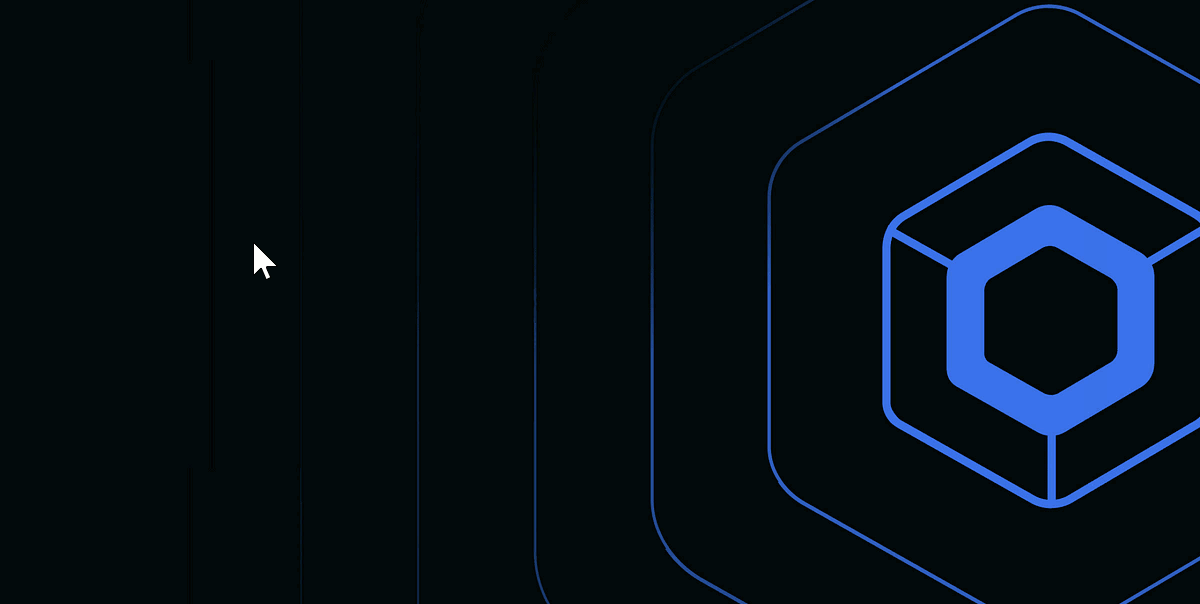
애플리케이션 종료 시 대화 상자를 표시하는 것과 같은 사용자 지정 로직을 사용하려면 onCloseRequest 콜백을 사용하여 닫기 동작을 재정의할 수 있습니다. 다음 코드 예제에서는 명령형 접근 방식(window.close()) 대신 선언형 접근 방식을 사용하여 상태 변경(isOpen = false)에 따라 창을 닫습니다.
import androidx.compose.material.Button
import androidx.compose.material.Text
import androidx.compose.runtime.getValue
import androidx.compose.runtime.mutableStateOf
import androidx.compose.runtime.remember
import androidx.compose.runtime.setValue
import androidx.compose.ui.window.DialogWindow
import androidx.compose.ui.window.Window
import androidx.compose.ui.window.application
fun main() = application {
var isOpen by remember { mutableStateOf(true) }
var isAskingToClose by remember { mutableStateOf(false) }
if (isOpen) {
Window(
onCloseRequest = { isAskingToClose = true },
title = "Important document"
) {
if (isAskingToClose) {
DialogWindow(
onCloseRequest = { isAskingToClose = false },
title = "Close without saving?"
) {
Button(
onClick = { isOpen = false }
) {
Text("Yes")
}
}
}
}
}
}"}
여러 창 작업
애플리케이션에 여러 창이 있는 경우, 애플리케이션 상태를 위한 별도의 클래스를 만들고 mutableStateListOf 변경에 따라 창을 열거나 닫을 수 있습니다.
import androidx.compose.runtime.Composable
import androidx.compose.runtime.key
import androidx.compose.runtime.mutableStateListOf
import androidx.compose.runtime.remember
import androidx.compose.ui.window.MenuBar
import androidx.compose.ui.window.Window
import androidx.compose.ui.window.application
fun main() = application {
val applicationState = remember { MyApplicationState() }
