トップレベルウィンドウの管理
デスクトップ版Compose Multiplatformは、ウィンドウを管理するためのさまざまな機能を提供します。ウィンドウをシステムトレイに隠したり、ドラッグ可能にしたり、サイズを調整したり、位置を変更したりできます。
ウィンドウを開く・閉じる
Window()関数を使用して通常のウィンドウを作成できます。コンポーザブルスコープに配置するには、applicationエントリーポイントでWindow()を使用します。
import androidx.compose.ui.window.Window
import androidx.compose.ui.window.application
fun main() = application {
Window(onCloseRequest = ::exitApplication) {
// Content of the window
}
}コンポーザブル関数として、Window()を使用すると、そのプロパティを宣言的に変更できます。たとえば、1つのタイトルでウィンドウを開き、後でタイトルを変更できます。
import androidx.compose.material.Button
import androidx.compose.material.Text
import androidx.compose.runtime.getValue
import androidx.compose.runtime.mutableStateOf
import androidx.compose.runtime.remember
import androidx.compose.runtime.setValue
import androidx.compose.ui.window.Window
import androidx.compose.ui.window.application
fun main() = application {
var fileName by remember { mutableStateOf("Untitled") }
Window(onCloseRequest = ::exitApplication, title = "$fileName - Editor") {
Button(onClick = { fileName = "note.txt" }) {
Text("Save")
}
}
}
条件を追加する
単純なif条件を使用してウィンドウを開閉することもできます。以下のコードサンプルでは、タスクの完了後にアプリケーションウィンドウが自動的に閉じられます。
import androidx.compose.material.Text
import androidx.compose.runtime.LaunchedEffect
import androidx.compose.runtime.getValue
import androidx.compose.runtime.mutableStateOf
import androidx.compose.runtime.remember
import androidx.compose.runtime.setValue
import androidx.compose.ui.window.Window
import androidx.compose.ui.window.application
import kotlinx.coroutines.delay
fun main() = application {
var isPerformingTask by remember { mutableStateOf(true) }
LaunchedEffect(Unit) {
// Do some heavy lifting
delay(2000)
isPerformingTask = false
}
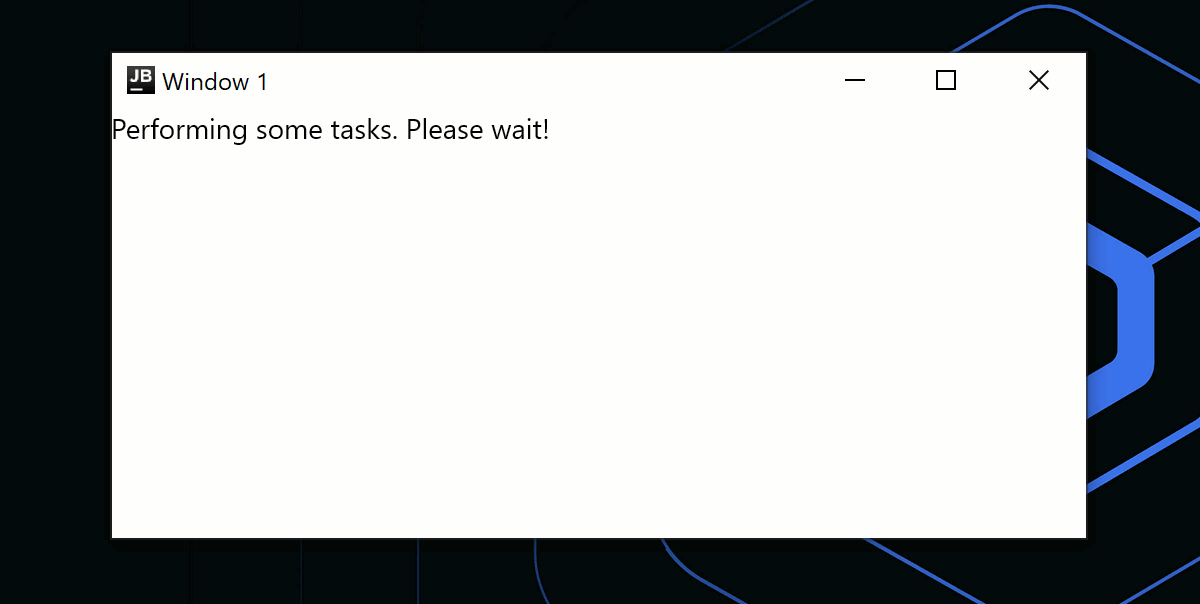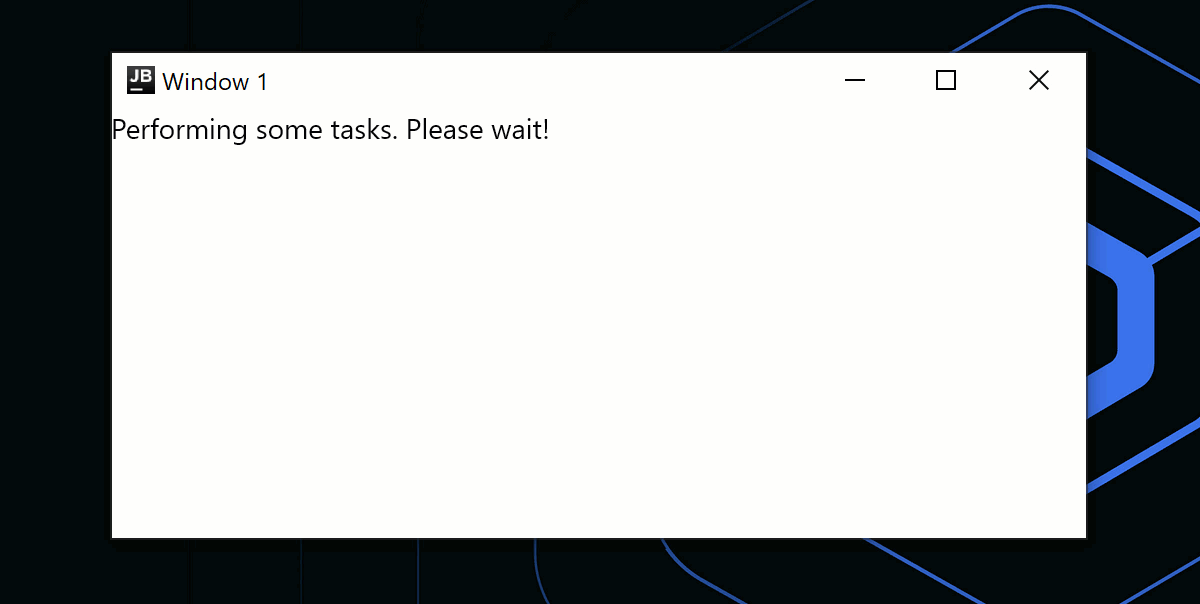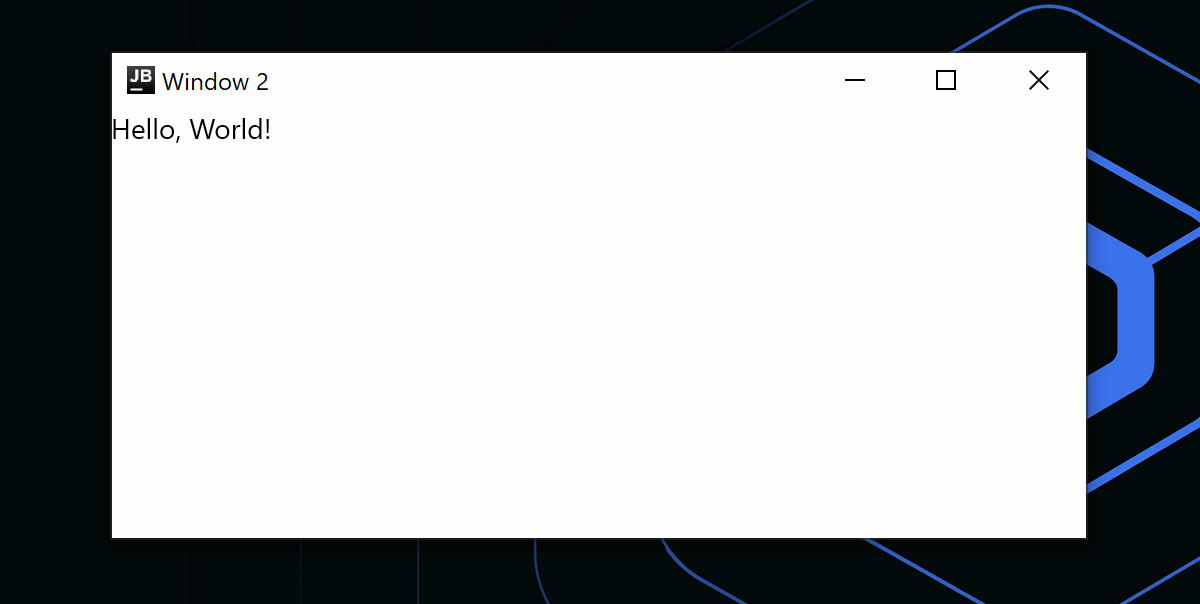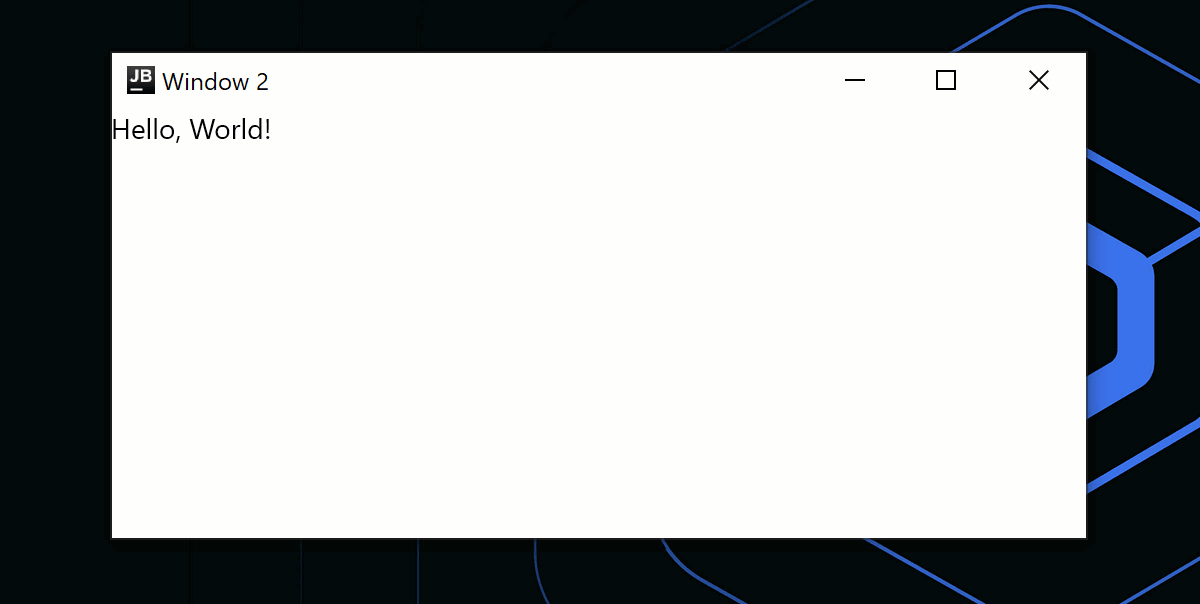
if (isPerformingTask) {
Window(
onCloseRequest = ::exitApplication,
title = "Window 1"
)
{
Text("Performing some tasks. Please wait!")
}
} else {
Window(
onCloseRequest = ::exitApplication,
title = "Window 2"
) {
Text("Hello, World!")
}
}
}
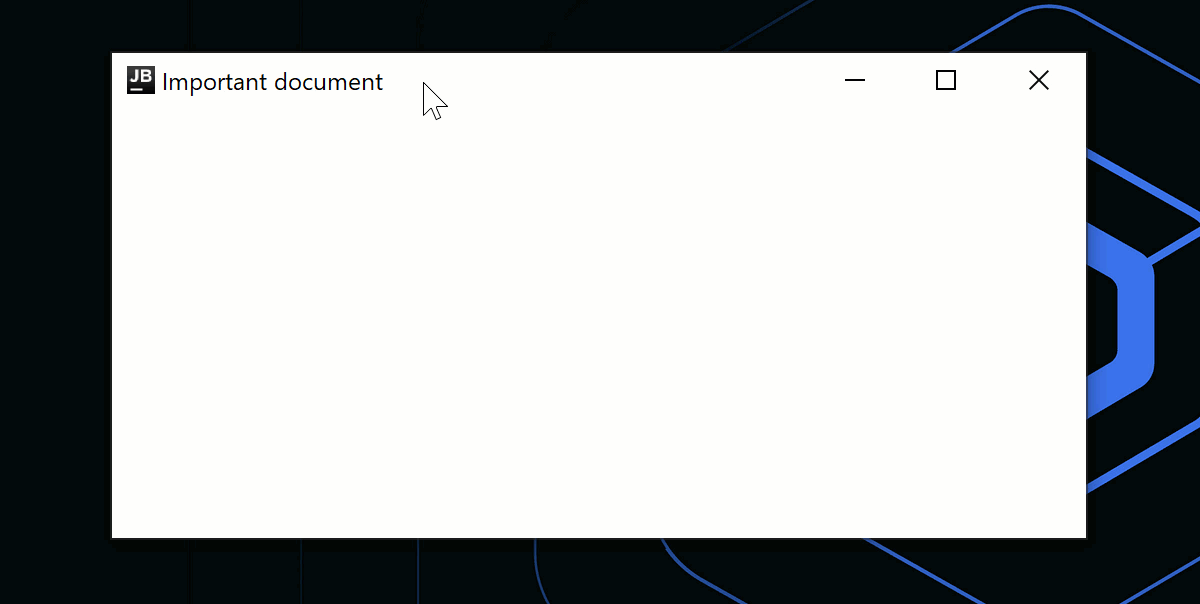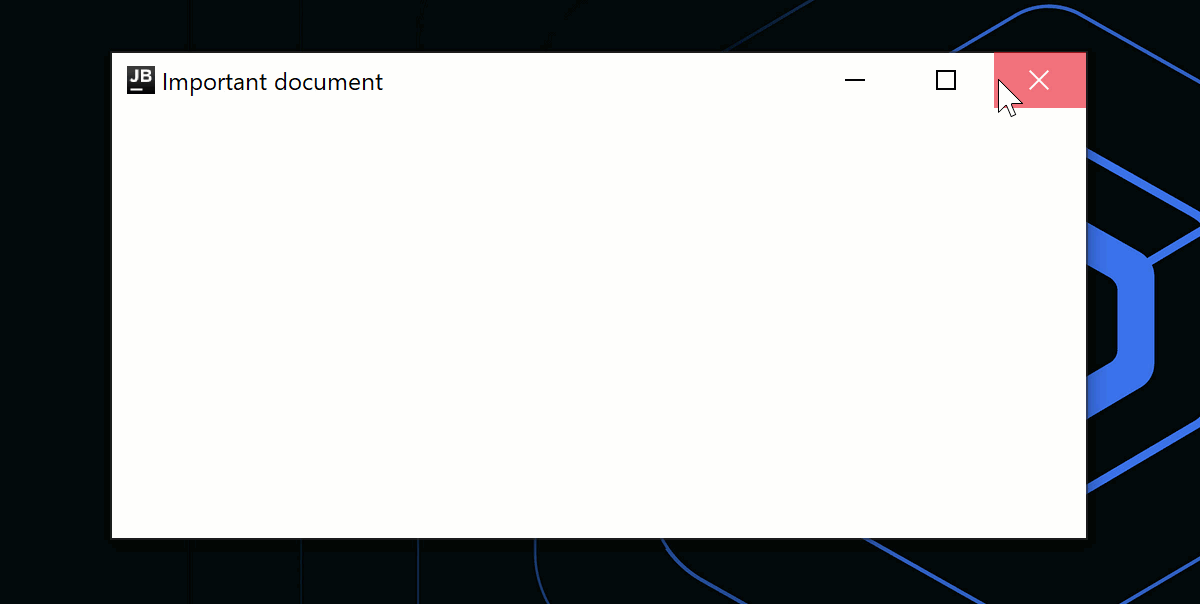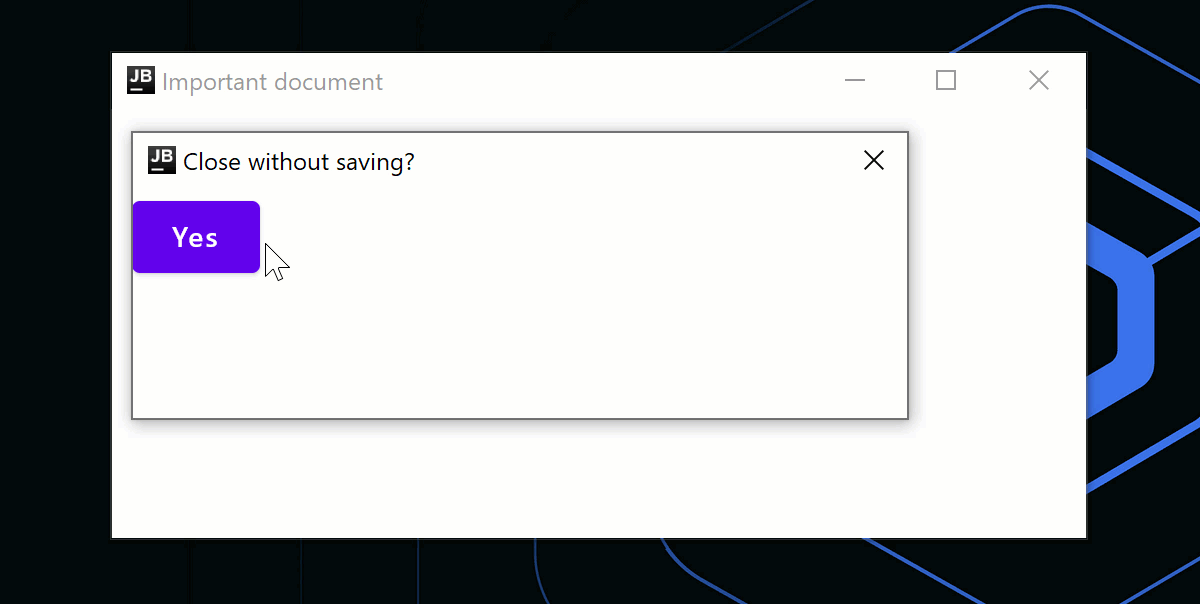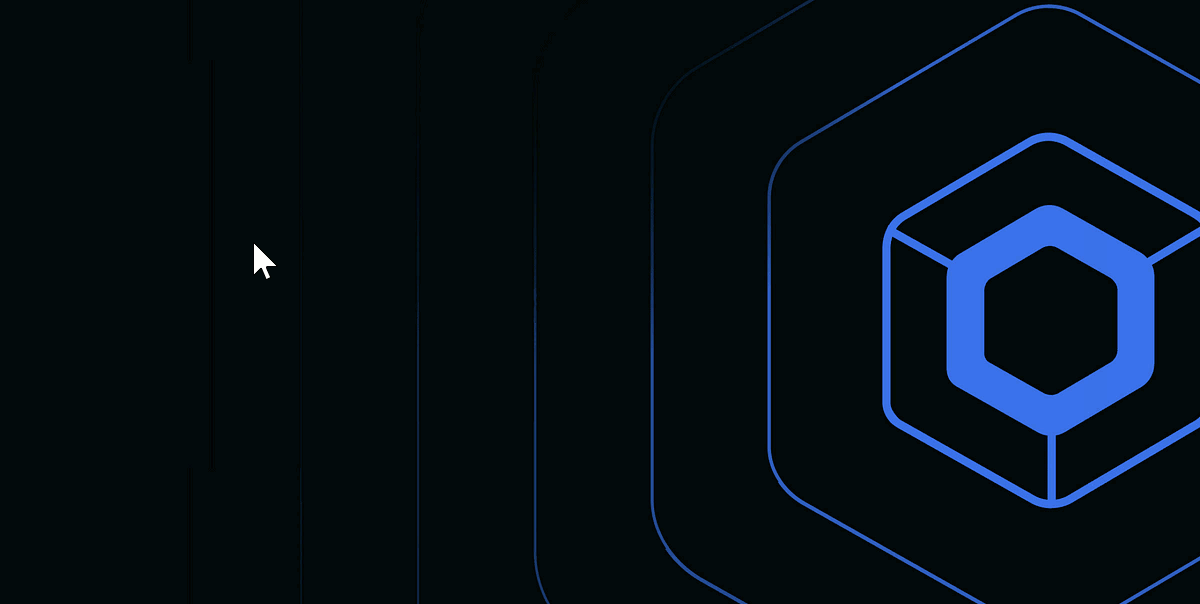
