UIKitフレームワークとの統合
Compose Multiplatformは、UIKitフレームワークと相互運用可能です。 Compose MultiplatformをUIKitアプリケーション内に組み込むことも、ネイティブのUIKitコンポーネントをCompose Multiplatform内に組み込むこともできます。 このページでは、Compose MultiplatformをUIKitアプリケーション内で使用する例と、UIKitコンポーネントをCompose Multiplatform UI内に組み込む例の両方を提供します。
SwiftUIとの相互運用性については、SwiftUIフレームワークとの統合の記事を参照してください。
UIKitアプリケーション内でCompose Multiplatformを使用する
Compose MultiplatformをUIKitアプリケーション内で使用するには、Compose Multiplatformのコードを任意のコンテナビューコントローラーに追加します。 この例では、UITabBarControllerクラス内でCompose Multiplatformを使用しています。
let composeViewController = Main_iosKt.ComposeOnly()
composeViewController.title = "Compose Multiplatform inside UIKit"
let anotherViewController = UIKitViewController()
anotherViewController.title = "UIKit"
// Set up the UITabBarController
let tabBarController = UITabBarController()
tabBarController.viewControllers = [
// Wrap the created ViewControllers in a UINavigationController to set titles
UINavigationController(rootViewController: composeViewController),
UINavigationController(rootViewController: anotherViewController)
]
tabBarController.tabBar.items?[0].title = "Compose"
