Spring Bootプロジェクトにデータベースのサポートを追加する
これはSpring BootとKotlin入門チュートリアルの第3部です。進む前に、前の手順を完了していることを確認してください。
KotlinでSpring Bootプロジェクトを作成する
Spring Bootプロジェクトにデータクラスを追加する
Spring Bootプロジェクトにデータベースのサポートを追加する
データベースアクセスにSpring Data CrudRepositoryを使用する
このチュートリアルのパートでは、Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) を使用して、データベースをプロジェクトに追加し、設定します。 JVMアプリケーションでは、JDBCを使用してデータベースと対話します。 Spring Frameworkは、利便性のために JdbcTemplate クラスを提供しており、JDBCの使用を簡素化し、よくあるエラーを回避するのに役立ちます。
データベースサポートを追加する
Spring Frameworkベースのアプリケーションでは、データベースアクセスロジックをいわゆる_サービス層_ (service layer) —ビジネスロジックが存在する場所— の中に実装するのが一般的な慣習です。 Springでは、クラスがアプリケーションのサービス層に属することを意味するために、@Service アノテーションでクラスをマークする必要があります。 このアプリケーションでは、この目的のために MessageService クラスを作成します。
同じパッケージに MessageService.kt ファイルと MessageService クラスを次のように作成します。
// MessageService.kt
package com.example.demo
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate
import java.util.*
@Service
class MessageService(private val db: JdbcTemplate) {
fun findMessages(): List<Message> = db.query("select * from messages") { response, _ ->
Message(response.getString("id"), response.getString("text"))
}
fun save(message: Message): Message {
db.update(
"insert into messages values ( ?, ? )",
message.id, message.text
)
return message
}
}コンストラクタ引数と依存性注入 – (private val db: JdbcTemplate)
Kotlinのクラスにはプライマリコンストラクタがあります。また、1つまたは複数のセカンダリコンストラクタを持つこともできます。 プライマリコンストラクタはクラスヘッダーの一部であり、クラス名とオプションの型パラメータの後に続きます。このケースでは、コンストラクタは (val db: JdbcTemplate) です。
val db: JdbcTemplate はコンストラクタの引数です。
末尾ラムダとSAM変換
findMessages() 関数は JdbcTemplate クラスの query() 関数を呼び出します。query() 関数は2つの引数を取ります。1つはStringインスタンスとしてのSQLクエリ、もう1つは行ごとに1つのオブジェクトをマッピングするコールバックです。
RowMapper インターフェースは1つのメソッドのみを宣言しているため、インターフェース名を省略してラムダ式で実装することが可能です。Kotlinコンパイラは、関数呼び出しのパラメータとして使用しているため、ラムダ式が変換されるべきインターフェースを認識しています。これはKotlinにおけるSAM変換として知られています。
SAM変換の後、query関数は2つの引数、すなわち最初の位置にString、最後の位置にラムダ式を持つことになります。Kotlinの規約によれば、関数の最後のパラメータが関数である場合、対応する引数として渡されるラムダ式は括弧の外に配置できます。このような構文は末尾ラムダとも呼ばれます。