アプリケーション終了時に、ダイアログ表示などのカスタムロジックを使用したい場合は、onCloseRequestコールバックを使用してクローズアクションをオーバーライドできます。 以下のコードサンプルでは、命令型のアプローチ (window.close()) の代わりに、宣言型のアプローチを使用し、状態変更 (isOpen = false) に応答してウィンドウを閉じます。
import androidx.compose.material.Button
import androidx.compose.material.Text
import androidx.compose.runtime.getValue
import androidx.compose.runtime.mutableStateOf
import androidx.compose.runtime.remember
import androidx.compose.runtime.setValue
import androidx.compose.ui.window.DialogWindow
import androidx.compose.ui.window.Window
import androidx.compose.ui.window.application
fun main() = application {
var isOpen by remember { mutableStateOf(true) }
var isAskingToClose by remember { mutableStateOf(false) }
if (isOpen) {
Window(
onCloseRequest = { isAskingToClose = true },
title = "Important document"
) {
if (isAskingToClose) {
DialogWindow(
onCloseRequest = { isAskingToClose = false },
title = "Close without saving?"
) {
Button(
onClick = { isOpen = false }
) {
Text("Yes")
}
}
}
}
}
}"}
複数ウィンドウの操作
アプリケーションに複数のウィンドウがある場合、アプリケーションの状態のために個別のクラスを作成し、mutableStateListOfの変更に応答してウィンドウを開閉できます。
import androidx.compose.runtime.Composable
import androidx.compose.runtime.key
import androidx.compose.runtime.mutableStateListOf
import androidx.compose.runtime.remember
import androidx.compose.ui.window.MenuBar
import androidx.compose.ui.window.Window
import androidx.compose.ui.window.application
fun main() = application {
val applicationState = remember { MyApplicationState() }
for (window in applicationState.windows) {
key(window) {
MyWindow(window)
}
}
}
@Composable
private fun MyWindow(
state: MyWindowState
) = Window(onCloseRequest = state::close, title = state.title) {
MenuBar {
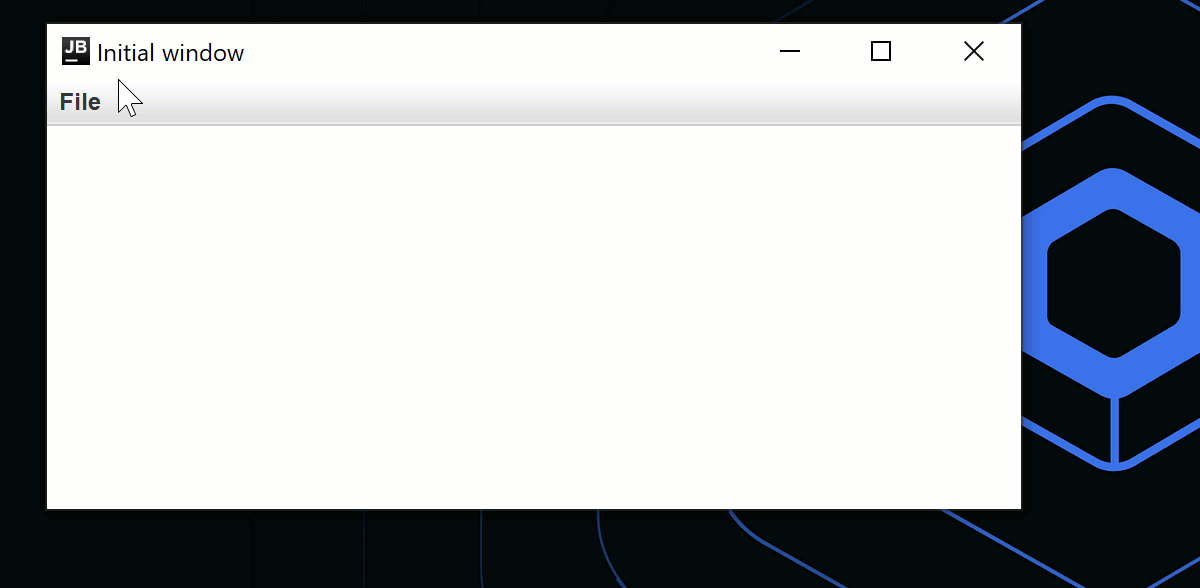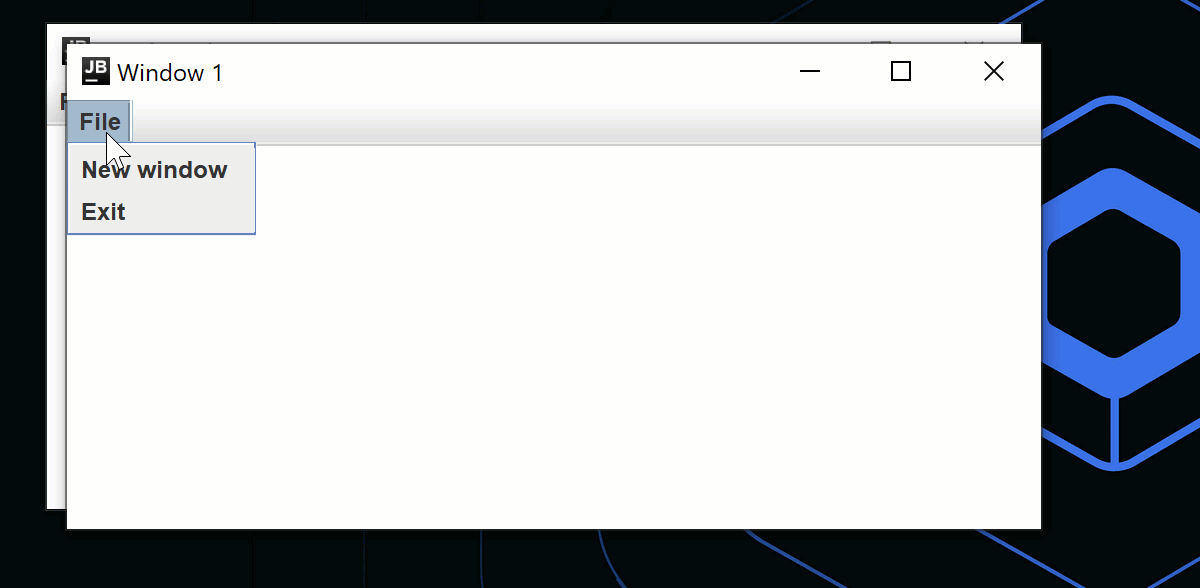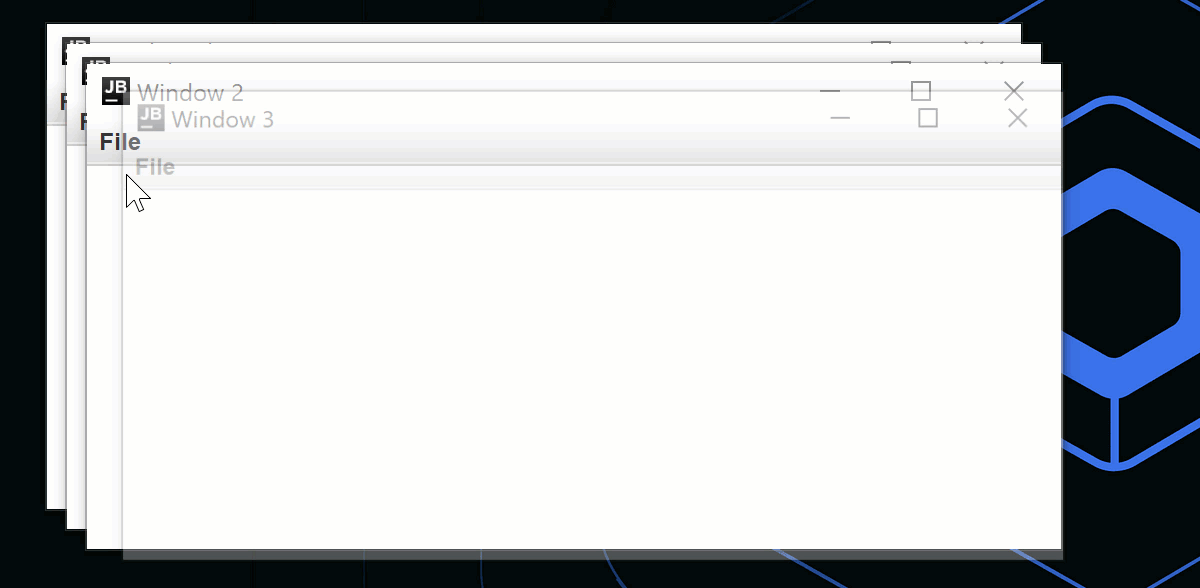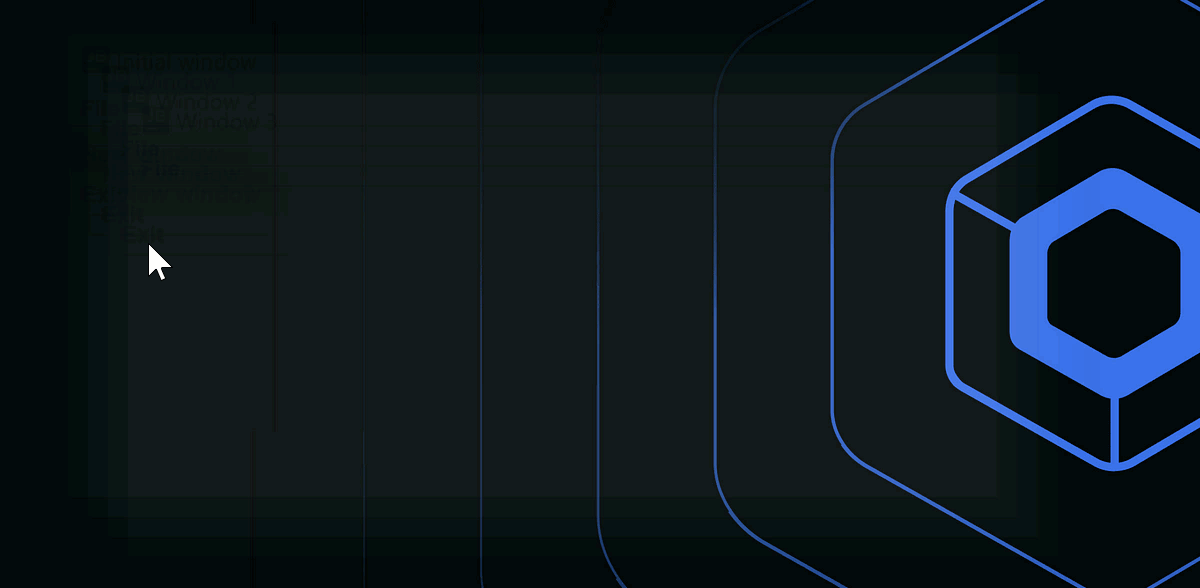
Menu("File") {
Item("New window", onClick = state.openNewWindow)
Item("Exit", onClick = state.exit)
}
}
}
private class MyApplicationState {
val windows = mutableStateListOf<MyWindowState>()
init {
windows += MyWindowState("Initial window")
}
fun openNewWindow() {