for (window in applicationState.windows) {
key(window) {
MyWindow(window)
}
}
}
@Composable
private fun MyWindow(
state: MyWindowState
) = Window(onCloseRequest = state::close, title = state.title) {
MenuBar {
Menu("File") {
Item("New window", onClick = state.openNewWindow)
Item("Exit", onClick = state.exit)
}
}
}
private class MyApplicationState {
val windows = mutableStateListOf<MyWindowState>()
init {
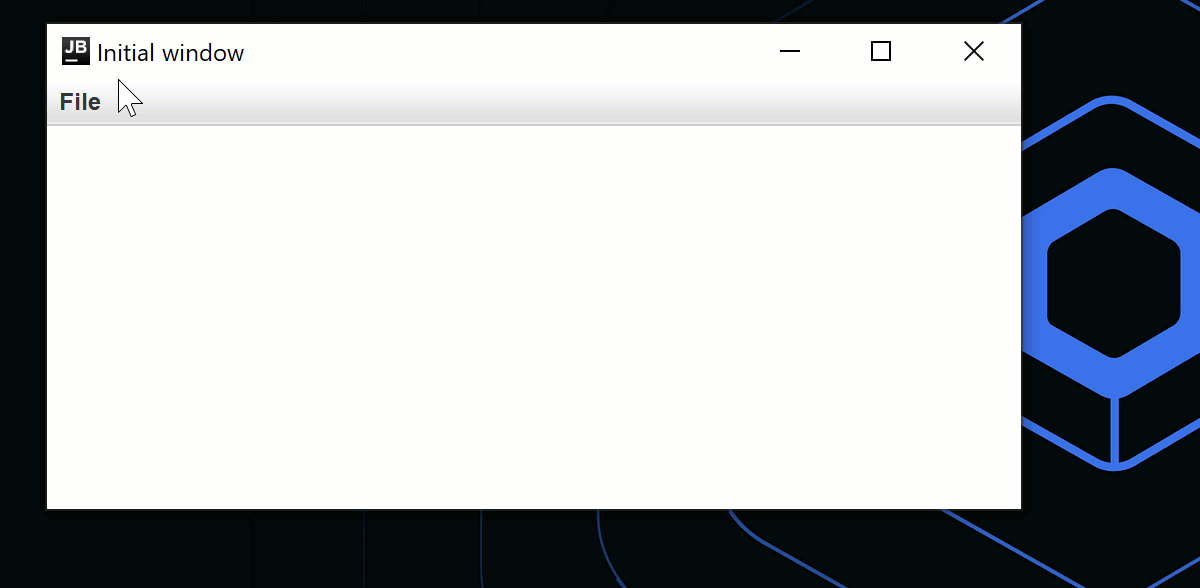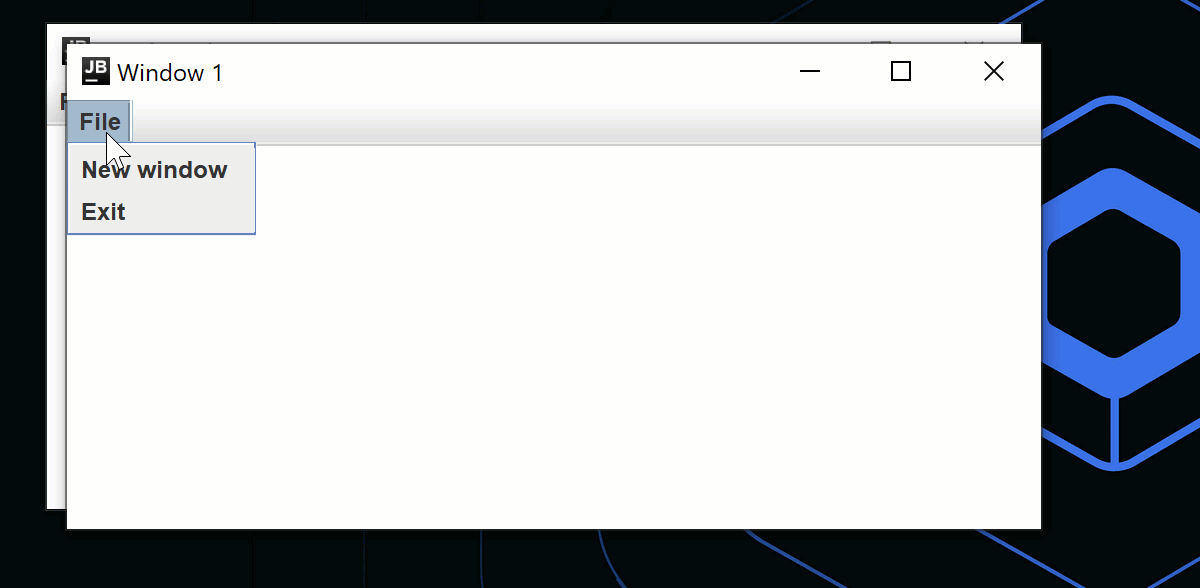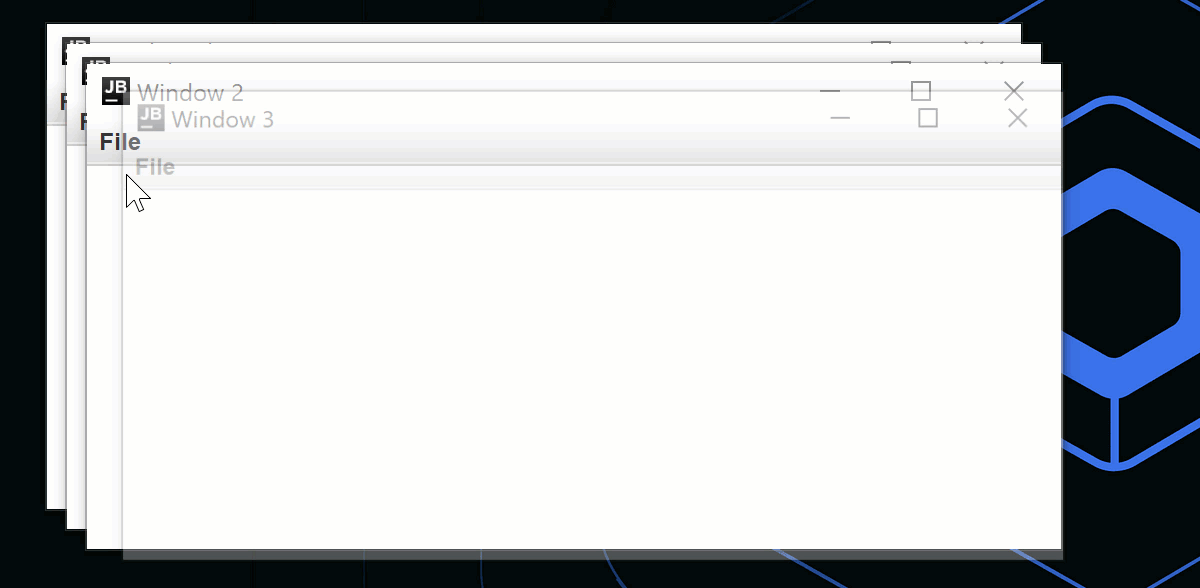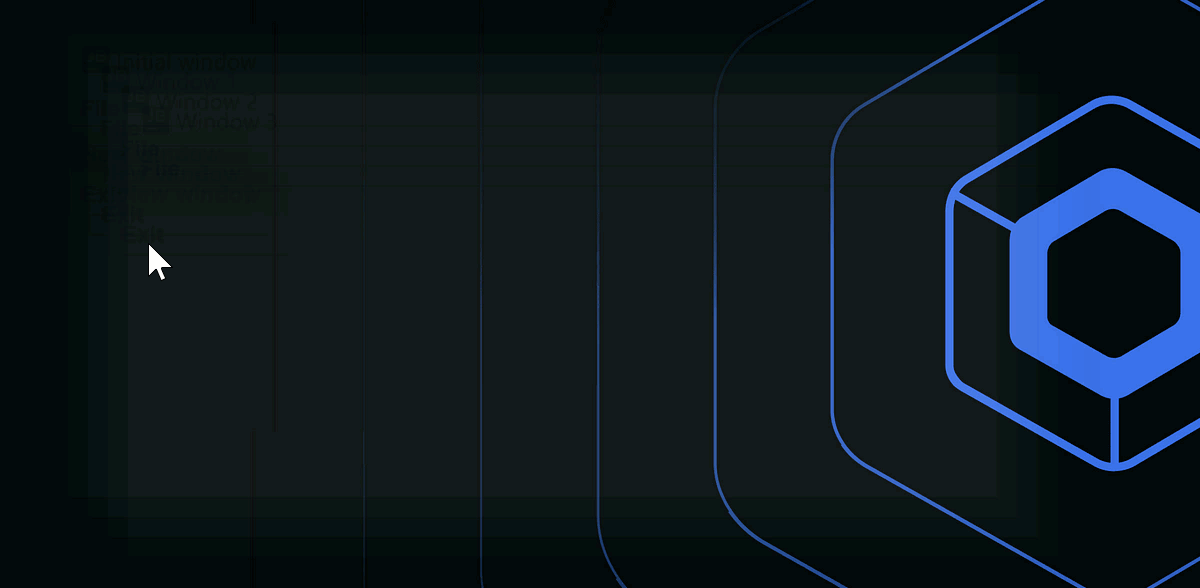
windows += MyWindowState("Initial window")
}
fun openNewWindow() {
windows += MyWindowState("Window ${windows.size}")
}
fun exit() {
windows.clear()
}
private fun MyWindowState(
title: String
) = MyWindowState(
title,
openNewWindow = ::openNewWindow,
exit = ::exit,
windows::remove
)
}
private class MyWindowState(
val title: String,
val openNewWindow: () -> Unit,
val exit: () -> Unit,
private val close: (MyWindowState) -> Unit
) {
fun close() = close(this)
}
더 복잡한 예제는 코드 뷰어(Code Viewer) 샘플을 참조하세요.
창을 시스템 트레이로 최소화하기
창을 닫는 대신 숨기려면 windowState.isVisible 상태를 변경할 수 있습니다.
import androidx.compose.material.Text
import androidx.compose.runtime.LaunchedEffect
import androidx.compose.runtime.getValue
import androidx.compose.runtime.mutableStateOf
import androidx.compose.runtime.remember
import androidx.compose.runtime.setValue
import androidx.compose.ui.geometry.Size
import androidx.compose.ui.graphics.Color