tabBarController.tabBar.items?[1].title = "UIKit"このコードを使用すると、アプリケーションは次のようになります。
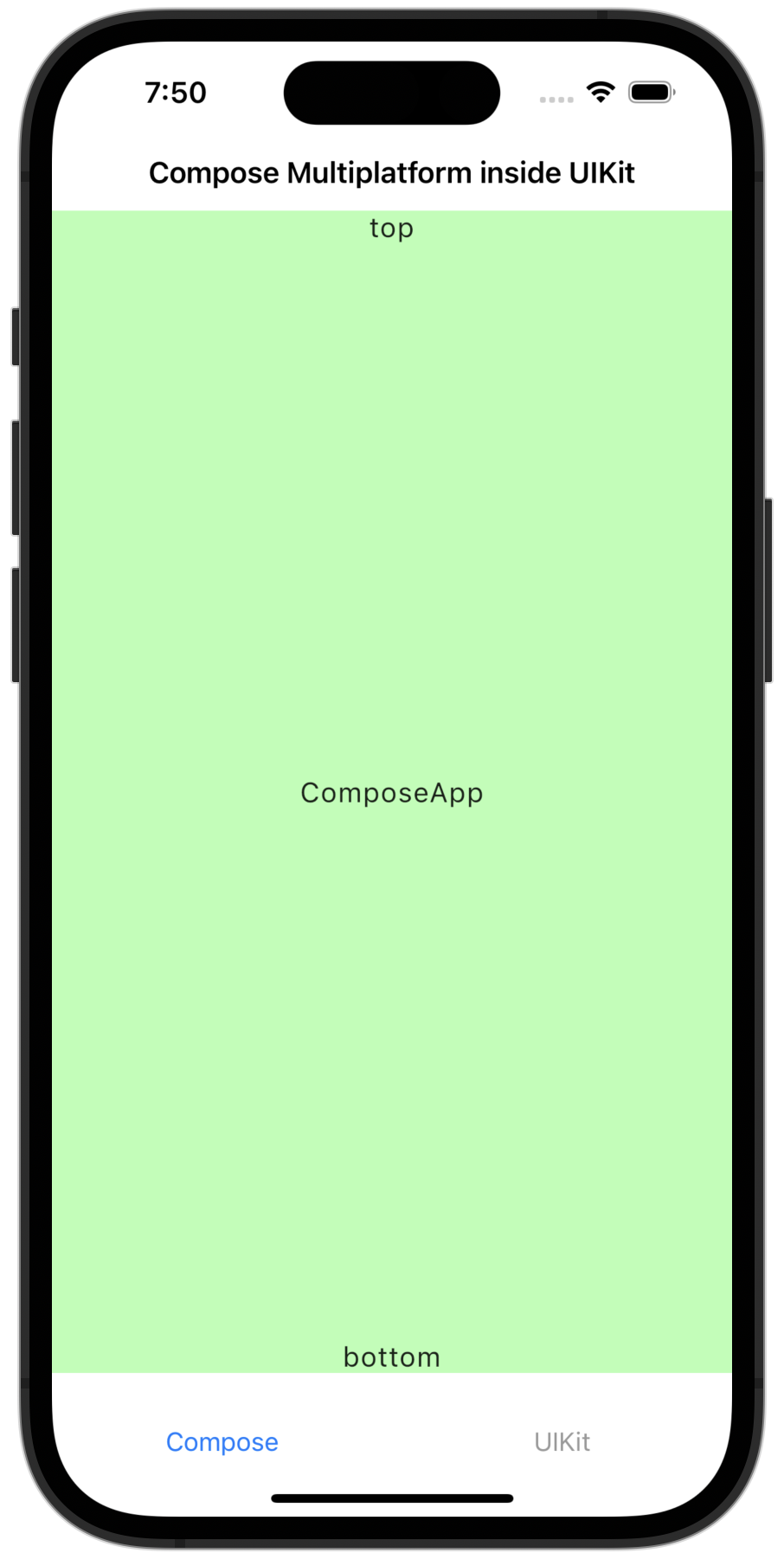
このコードは、サンプルプロジェクトで確認できます。
Compose Multiplatform内でUIKitを使用する
Compose Multiplatform内でUIKit要素を使用するには、使用したいUIKit要素をCompose MultiplatformのUIKitViewに追加します。 このコードは純粋にKotlinで記述することも、Swiftを使用することもできます。
マップビュー
Compose Multiplatformでマップビューを実装するには、UIKitのMKMapViewコンポーネントを使用できます。 コンポーネントのサイズは、Compose MultiplatformのModifier.size()またはModifier.fillMaxSize()関数を使用して設定します。
UIKitView(
factory = { MKMapView() },
modifier = Modifier.size(300.dp),
)このコードを使用すると、アプリケーションは次のようになります。
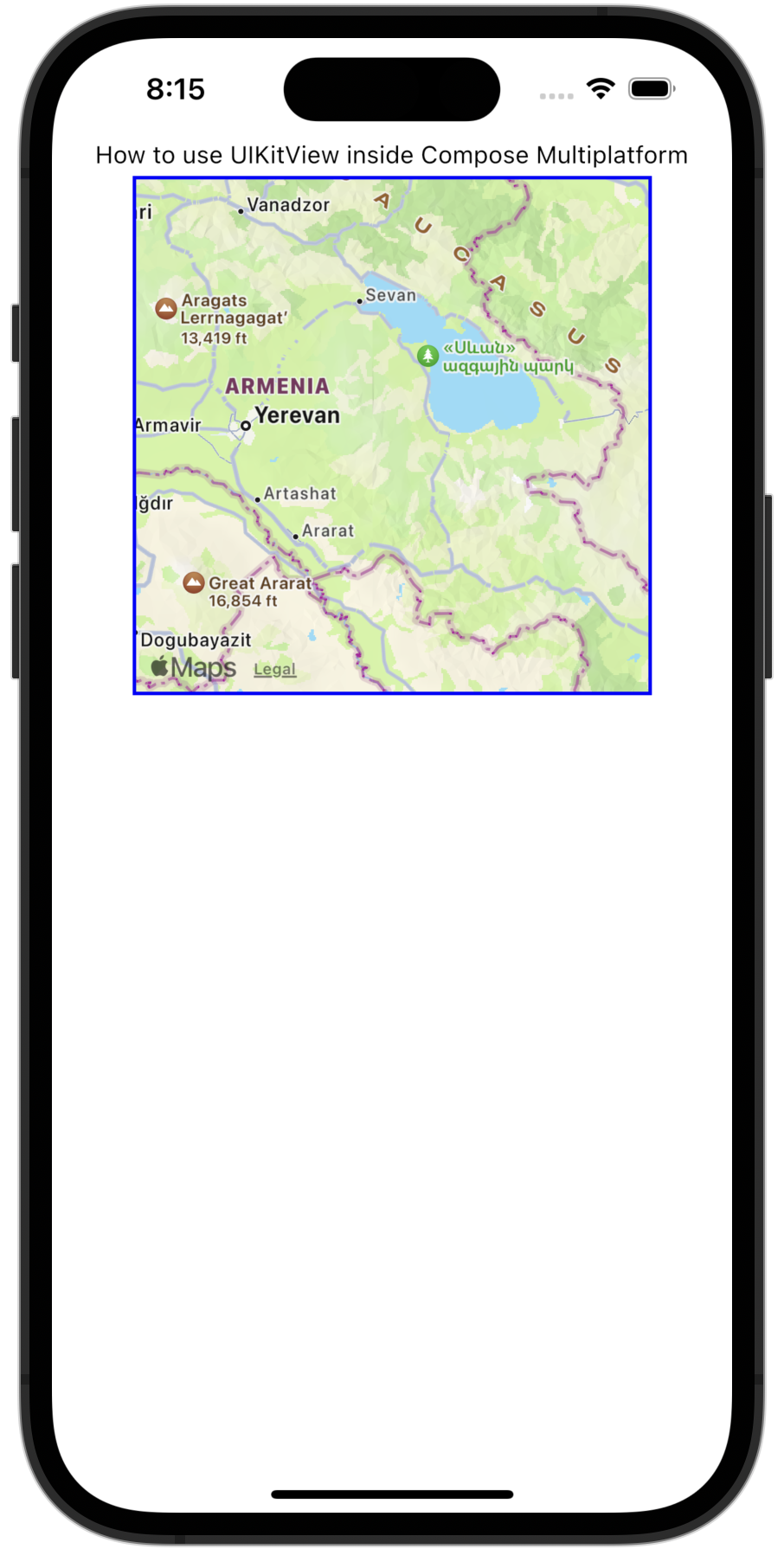
次に、より高度な例を見てみましょう。このコードは、UIKitのUITextFieldをCompose Multiplatformでラップしています。
@OptIn(ExperimentalForeignApi::class)
@Composable
fun UseUITextField(modifier: Modifier = Modifier) {
// Holds the state of the text in Compose
var message by remember { mutableStateOf("Hello, World!") }
UIKitView(
factory = {
// Creates a UITextField integrated with Compose state
val textField = object : UITextField(CGRectMake(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0)) {
@ObjCAction
fun editingChanged() {
// Updates the Compose state when text changes in UITextField