windows += MyWindowState("Window ${windows.size}")
}
fun exit() {
windows.clear()
}
private fun MyWindowState(
title: String
) = MyWindowState(
title,
openNewWindow = ::openNewWindow,
exit = ::exit,
windows::remove
)
}
private class MyWindowState(
val title: String,
val openNewWindow: () -> Unit,
val exit: () -> Unit,
private val close: (MyWindowState) -> Unit
) {
fun close() = close(this)
}
より複雑な例については、Code Viewerサンプルを参照してください。
ウィンドウをシステムトレイに最小化する
ウィンドウを閉じる代わりに非表示にするには、windowState.isVisibleの状態を変更します。
import androidx.compose.material.Text
import androidx.compose.runtime.LaunchedEffect
import androidx.compose.runtime.getValue
import androidx.compose.runtime.mutableStateOf
import androidx.compose.runtime.remember
import androidx.compose.runtime.setValue
import androidx.compose.ui.geometry.Size
import androidx.compose.ui.graphics.Color
import androidx.compose.ui.graphics.drawscope.DrawScope
import androidx.compose.ui.graphics.painter.Painter
import androidx.compose.ui.window.Tray
import androidx.compose.ui.window.Window
import androidx.compose.ui.window.application
import kotlinx.coroutines.delay
fun main() = application {
var isVisible by remember { mutableStateOf(true) }
Window(
onCloseRequest = { isVisible = false },
visible = isVisible,
title = "Counter",
) {
var counter by remember { mutableStateOf(0) }
LaunchedEffect(Unit) {
while (true) {
counter++
delay(1000)
}
}
Text(counter.toString())
}
if (!isVisible) {
Tray(
TrayIcon,
tooltip = "Counter",
onAction = { isVisible = true },
menu = {
Item("Exit", onClick = ::exitApplication)
},
)
}
}
object TrayIcon : Painter() {
override val intrinsicSize = Size(256f, 256f)
override fun DrawScope.onDraw() {
drawOval(Color(0xFFFFA500))
}
},"}

singleWindowApplication() 関数
singleWindowApplication()関数を呼び出すことで、シングルウィンドウアプリケーションを作成できます。
singleWindowApplication()関数は使いやすいですが、以下の制限があります。
- アプリケーションはウィンドウを1つしか持てません。
- カスタムのクローズロジックを追加できません。
- 実行時にウィンドウの属性を変更できません。
import androidx.compose.ui.window.singleWindowApplication
fun main() = singleWindowApplication {
// Content of the window
}代替案として、applicationエントリーポイントでWindow()コンポーザブルを使用できます。
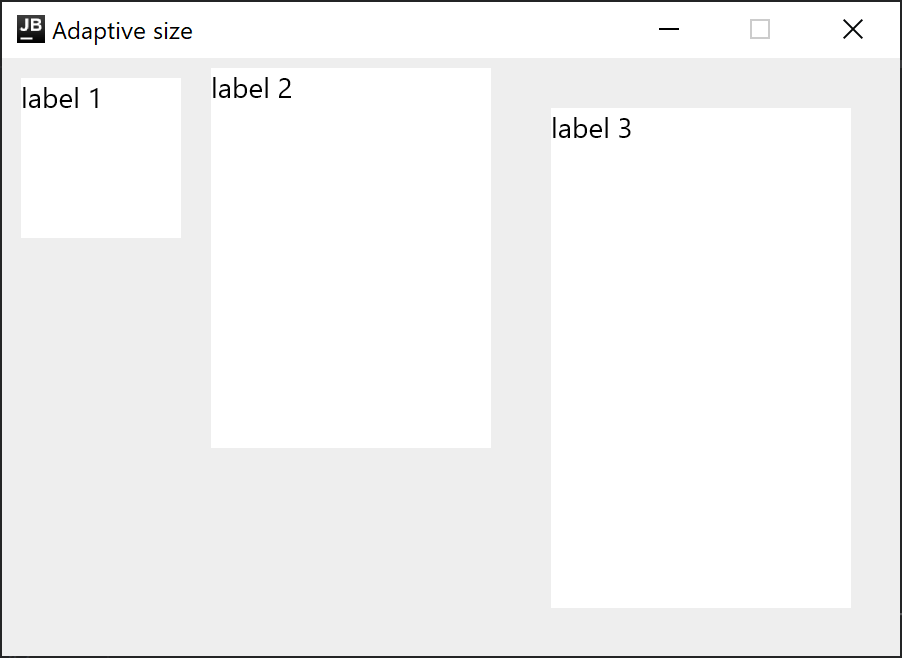
適応型ウィンドウサイズ