未使用のラムダ引数に対するアンダースコア
複数のパラメータを持つラムダの場合、使用しないパラメータの名前をアンダースコア _ 文字に置き換えることができます。
したがって、query関数の呼び出しの最終的な構文は次のようになります。
MessageControllerクラスを更新する
MessageController.kt を更新して、新しい MessageService クラスを使用するようにします。
// MessageController.kt
package com.example.demo
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController
import java.net.URI
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/")
class MessageController(private val service: MessageService) {
@GetMapping
fun listMessages() = service.findMessages()
@PostMapping
fun post(@RequestBody message: Message): ResponseEntity<Message> {
val savedMessage = service.save(message)
return ResponseEntity.created(URI("/${savedMessage.id}")).body(savedMessage)
}
}@PostMapping アノテーション
HTTP POSTリクエストを処理するメソッドには @PostMapping アノテーションを付与する必要があります。HTTP Bodyコンテンツとして送信されたJSONをオブジェクトに変換できるようにするには、メソッド引数に @RequestBody アノテーションを使用する必要があります。Jacksonライブラリがアプリケーションのクラスパスにあるおかげで、変換は自動的に行われます。
ResponseEntity
ResponseEntity は、ステータスコード、ヘッダー、ボディを含むHTTPレスポンス全体を表します。
created() メソッドを使用すると、レスポンスのステータスコード (201) を設定し、作成されたリソースのコンテキストパスを示すロケーションヘッダーを設定できます。
MessageServiceクラスを更新する
Message クラスの id はnull許容のStringとして宣言されていました。
data class Message(val id: String?, val text: String)しかし、データベースに null を id 値として保存するのは正しくありません。この状況を適切に処理する必要があります。
MessageService.kt ファイルのコードを更新し、メッセージをデータベースに保存する際に id が null の場合に新しい値を生成するようにします。
// MessageService.kt
package com.example.demo
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.query
import java.util.UUID
@Service
class MessageService(private val db: JdbcTemplate) {
fun findMessages(): List<Message> = db.query("select * from messages") { response, _ ->
Message(response.getString("id"), response.getString("text"))
}
fun save(message: Message): Message {
val id = message.id ?: UUID.randomUUID().toString() // idがnullの場合に新しいidを生成する
db.update(
"insert into messages values ( ?, ? )",
id, message.text
)