message = text ?: ""
}
}
// Adds a listener for text changes within the UITextField
textField.addTarget(
target = textField,
action = NSSelectorFromString(textField::editingChanged.name),
forControlEvents = UIControlEventEditingChanged
)
textField
},
modifier = modifier.fillMaxWidth().height(30.dp),
update = { textField ->
// Updates UITextField text from Compose state
textField.text = message
}
)
}factoryパラメータには、UITextFieldへの変更を検出するためのeditingChanged()関数とtextField.addTarget()リスナーが含まれています。editingChanged()関数には、Objective-Cコードと相互運用できるように@ObjCActionがアノテーションされています。addTarget()関数のactionパラメータは、editingChanged()関数の名前を渡し、UIControlEventEditingChangedイベントに応答してそれをトリガーします。UIKitView()のupdateパラメータは、観測可能なmessage状態が値を変更したときに呼び出されます。- この関数は
UITextFieldのtext属性を更新し、ユーザーが更新された値を確認できるようにします。
この例のコードは、サンプルプロジェクトで確認できます。
カメラビュー
Compose Multiplatformでカメラビューを実装するには、UIKitのAVCaptureSessionとAVCaptureVideoPreviewLayerコンポーネントを使用できます。
これにより、アプリケーションはデバイスのカメラにアクセスし、ライブプレビューを表示できます。
基本的なカメラビューを実装する方法の例を次に示します。
UIKitView(
factory = {
val session = AVCaptureSession().apply {
val device = AVCaptureDevice.defaultDeviceWithMediaType(AVMediaTypeVideo)!!