期待されるコンテンツのサイズが不明で、最適なウィンドウの寸法を事前に指定できない場合、WindowSizeの寸法を1つまたは両方Dp.Unspecifiedに設定できます。デスクトップ版Compose Multiplatformは、コンテンツに合わせてウィンドウの初期サイズを自動的に調整します。
import androidx.compose.foundation.background
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Column
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Row
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.padding
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.size
import androidx.compose.material.Text
import androidx.compose.ui.Modifier
import androidx.compose.ui.graphics.Color
import androidx.compose.ui.unit.Dp
import androidx.compose.ui.unit.dp
import androidx.compose.ui.window.Window
import androidx.compose.ui.window.application
import androidx.compose.ui.window.rememberWindowState
fun main() = application {
Window(
onCloseRequest = ::exitApplication,
state = rememberWindowState(width = Dp.Unspecified, height = Dp.Unspecified),
title = "Adaptive size",
resizable = false
) {
Column(Modifier.background(Color(0xFFEEEEEE))) {
Row {
Text("label 1", Modifier.size(100.dp, 100.dp).padding(10.dp).background(Color.White))
Text("label 2", Modifier.size(150.dp, 200.dp).padding(5.dp).background(Color.White))
Text("label 3", Modifier.size(200.dp, 300.dp).padding(25.dp).background(Color.White))
}
}
}
}
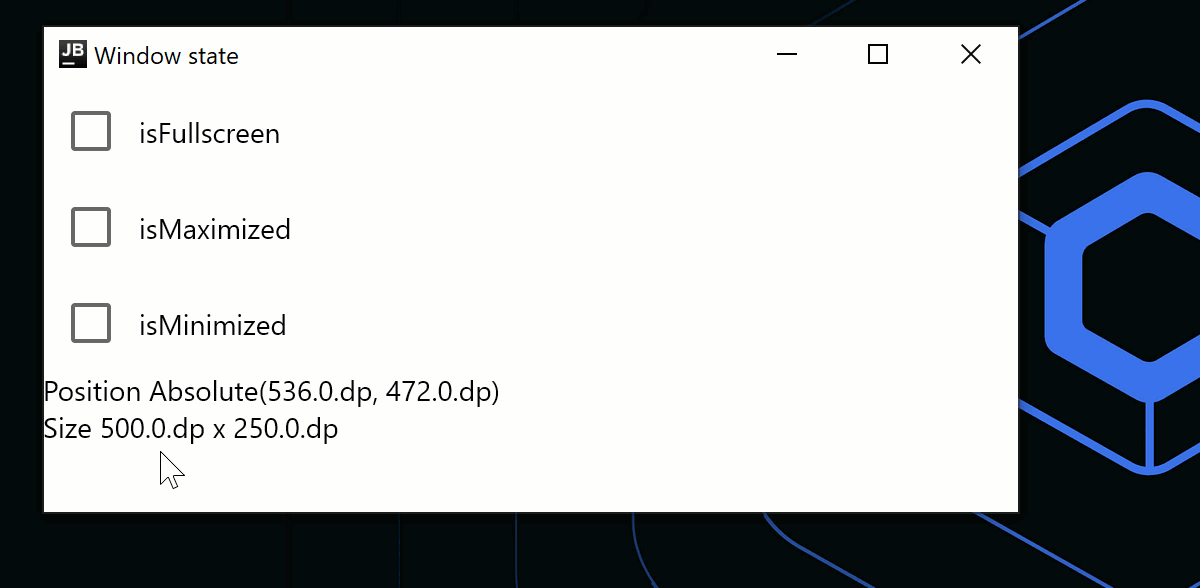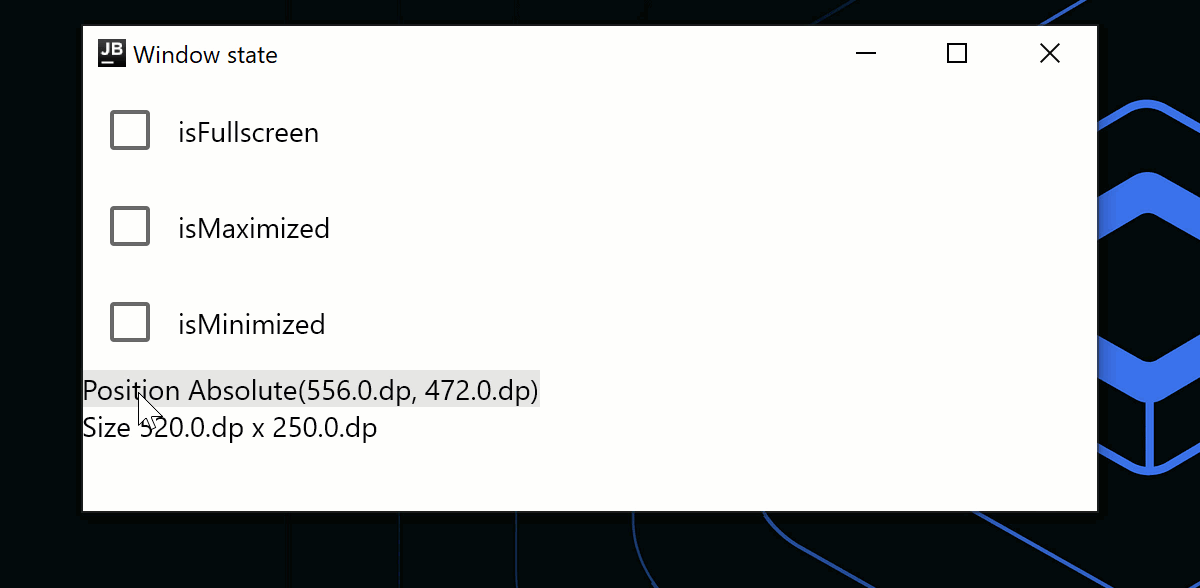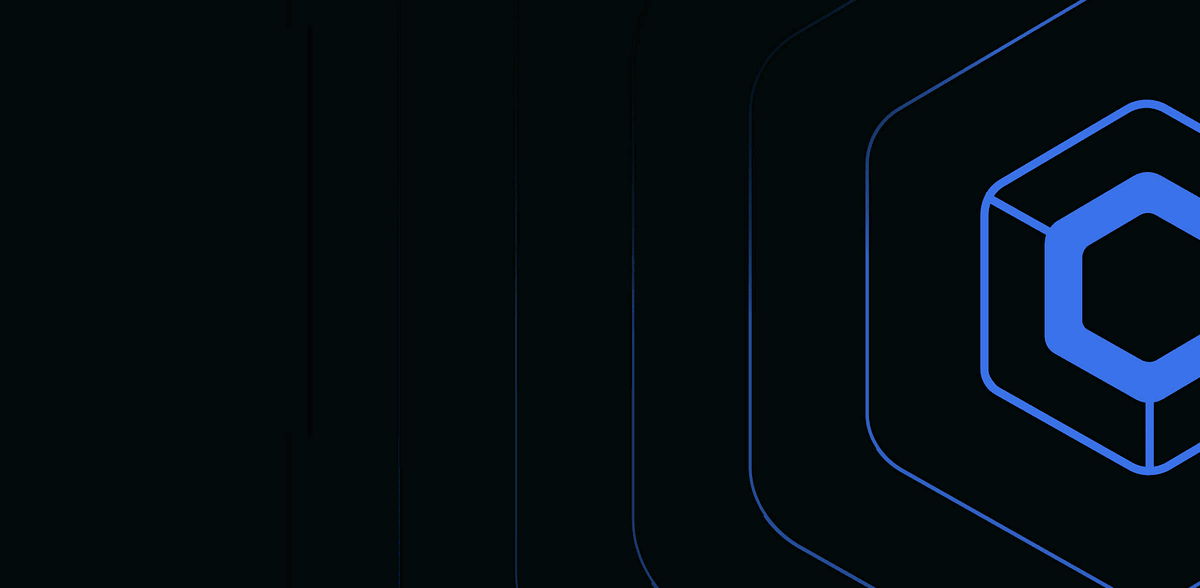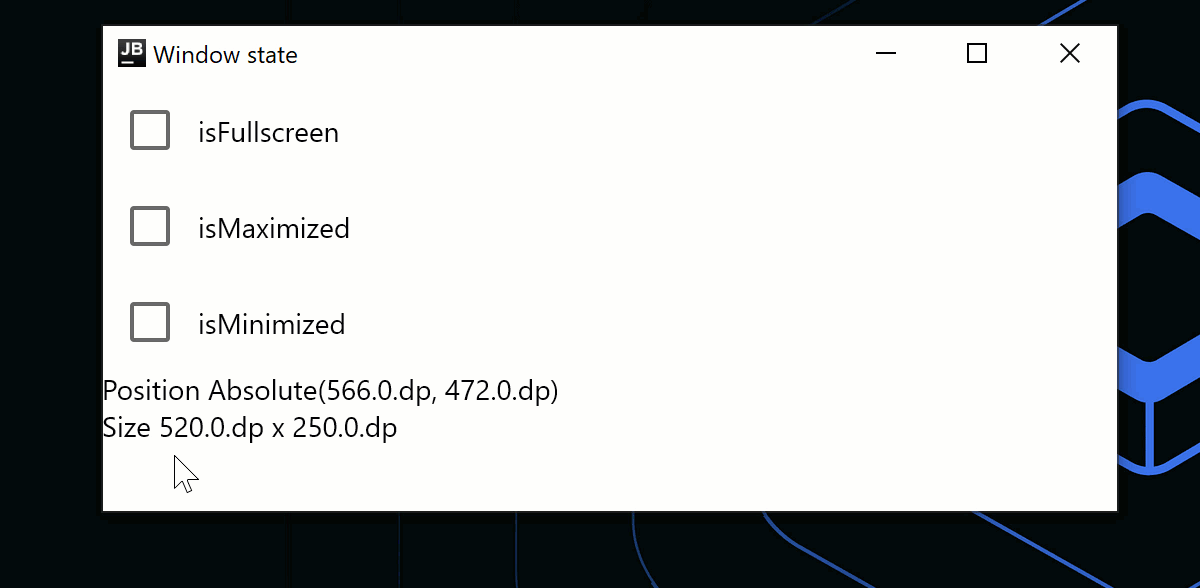
ウィンドウの状態を変更する
WindowStateは、ウィンドウの配置、現在の位置、およびサイズのための個別のAPIクラスです。placement属性を使用すると、ウィンドウが画面上にどのように配置されるか (フローティング、最大化/最小化、またはフルスクリーン) を指定できます。 状態の変更はすべて自動的な再コンポジションをトリガーします。ウィンドウの状態を変更するには、コールバックを使用するか、コンポーザブル内でオブザーブします。
import androidx.compose.foundation.clickable
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Column
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Row
import androidx.compose.material.Checkbox
import androidx.compose.material.Text
import androidx.compose.ui.Alignment
import androidx.compose.ui.Modifier
import androidx.compose.ui.unit.dp
import androidx.compose.ui.window.Window
import androidx.compose.ui.window.WindowPlacement
import androidx.compose.ui.window.WindowPosition
import androidx.compose.ui.window.application
import androidx.compose.ui.window.rememberWindowState