import androidx.compose.ui.graphics.drawscope.DrawScope
import androidx.compose.ui.graphics.painter.Painter
import androidx.compose.ui.window.Tray
import androidx.compose.ui.window.Window
import androidx.compose.ui.window.application
import kotlinx.coroutines.delay
fun main() = application {
var isVisible by remember { mutableStateOf(true) }
Window(
onCloseRequest = { isVisible = false },
visible = isVisible,
title = "Counter",
) {
var counter by remember { mutableStateOf(0) }
LaunchedEffect(Unit) {
while (true) {
counter++
delay(1000)
}
}
Text(counter.toString())
}
if (!isVisible) {
Tray(
TrayIcon,
tooltip = "Counter",
onAction = { isVisible = true },
menu = {
Item("Exit", onClick = ::exitApplication)
},
)
}
}
object TrayIcon : Painter() {
override val intrinsicSize = Size(256f, 256f)
override fun DrawScope.onDraw() {
drawOval(Color(0xFFFFA500))
}
},"}

singleWindowApplication() 함수
singleWindowApplication() 함수를 호출하여 단일 창 애플리케이션을 만들 수 있습니다.
singleWindowApplication() 함수는 사용하기 더 쉽지만 다음과 같은 제약 사항이 있습니다.
- 애플리케이션은 하나의 창만 가질 수 있습니다.
- 사용자 지정 닫기 로직을 추가할 수 없습니다.
- 런타임에 창의 속성을 변경할 수 없습니다.
import androidx.compose.ui.window.singleWindowApplication
fun main() = singleWindowApplication {
// Content of the window
}대안으로 application 진입점에서 Window() 컴포저블을 사용할 수 있습니다.
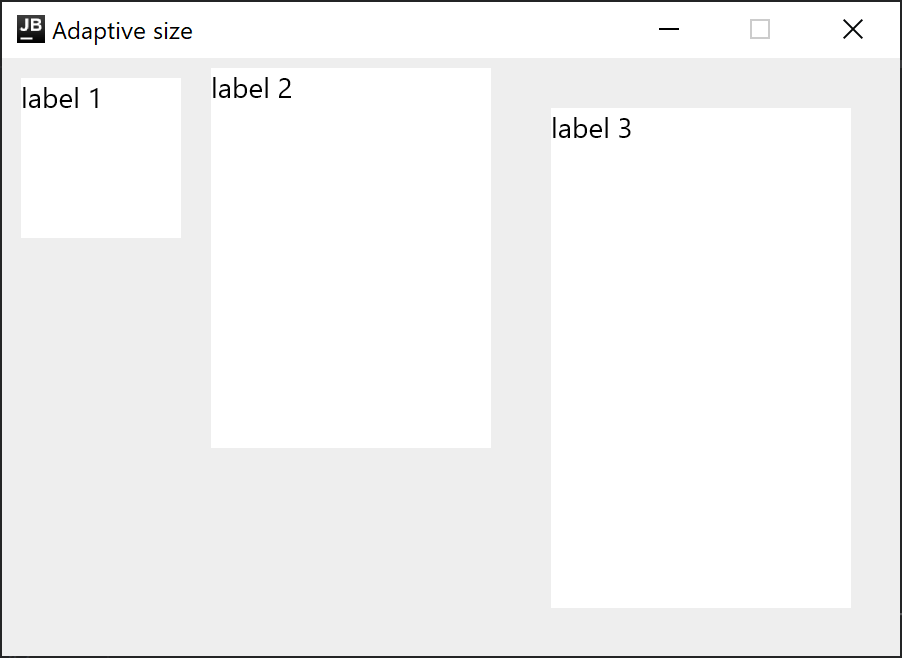
적응형 창 크기
예상되는 콘텐츠의 크기를 모르고 최적의 창 크기를 미리 지정할 수 없는 경우, WindowSize의 하나 또는 두 차원을 Dp.Unspecified로 설정할 수 있습니다. 데스크톱용 Compose Multiplatform은 콘텐츠에 맞게 창의 초기 크기를 자동으로 조정합니다.