val input = AVCaptureDeviceInput.deviceInputWithDevice(device, null)!!
addInput(input)
}
val previewLayer = AVCaptureVideoPreviewLayer(session)
session.startRunning()
object : UIView() {
override fun layoutSubviews() {
super.layoutSubviews()
previewLayer.frame = bounds
}
}.apply {
layer.addSublayer(previewLayer)
}
},
modifier = Modifier.size(300.dp)
)次に、より高度な例を見てみましょう。このコードは、写真をキャプチャし、GPSメタデータを添付し、ネイティブのUIViewを使用してライブプレビューを表示します。
@OptIn(ExperimentalForeignApi::class)
@Composable
fun RealDeviceCamera(
camera: AVCaptureDevice,
onCapture: (picture: PictureData.Camera, image: PlatformStorableImage) -> Unit
) {
// Initializes AVCapturePhotoOutput for photo capturing
val capturePhotoOutput = remember { AVCapturePhotoOutput() }
// ...
// Defines a delegate to capture callback: process image data, attach GPS, setup onCapture
val photoCaptureDelegate = remember {
object : NSObject(), AVCapturePhotoCaptureDelegateProtocol {
override fun captureOutput(
output: AVCapturePhotoOutput,
didFinishProcessingPhoto: AVCapturePhoto,
error: NSError?
) {
val photoData = didFinishProcessingPhoto.fileDataRepresentation()
if (photoData != null) {
val gps = locationManager.location?.toGps() ?: GpsPosition(0.0, 0.0)
val uiImage = UIImage(photoData)
onCapture(
createCameraPictureData(
name = nameAndDescription.name,
description = nameAndDescription.description,
gps = gps
),
IosStorableImage(uiImage)
)
}
capturePhotoStarted = false
}
}
}
// ...
// Sets up AVCaptureSession for photo capture
val captureSession: AVCaptureSession = remember {
AVCaptureSession().also { captureSession ->
captureSession.sessionPreset = AVCaptureSessionPresetPhoto
val captureDeviceInput: AVCaptureDeviceInput =
deviceInputWithDevice(device = camera, error = null)!!
captureSession.addInput(captureDeviceInput)
captureSession.addOutput(capturePhotoOutput)
}
}
// Sets up AVCaptureVideoPreviewLayer for the live camera preview
val cameraPreviewLayer = remember {
AVCaptureVideoPreviewLayer(session = captureSession)
}
// ...
// Creates a native UIView with the native camera preview layer
UIKitView(
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize().background(Color.Black),
factory = {
val cameraContainer = object: UIView(frame = CGRectZero.readValue()) {
override fun layoutSubviews() {
CATransaction.begin()
CATransaction.setValue(true, kCATransactionDisableActions)
layer.setFrame(frame)
cameraPreviewLayer.setFrame(frame)
CATransaction.commit()
}
}
cameraContainer.layer.addSublayer(cameraPreviewLayer)
cameraPreviewLayer.videoGravity = AVLayerVideoGravityResizeAspectFill
captureSession.startRunning()
cameraContainer
},
)
// ...