fun main() = application {
val state = rememberWindowState(placement = WindowPlacement.Maximized)
Window(onCloseRequest = ::exitApplication, state, title = "Window state") {
Column {
Row(verticalAlignment = Alignment.CenterVertically) {
Checkbox(
state.placement == WindowPlacement.Fullscreen,
{
state.placement = if (it) {
WindowPlacement.Fullscreen
} else {
WindowPlacement.Floating
}
}
)
Text("isFullscreen")
}
Row(verticalAlignment = Alignment.CenterVertically) {
Checkbox(
state.placement == WindowPlacement.Maximized,
{
state.placement = if (it) {
WindowPlacement.Maximized
} else {
WindowPlacement.Floating
}
}
)
Text("isMaximized")
}
Row(verticalAlignment = Alignment.CenterVertically) {
Checkbox(state.isMinimized, { state.isMinimized = !state.isMinimized })
Text("isMinimized")
}
Text(
"Position ${state.position}",
Modifier.clickable {
val position = state.position
if (position is WindowPosition.Absolute) {
state.position = position.copy(x = state.position.x + 10.dp)
}
}
)
Text(
"Size ${state.size}",
Modifier.clickable {
state.size = state.size.copy(width = state.size.width + 10.dp)
}
)
}
}
}
ウィンドウの状態をリッスンする
状態の変更に反応し、値を別の非コンポーザブルなアプリケーションレベル(たとえば、データベースに書き込むなど)に送信する必要がある場合は、snapshotFlow()関数を使用できます。この関数は、コンポーザブルの状態の現在の値をキャプチャします。
import androidx.compose.runtime.LaunchedEffect
import androidx.compose.runtime.snapshotFlow
import androidx.compose.ui.unit.DpSize
import androidx.compose.ui.window.Window
import androidx.compose.ui.window.WindowPosition
import androidx.compose.ui.window.application
import androidx.compose.ui.window.rememberWindowState
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.filter
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.launchIn
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.onEach
fun main() = application {
val state = rememberWindowState()
Window(onCloseRequest = ::exitApplication, state) {
LaunchedEffect(state) {
snapshotFlow { state.size }
.onEach(::onWindowResize)
.launchIn(this)
snapshotFlow { state.position }
.filter { it.isSpecified }
.onEach(::onWindowRelocate)
.launchIn(this)
}
}
}
private fun onWindowResize(size: DpSize) {
println("onWindowResize $size")
}