import androidx.compose.foundation.background
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Column
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Row
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.padding
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.size
import androidx.compose.material.Text
import androidx.compose.ui.Modifier
import androidx.compose.ui.graphics.Color
import androidx.compose.ui.unit.Dp
import androidx.compose.ui.unit.dp
import androidx.compose.ui.window.Window
import androidx.compose.ui.window.application
import androidx.compose.ui.window.rememberWindowState
fun main() = application {
Window(
onCloseRequest = ::exitApplication,
state = rememberWindowState(width = Dp.Unspecified, height = Dp.Unspecified),
title = "Adaptive size",
resizable = false
) {
Column(Modifier.background(Color(0xFFEEEEEE))) {
Row {
Text("label 1", Modifier.size(100.dp, 100.dp).padding(10.dp).background(Color.White))
Text("label 2", Modifier.size(150.dp, 200.dp).padding(5.dp).background(Color.White))
Text("label 3", Modifier.size(200.dp, 300.dp).padding(25.dp).background(Color.White))
}
}
}
}
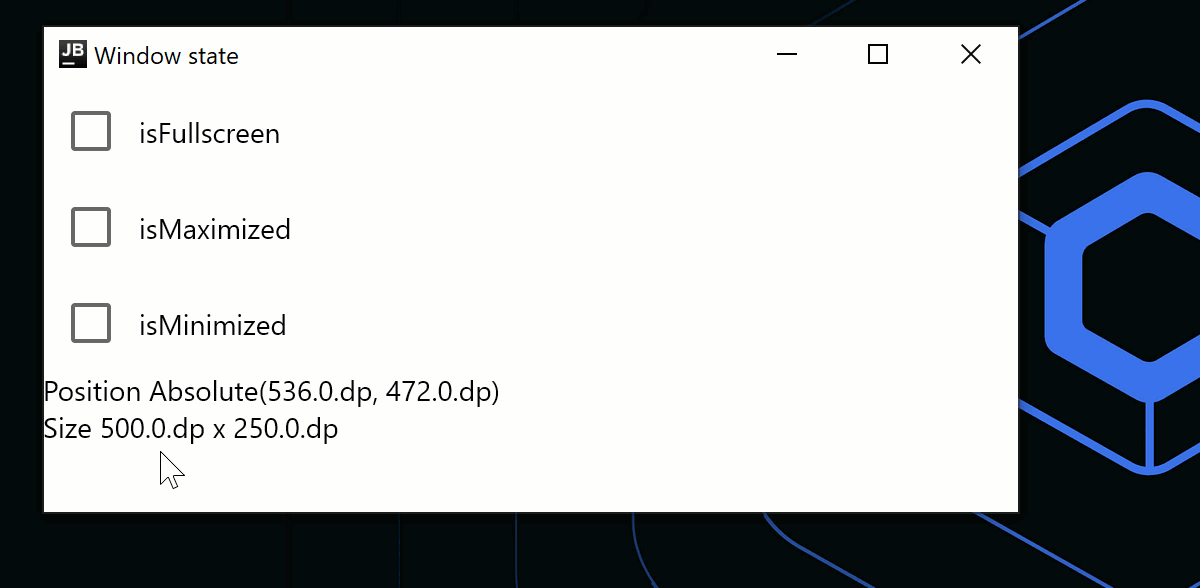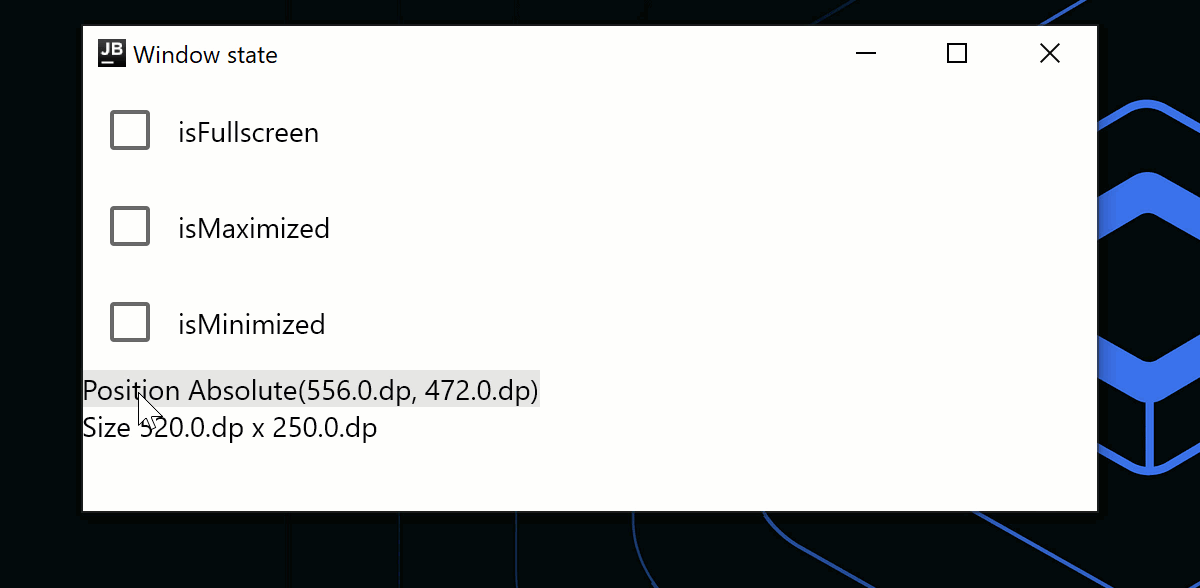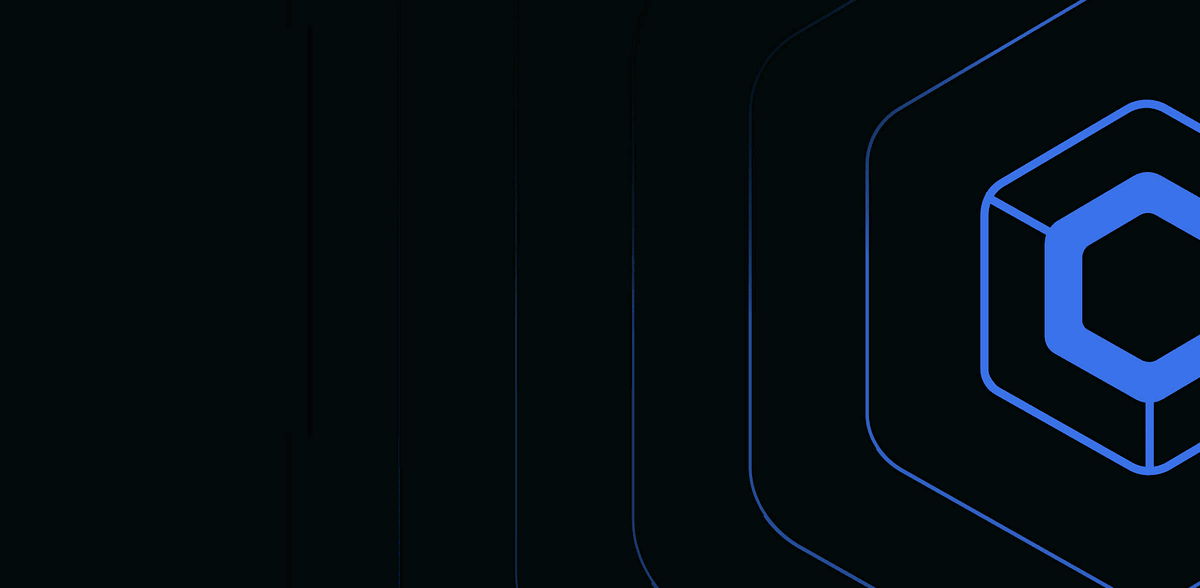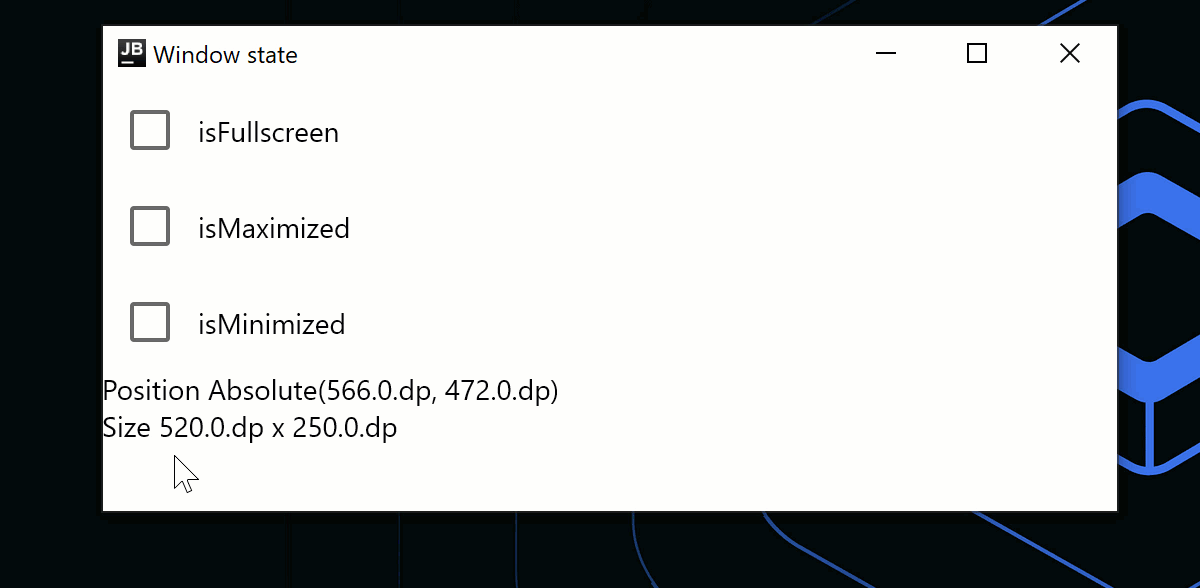
창 상태 변경
WindowState는 창 배치(placement), 현재 위치 및 크기를 위한 별도의 API 클래스입니다. placement 속성을 사용하면 창이 화면에 어떻게 배치되는지(플로팅, 최대화/최소화 또는 전체 화면) 지정할 수 있습니다. 상태 변경은 자동 리컴포지션을 트리거합니다. 창 상태를 변경하려면 콜백을 사용하거나 컴포저블에서 관찰합니다.
import androidx.compose.foundation.clickable
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Column
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Row