// Creates a Compose button that executes the capturePhotoWithSettings callback when pressed
CircularButton(
imageVector = IconPhotoCamera,
modifier = Modifier.align(Alignment.BottomCenter).padding(36.dp),
enabled = !capturePhotoStarted,
) {
capturePhotoStarted = true
val photoSettings = AVCapturePhotoSettings.photoSettingsWithFormat(
format = mapOf(AVVideoCodecKey to AVVideoCodecTypeJPEG)
)
if (camera.position == AVCaptureDevicePositionFront) {
capturePhotoOutput.connectionWithMediaType(AVMediaTypeVideo)
?.automaticallyAdjustsVideoMirroring = false
capturePhotoOutput.connectionWithMediaType(AVMediaTypeVideo)
?.videoMirrored = true
}
capturePhotoOutput.capturePhotoWithSettings(
settings = photoSettings,
delegate = photoCaptureDelegate
)
}
}"}
RealDeviceCameraコンポーザブルは、次のタスクを実行します。
AVCaptureSessionとAVCaptureVideoPreviewLayerを使用して、ネイティブのカメラプレビューを設定します。- カスタムの
UIViewサブクラスをホストするUIKitViewを作成します。このサブクラスは、レイアウトの更新を管理し、プレビューレイヤーを埋め込みます。 AVCapturePhotoOutputを初期化し、写真のキャプチャを処理するためのデリゲートを設定します。CLLocationManager(locationManagerを介して)を使用して、キャプチャ時にGPS座標を取得します。- キャプチャした画像を
UIImageに変換し、PlatformStorableImageとしてラップし、onCaptureを介して名前、説明、GPS位置などのメタデータを提供します。 - キャプチャをトリガーするための円形のコンポーザブルボタンを表示します。
- 自然なセルフィー動作に合わせるために、前面カメラを使用する際にミラーリング設定を適用します。
- アニメーションを回避するために、
CATransactionを使用してlayoutSubviews()でプレビューレイアウトを動的に更新します。
実機でテストするには、アプリの
Info.plistファイルにNSCameraUsageDescriptionキーを追加する必要があります。 これがないと、アプリは実行時にクラッシュします。
この例の全コードは、ImageViewerサンプルプロジェクトで確認できます。
ウェブビュー
Compose Multiplatformでウェブビューを実装するには、UIKitのWKWebViewコンポーネントを使用できます。 これにより、アプリケーションはUI内でウェブコンテンツを表示し、操作できます。 コンポーネントのサイズは、Compose MultiplatformのModifier.size()またはModifier.fillMaxSize()関数を使用して設定します。
UIKitView(
factory = {
WKWebView().apply {
loadRequest(NSURLRequest(URL = NSURL(string = "https://www.jetbrains.com")))
}
},
modifier = Modifier.size(300.dp)
)次に、より高度な例を見てみましょう。このコードは、ナビゲーションデリゲートを使用してウェブビューを設定し、KotlinとJavaScript間の通信を可能にします。
@Composable
fun WebViewWithDelegate(
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
initialUrl: String = "https://www.jetbrains.com",
onNavigationChange: (String) -> Unit = {}
) {
// Creates a delegate to listen for navigation events
val delegate = remember {
object : NSObject(), WKNavigationDelegateProtocol {
override fun webView(
webView: WKWebView,
didFinishNavigation: WKNavigation?
) {
// Updates the current URL after navigation is complete
onNavigationChange(webView.URL?.absoluteString ?: "")
}
}
}
UIKitView(
modifier = modifier,
factory = {
// Instantiates a WKWebView and sets its delegate
val webView = WKWebView().apply {
navigationDelegate = delegate
loadRequest(NSURLRequest(uRL = NSURL(string = initialUrl)))
}
webView
},
update = { webView ->
// Reloads the web page if the URL changes
if (webView.URL?.absoluteString != initialUrl) {
webView.loadRequest(NSURLRequest(uRL = NSURL(string = initialUrl)))
}
}
)
}WebViewWithDelegateコンポーザブルは、次のタスクを実行します。
WKNavigationDelegateProtocolインターフェースを実装する安定したデリゲートオブジェクトを作成します。 このオブジェクトは、Composeのrememberを使用して再コンポジション間で記憶されます。WKWebViewをインスタンス化し、UIKitViewを使用して埋め込み、記憶されたデリゲートを割り当てて設定します。initialUrlパラメータによって提供される初期ウェブページをロードします。- デリゲートを介してナビゲーションの変更を監視し、
onNavigationChangeコールバックを介して現在のURLを渡します。 updateパラメータを使用して、リクエストされたURLの変更を監視し、それに応じてウェブページを再ロードします。
次のステップ
Compose MultiplatformをSwiftUIフレームワークと統合する方法についても確認できます。