private fun onWindowRelocate(position: WindowPosition) {
println("onWindowRelocate $position")
}.onEach(::onWindowResize)"}
ダイアログ
Window()コンポーザブルを使用して通常のウィンドウを作成し、DialogWindow()コンポーザブルを使用して、ユーザーがモーダルウィンドウを閉じるまで親をロックするモーダルウィンドウを作成できます。
以下のコードサンプルは、これらのコンポーザブルを組み合わせて通常のウィンドウとモーダルウィンドウを作成する方法を示しています。
import androidx.compose.material.Button
import androidx.compose.material.Text
import androidx.compose.runtime.getValue
import androidx.compose.runtime.mutableStateOf
import androidx.compose.runtime.remember
import androidx.compose.runtime.setValue
import androidx.compose.ui.Alignment
import androidx.compose.ui.window.DialogWindow
import androidx.compose.ui.window.Window
import androidx.compose.ui.window.WindowPosition
import androidx.compose.ui.window.application
import androidx.compose.ui.window.rememberDialogState
fun main() = application {
Window(
onCloseRequest = ::exitApplication,
) {
var isDialogOpen by remember { mutableStateOf(false) }
Button(onClick = { isDialogOpen = true }) {
Text(text = "Open dialog")
}
if (isDialogOpen) {
DialogWindow(
onCloseRequest = { isDialogOpen = false },
state = rememberDialogState(position = WindowPosition(Alignment.Center))
) {
// Content of the window
}
}
}
},"}
ドラッグ可能なウィンドウ領域
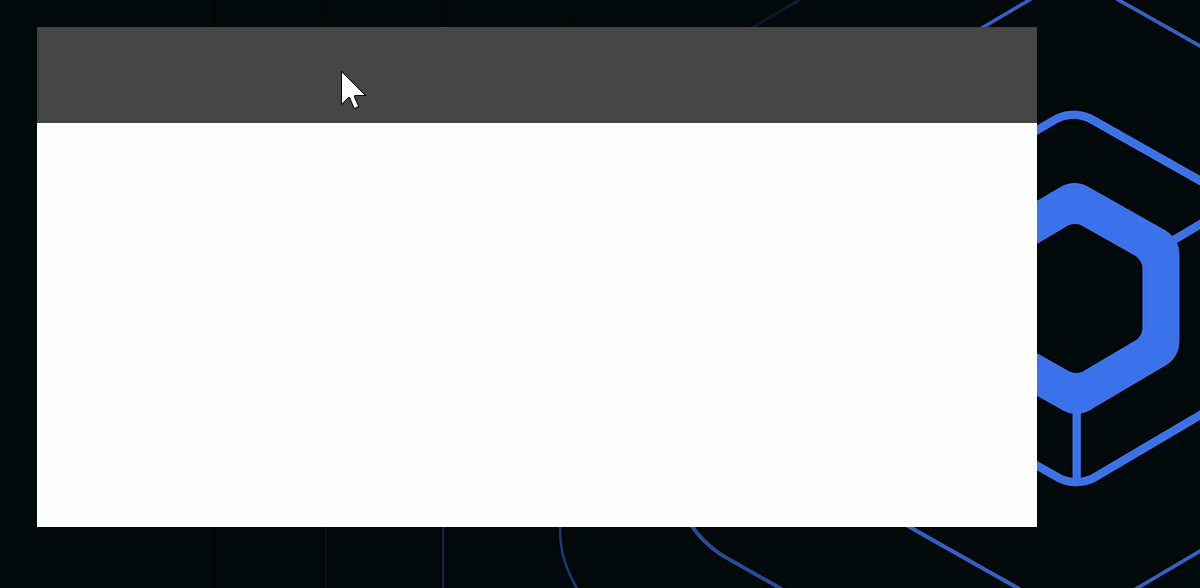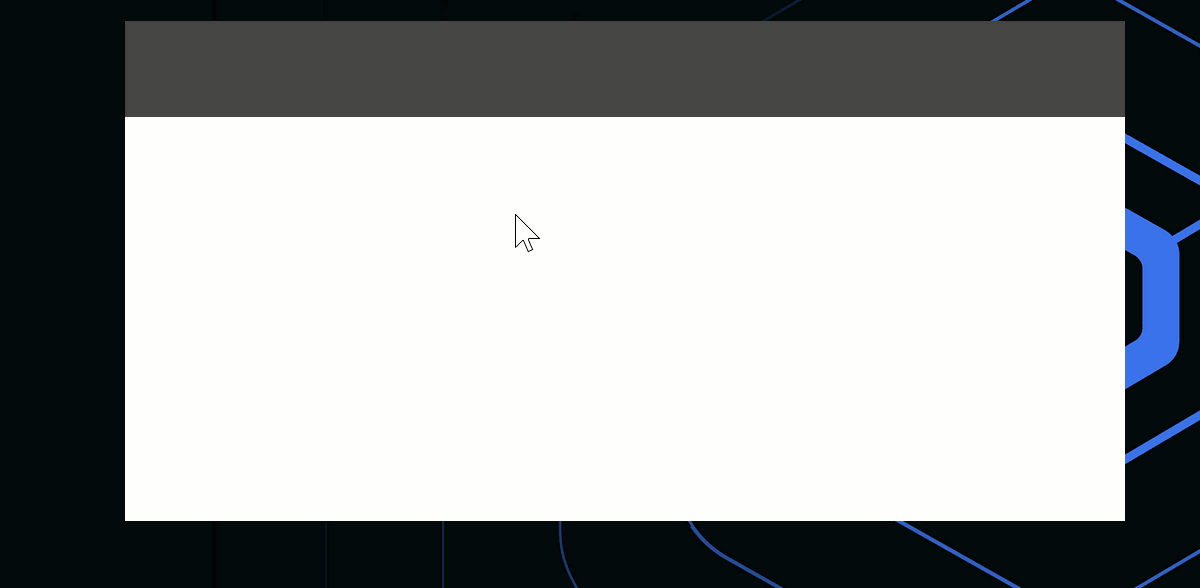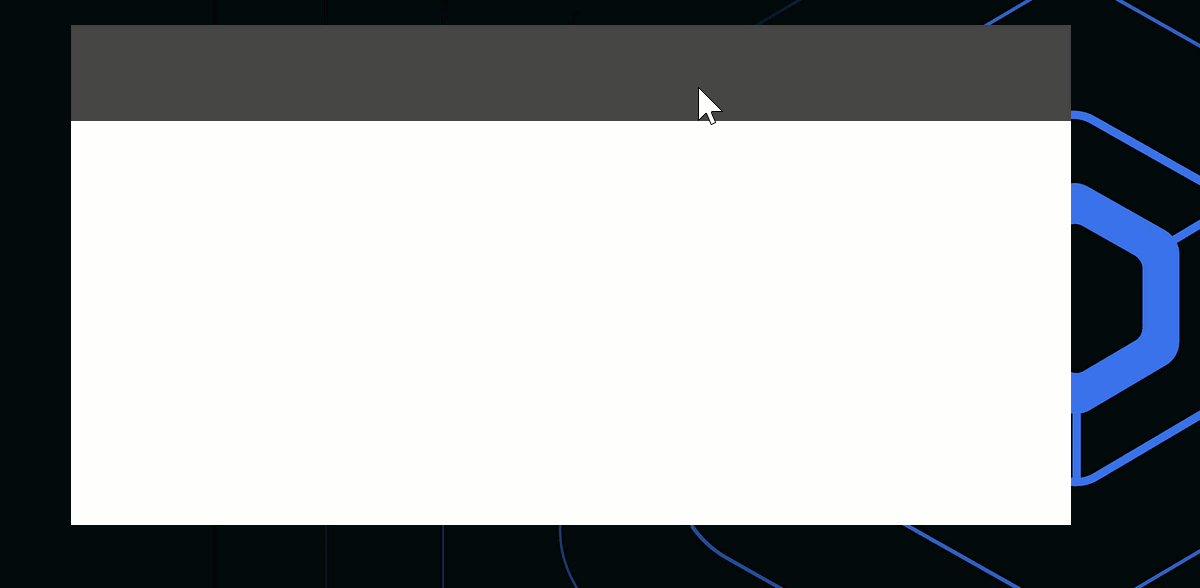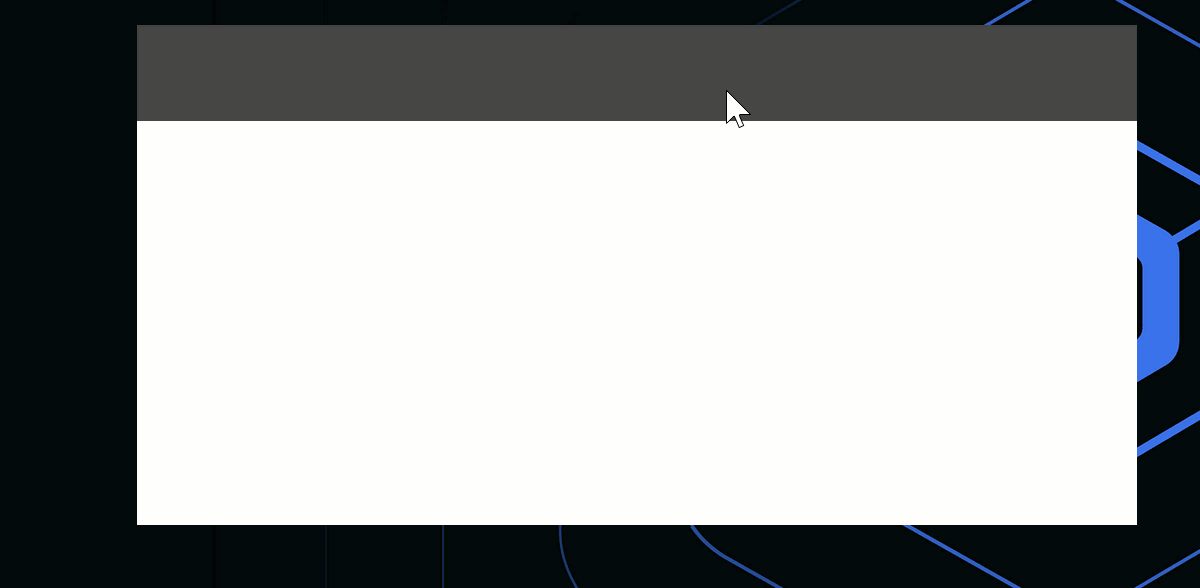
装飾なしのウィンドウにカスタムのドラッグ可能なタイトルバーを追加したり、ウィンドウ全体をドラッグ可能にしたりするには、WindowDraggableArea()コンポーザブルを使用できます。
import androidx.compose.foundation.background
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Box
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.fillMaxWidth
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.height
import androidx.compose.foundation.window.WindowDraggableArea
import androidx.compose.ui.Modifier
import androidx.compose.ui.graphics.Color
import androidx.compose.ui.unit.dp
import androidx.compose.ui.window.Window
import androidx.compose.ui.window.application
fun main() = application {
Window(onCloseRequest = ::exitApplication, undecorated = true) {
WindowDraggableArea {
Box(Modifier.fillMaxWidth().height(48.dp).background(Color.DarkGray))
}
}
}"}