import androidx.compose.material.Checkbox
import androidx.compose.material.Text
import androidx.compose.ui.Alignment
import androidx.compose.ui.Modifier
import androidx.compose.ui.unit.dp
import androidx.compose.ui.window.Window
import androidx.compose.ui.window.WindowPlacement
import androidx.compose.ui.window.WindowPosition
import androidx.compose.ui.window.application
import androidx.compose.ui.window.rememberWindowState
fun main() = application {
val state = rememberWindowState(placement = WindowPlacement.Maximized)
Window(onCloseRequest = ::exitApplication, state, title = "Window state") {
Column {
Row(verticalAlignment = Alignment.CenterVertically) {
Checkbox(
state.placement == WindowPlacement.Fullscreen,
{
state.placement = if (it) {
WindowPlacement.Fullscreen
} else {
WindowPlacement.Floating
}
}
)
Text("isFullscreen")
}
Row(verticalAlignment = Alignment.CenterVertically) {
Checkbox(
state.placement == WindowPlacement.Maximized,
{
state.placement = if (it) {
WindowPlacement.Maximized
} else {
WindowPlacement.Floating
}
}
)
Text("isMaximized")
}
Row(verticalAlignment = Alignment.CenterVertically) {
Checkbox(state.isMinimized, { state.isMinimized = !state.isMinimized })
Text("isMinimized")
}
Text(
"Position ${state.position}",
Modifier.clickable {
val position = state.position
if (position is WindowPosition.Absolute) {
state.position = position.copy(x = state.position.x + 10.dp)
}
}
)
Text(
"Size ${state.size}",
Modifier.clickable {
state.size = state.size.copy(width = state.size.width + 10.dp)
}
)
}
}
}
창 상태 수신 대기
상태 변경에 반응하여 다른 비-컴포저블 애플리케이션 레벨로 값을 전송해야 하는 경우(예: 데이터베이스에 작성) snapshotFlow() 함수를 사용할 수 있습니다. 이 함수는 컴포저블 상태의 현재 값을 캡처합니다.
import androidx.compose.runtime.LaunchedEffect
import androidx.compose.runtime.snapshotFlow
import androidx.compose.ui.unit.DpSize
import androidx.compose.ui.window.Window
import androidx.compose.ui.window.WindowPosition
import androidx.compose.ui.window.application
import androidx.compose.ui.window.rememberWindowState
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.filter
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.launchIn
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.onEach
fun main() = application {
val state = rememberWindowState()
Window(onCloseRequest = ::exitApplication, state) {
LaunchedEffect(state) {
snapshotFlow { state.size }
.onEach(::onWindowResize)
.launchIn(this)
snapshotFlow { state.position }
.filter { it.isSpecified }
.onEach(::onWindowRelocate)
.launchIn(this)
}
}
}
private fun onWindowResize(size: DpSize) {
println("onWindowResize $size")
}
private fun onWindowRelocate(position: WindowPosition) {
println("onWindowRelocate $position")
}.onEach(::onWindowResize)"}
대화 상자
Window() 컴포저블을 사용하여 일반 창을 만들 수 있으며, DialogWindow() 컴포저블을 사용하여 사용자가 모달 창을 닫을 때까지 부모 창을 잠그는 모달 창을 만들 수 있습니다.
다음 코드 예제는 이러한 컴포저블을 사용하여 일반 창과 모달 창을 결합하는 방법을 보여줍니다.