WindowDraggableArea()は、singleWindowApplication()、Window()、およびDialogWindow()コンポーザブル内でのみ使用できます。他のコンポーザブル関数で呼び出すには、WindowScopeを受信側スコープとして使用します。
import androidx.compose.foundation.background
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Box
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.fillMaxWidth
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.height
import androidx.compose.foundation.window.WindowDraggableArea
import androidx.compose.runtime.Composable
import androidx.compose.ui.Modifier
import androidx.compose.ui.graphics.Color
import androidx.compose.ui.unit.dp
import androidx.compose.ui.window.Window
import androidx.compose.ui.window.WindowScope
import androidx.compose.ui.window.application
fun main() = application {
Window(onCloseRequest = ::exitApplication, undecorated = true) {
AppWindowTitleBar()
}
}
@Composable
private fun WindowScope.AppWindowTitleBar() = WindowDraggableArea {
Box(Modifier.fillMaxWidth().height(48.dp).background(Color.DarkGray))
}
透過ウィンドウとその他のカスタマイズ
透過ウィンドウを作成するには、Window()関数にtransparent=trueとundecorated=trueの2つのパラメータを渡します。透過ウィンドウは装飾できないため、装飾なしである必要があります。
以下のコードサンプルは、コンポーザブルを組み合わせて角の丸い透過ウィンドウを作成する方法を示しています。
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.fillMaxSize
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.padding
import androidx.compose.foundation.shape.RoundedCornerShape
import androidx.compose.material.Surface
import androidx.compose.runtime.mutableStateOf
import androidx.compose.runtime.remember
import androidx.compose.ui.Modifier
import androidx.compose.ui.draw.shadow
import androidx.compose.ui.graphics.Color
import androidx.compose.ui.unit.dp
import androidx.compose.ui.window.Window
import androidx.compose.ui.window.application
import androidx.compose.material.Text
import androidx.compose.runtime.*
fun main() = application {
var isOpen by remember { mutableStateOf(true) }
if (isOpen) {
Window(
onCloseRequest = { isOpen = false },
title = "Transparent Window Example",
transparent = true,
// Transparent window must be undecorated
undecorated = true,
) {
Surface(
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize().padding(5.dp).shadow(3.dp, RoundedCornerShape(20.dp)),
color = Color.Transparent,