import androidx.compose.material.Button
import androidx.compose.material.Text
import androidx.compose.runtime.getValue
import androidx.compose.runtime.mutableStateOf
import androidx.compose.runtime.remember
import androidx.compose.runtime.setValue
import androidx.compose.ui.Alignment
import androidx.compose.ui.window.DialogWindow
import androidx.compose.ui.window.Window
import androidx.compose.ui.window.WindowPosition
import androidx.compose.ui.window.application
import androidx.compose.ui.window.rememberDialogState
fun main() = application {
Window(
onCloseRequest = ::exitApplication,
) {
var isDialogOpen by remember { mutableStateOf(false) }
Button(onClick = { isDialogOpen = true }) {
Text(text = "Open dialog")
}
if (isDialogOpen) {
DialogWindow(
onCloseRequest = { isDialogOpen = false },
state = rememberDialogState(position = WindowPosition(Alignment.Center))
) {
// Content of the window
}
}
}
},"}
드래그 가능한 창 영역
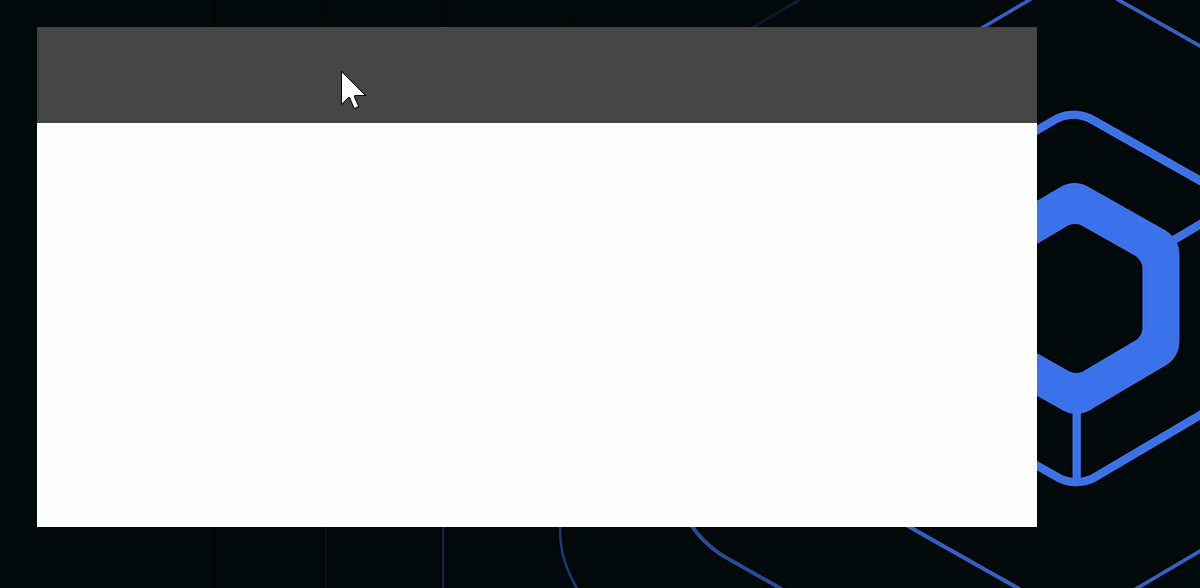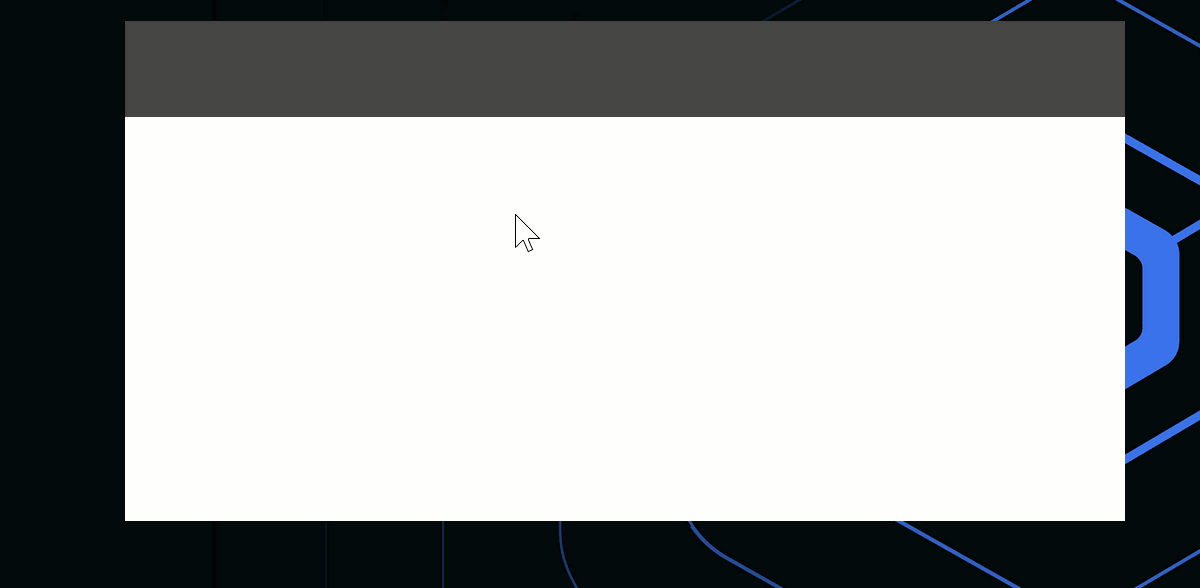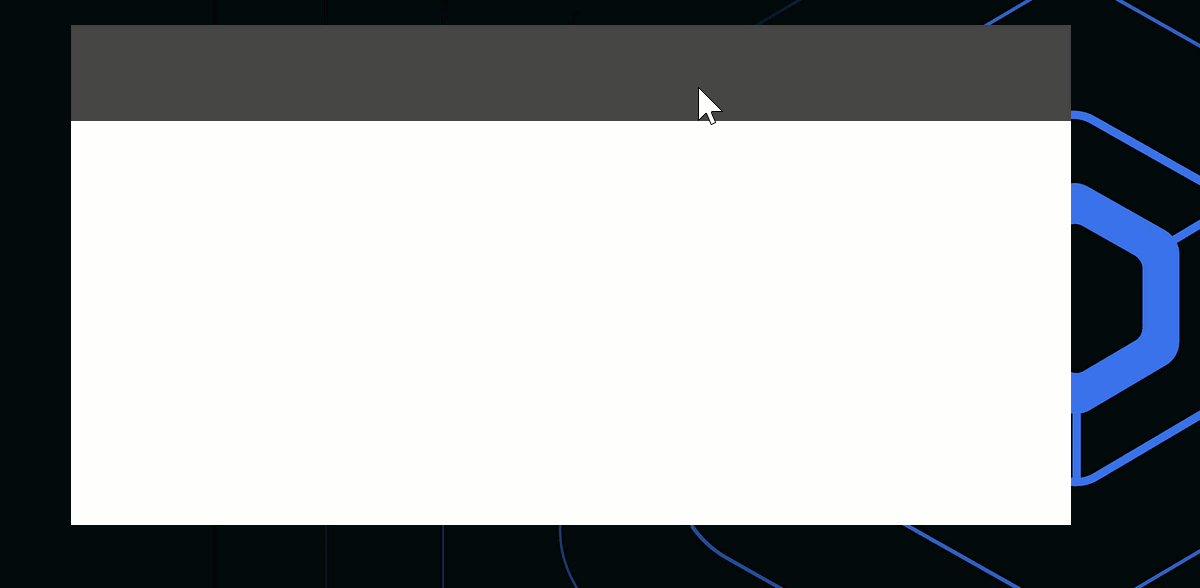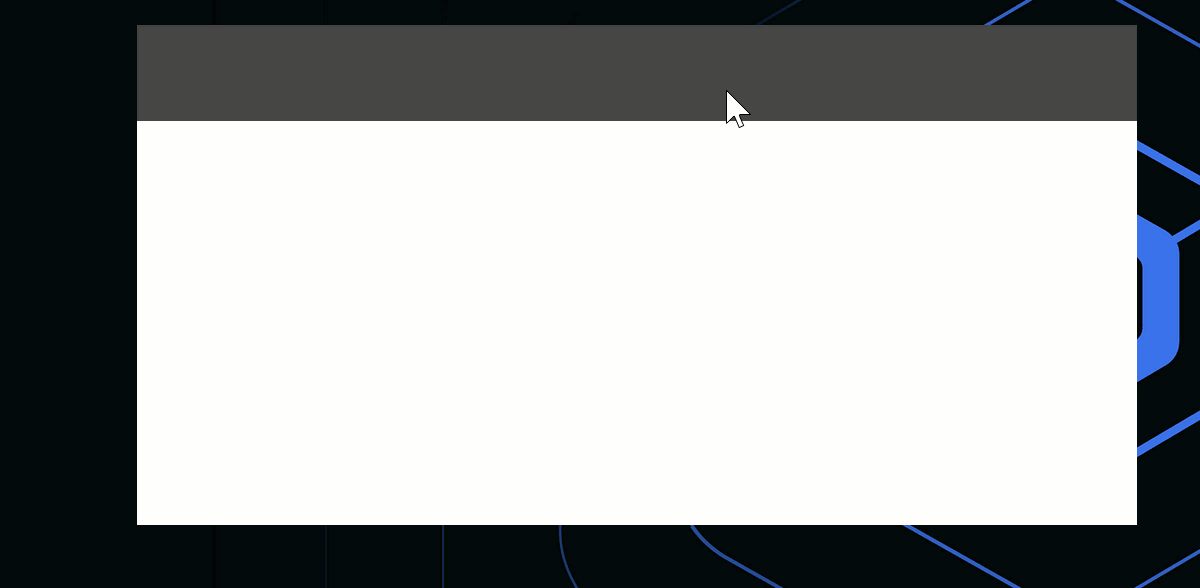
장식 없는 창에 사용자 지정 드래그 가능한 제목 표시줄을 추가하거나 전체 창을 드래그 가능하게 만들려면 WindowDraggableArea() 컴포저블을 사용할 수 있습니다.
import androidx.compose.foundation.background
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Box
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.fillMaxWidth
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.height
import androidx.compose.foundation.window.WindowDraggableArea
import androidx.compose.ui.Modifier
import androidx.compose.ui.graphics.Color
import androidx.compose.ui.unit.dp
import androidx.compose.ui.window.Window
import androidx.compose.ui.window.application
fun main() = application {
Window(onCloseRequest = ::exitApplication, undecorated = true) {
WindowDraggableArea {
Box(Modifier.fillMaxWidth().height(48.dp).background(Color.DarkGray))
}
}
}"}
WindowDraggableArea()는 singleWindowApplication(), Window(), DialogWindow() 컴포저블 내부에서만 사용될 수 있습니다. 다른 컴포저블 함수에서 호출하려면 WindowScope를 리시버 스코프로 사용합니다.
import androidx.compose.foundation.background
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Box
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.fillMaxWidth
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.height
import androidx.compose.foundation.window.WindowDraggableArea
import androidx.compose.runtime.Composable
import androidx.compose.ui.Modifier
import androidx.compose.ui.graphics.Color
import androidx.compose.ui.unit.dp
import androidx.compose.ui.window.Window
import androidx.compose.ui.window.WindowScope
import androidx.compose.ui.window.application
fun main() = application {
Window(onCloseRequest = ::exitApplication, undecorated = true) {
AppWindowTitleBar()
}
}
@Composable
private fun WindowScope.AppWindowTitleBar() = WindowDraggableArea {
Box(Modifier.fillMaxWidth().height(48.dp).background(Color.DarkGray))
}
투명 창 및 기타 사용자 지정
투명 창을 만들려면 Window() 함수에 transparent=true와 undecorated=true 두 매개변수를 전달합니다. 투명 창은 장식될 수 없기 때문에 장식 없어야 합니다.
다음 코드 예제는 컴포저블을 결합하여 둥근 모서리를 가진 투명 창을 만드는 방법을 보여줍니다.
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.fillMaxSize
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.padding
import androidx.compose.foundation.shape.RoundedCornerShape
import androidx.compose.material.Surface
import androidx.compose.runtime.mutableStateOf
import androidx.compose.runtime.remember
import androidx.compose.ui.Modifier
import androidx.compose.ui.draw.shadow
import androidx.compose.ui.graphics.Color
import androidx.compose.ui.unit.dp
import androidx.compose.ui.window.Window
import androidx.compose.ui.window.application
import androidx.compose.material.Text
import androidx.compose.runtime.*
fun main() = application {
var isOpen by remember { mutableStateOf(true) }
if (isOpen) {
Window(
onCloseRequest = { isOpen = false },
title = "Transparent Window Example",
transparent = true,
// Transparent window must be undecorated
undecorated = true,
) {
Surface(
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize().padding(5.dp).shadow(3.dp, RoundedCornerShape(20.dp)),
color = Color.Transparent,
// Window with rounded corners
shape = RoundedCornerShape(20.dp)
) {
Text("Hello World!", color = Color.White)
}
}
}
}Swing 상호 운용성
데스크톱용 Compose Multiplatform은 내부적으로 Swing을 사용하므로 Swing을 직접 사용하여 창을 만들 수 있습니다.
import androidx.compose.ui.awt.ComposeWindow
import java.awt.Dimension
import javax.swing.JFrame
import javax.swing.SwingUtilities
fun main() = SwingUtilities.invokeLater {
ComposeWindow().apply {
size = Dimension(300, 300)
defaultCloseOperation = JFrame.DISPOSE_ON_CLOSE
setContent {
// Content of the window
}
isVisible = true
}
}Window() 컴포저블의 스코프를 사용할 수도 있습니다. 다음 코드 예제에서 window는 Window() 내부에 생성된 ComposeWindow입니다.
import androidx.compose.runtime.LaunchedEffect
import androidx.compose.ui.window.singleWindowApplication
import java.awt.datatransfer.DataFlavor
import java.awt.dnd.DnDConstants
import java.awt.dnd.DropTarget
import java.awt.dnd.DropTargetAdapter
import java.awt.dnd.DropTargetDropEvent
fun main() = singleWindowApplication {
LaunchedEffect(Unit) {
window.dropTarget = DropTarget().apply {
addDropTargetListener(object : DropTargetAdapter() {
override fun drop(event: DropTargetDropEvent) {
event.acceptDrop(DnDConstants.ACTION_COPY)
val fileName = event.transferable.getTransferData(DataFlavor.javaFileListFlavor)
println(fileName)
}
})
}
}
}Swing으로 구현된 대화 상자를 사용해야 하는 경우, 이를 컴포저블 함수로 래핑할 수 있습니다.
import androidx.compose.runtime.Composable
import androidx.compose.runtime.getValue
import androidx.compose.runtime.mutableStateOf
import androidx.compose.runtime.remember
import androidx.compose.runtime.setValue
import androidx.compose.ui.window.AwtWindow
import androidx.compose.ui.window.application
import java.awt.FileDialog
import java.awt.Frame
fun main() = application {
var isOpen by remember { mutableStateOf(true) }
if (isOpen) {
FileDialog(
onCloseRequest = {
isOpen = false
println("Result $it")
}
)
}
}
@Composable
private fun FileDialog(
parent: Frame? = null,
onCloseRequest: (result: String?) -> Unit
) = AwtWindow(
create = {
object : FileDialog(parent, "Choose a file", LOAD) {
override fun setVisible(value: Boolean) {
super.setVisible(value)
if (value) {
onCloseRequest(file)
}
}
}
},
dispose = FileDialog::dispose
)다음 단계
다른 데스크톱 컴포넌트에 대한 튜토리얼을 살펴보세요.