// Window with rounded corners
shape = RoundedCornerShape(20.dp)
) {
Text("Hello World!", color = Color.White)
}
}
}
}Swingの相互運用性
デスクトップ版Compose Multiplatformは内部でSwingを使用しているため、Swingを直接使用してウィンドウを作成できます。
import androidx.compose.ui.awt.ComposeWindow
import java.awt.Dimension
import javax.swing.JFrame
import javax.swing.SwingUtilities
fun main() = SwingUtilities.invokeLater {
ComposeWindow().apply {
size = Dimension(300, 300)
defaultCloseOperation = JFrame.DISPOSE_ON_CLOSE
setContent {
// Content of the window
}
isVisible = true
}
}Window()コンポーザブルのスコープも使用できます。以下のコードサンプルでは、windowはWindow()内で作成されたComposeWindowです。
import androidx.compose.runtime.LaunchedEffect
import androidx.compose.ui.window.singleWindowApplication
import java.awt.datatransfer.DataFlavor
import java.awt.dnd.DnDConstants
import java.awt.dnd.DropTarget
import java.awt.dnd.DropTargetAdapter
import java.awt.dnd.DropTargetDropEvent
fun main() = singleWindowApplication {
LaunchedEffect(Unit) {
window.dropTarget = DropTarget().apply {
addDropTargetListener(object : DropTargetAdapter() {
override fun drop(event: DropTargetDropEvent) {
event.acceptDrop(DnDConstants.ACTION_COPY)
val fileName = event.transferable.getTransferData(DataFlavor.javaFileListFlavor)
println(fileName)
}
})
}
}
}Swingで実装されたダイアログを使用する必要がある場合は、それをコンポーザブル関数でラップできます。
import androidx.compose.runtime.Composable
import androidx.compose.runtime.getValue
import androidx.compose.runtime.mutableStateOf
import androidx.compose.runtime.remember
import androidx.compose.runtime.setValue
import androidx.compose.ui.window.AwtWindow
import androidx.compose.ui.window.application
import java.awt.FileDialog
import java.awt.Frame
fun main() = application {
var isOpen by remember { mutableStateOf(true) }
if (isOpen) {
FileDialog(
onCloseRequest = {
isOpen = false
println("Result $it")
}
)
}
}
@Composable
private fun FileDialog(
parent: Frame? = null,
onCloseRequest: (result: String?) -> Unit
) = AwtWindow(
create = {
object : FileDialog(parent, "Choose a file", LOAD) {
override fun setVisible(value: Boolean) {
super.setVisible(value)
if (value) {
onCloseRequest(file)
}
}
}
},
dispose = FileDialog::dispose
)次に行うこと
その他のデスクトップコンポーネントに関するチュートリアルを探索してください。