return message.copy(id = id) // 新しいidを持つメッセージのコピーを返す
}
}エルビス演算子 – ?:
コード message.id ?: UUID.randomUUID().toString() は、エルビス演算子 (if-not-null-else shorthand) ?: を使用しています。?: の左側の式が null でない場合、エルビス演算子はその値を返します。それ以外の場合は、右側の式を返します。右側の式は、左側が null の場合にのみ評価されることに注意してください。
アプリケーションコードはデータベースと連携する準備ができています。次に、データソースを設定する必要があります。
データベースを設定する
アプリケーションのデータベースを設定します。
src/main/resourcesディレクトリにschema.sqlファイルを作成します。このファイルにはデータベースオブジェクトの定義が格納されます。
src/main/resources/schema.sqlファイルを次のコードで更新します。sql-- schema.sql CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS messages ( id VARCHAR(60) PRIMARY KEY, text VARCHAR NOT NULL );これにより、
idとtextの2つのカラムを持つmessagesテーブルが作成されます。このテーブル構造はMessageクラスの構造と一致します。src/main/resourcesフォルダーにあるapplication.propertiesファイルを開き、次のアプリケーションプロパティを追加します。nonespring.application.name=demo spring.datasource.driver-class-name=org.h2.Driver spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:file:./data/testdb spring.datasource.username=name spring.datasource.password=password spring.sql.init.schema-locations=classpath:schema.sql spring.sql.init.mode=alwaysこれらの設定は、Spring Bootアプリケーションのデータベースを有効にします。 一般的なアプリケーションプロパティの完全なリストは、Spring ドキュメントを参照してください。
HTTPリクエストを介してデータベースにメッセージを追加する
以前に作成したエンドポイントを操作するには、HTTPクライアントを使用する必要があります。IntelliJ IDEAでは、組み込みHTTPクライアントを使用します。
アプリケーションを実行します。アプリケーションが起動して実行されたら、POSTリクエストを実行してメッセージをデータベースに保存できます。
プロジェクトのルートフォルダに
requests.httpファイルを作成し、次のHTTPリクエストを追加します。http### Post "Hello!" POST http://localhost:8080/ Content-Type: application/json { "text": "Hello!" } ### Post "Bonjour!" POST http://localhost:8080/ Content-Type: application/json { "text": "Bonjour!" } ### Post "Privet!" POST http://localhost:8080/ Content-Type: application/json { "text": "Privet!" } ### Get all the messages GET http://localhost:8080/すべてのPOSTリクエストを実行します。リクエスト宣言の横にあるガターの緑色の実行アイコンを使用します。 これらのリクエストは、テキストメッセージをデータベースに書き込みます。
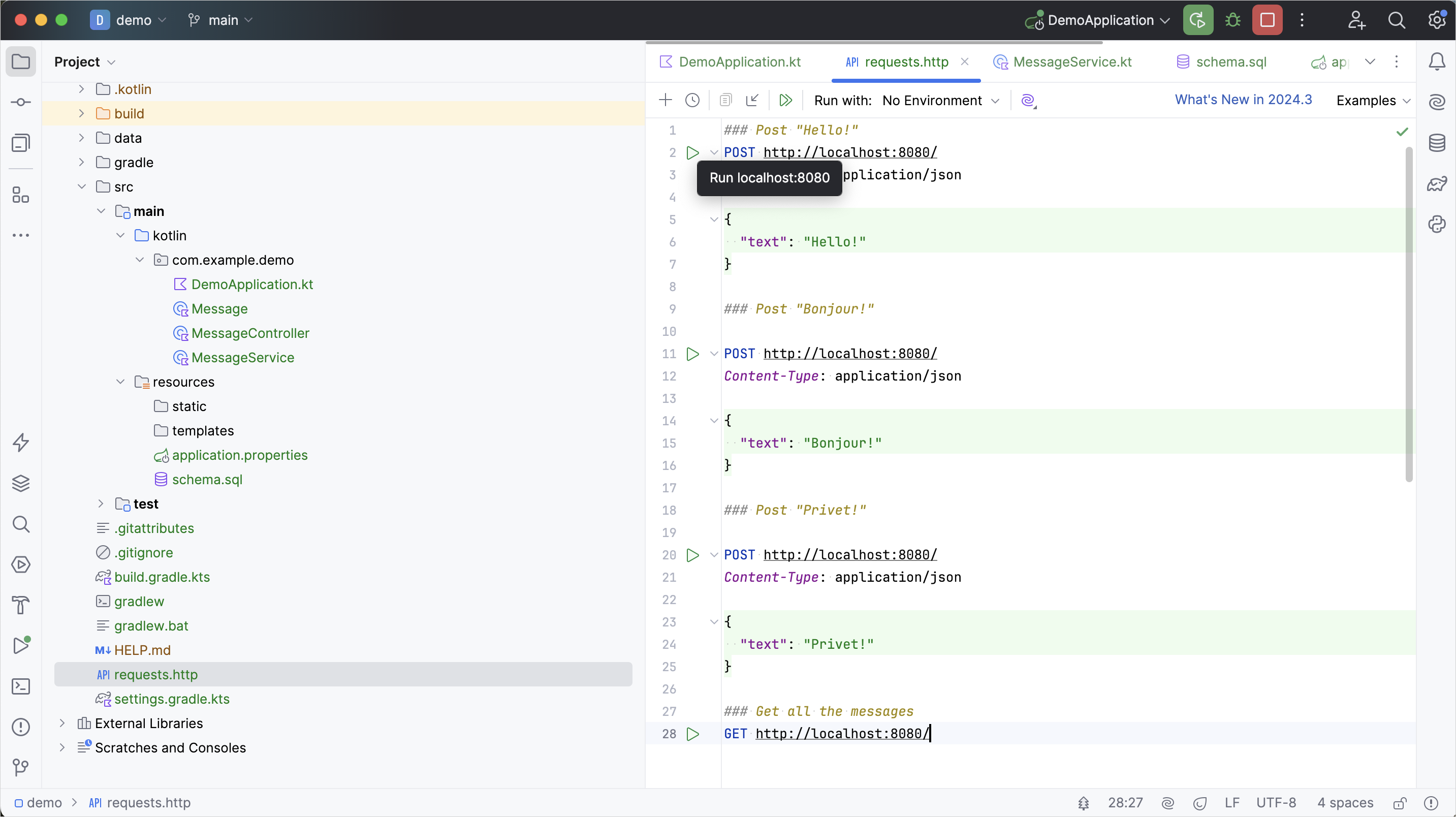
GETリクエストを実行し、Runツールウィンドウで結果を確認します。
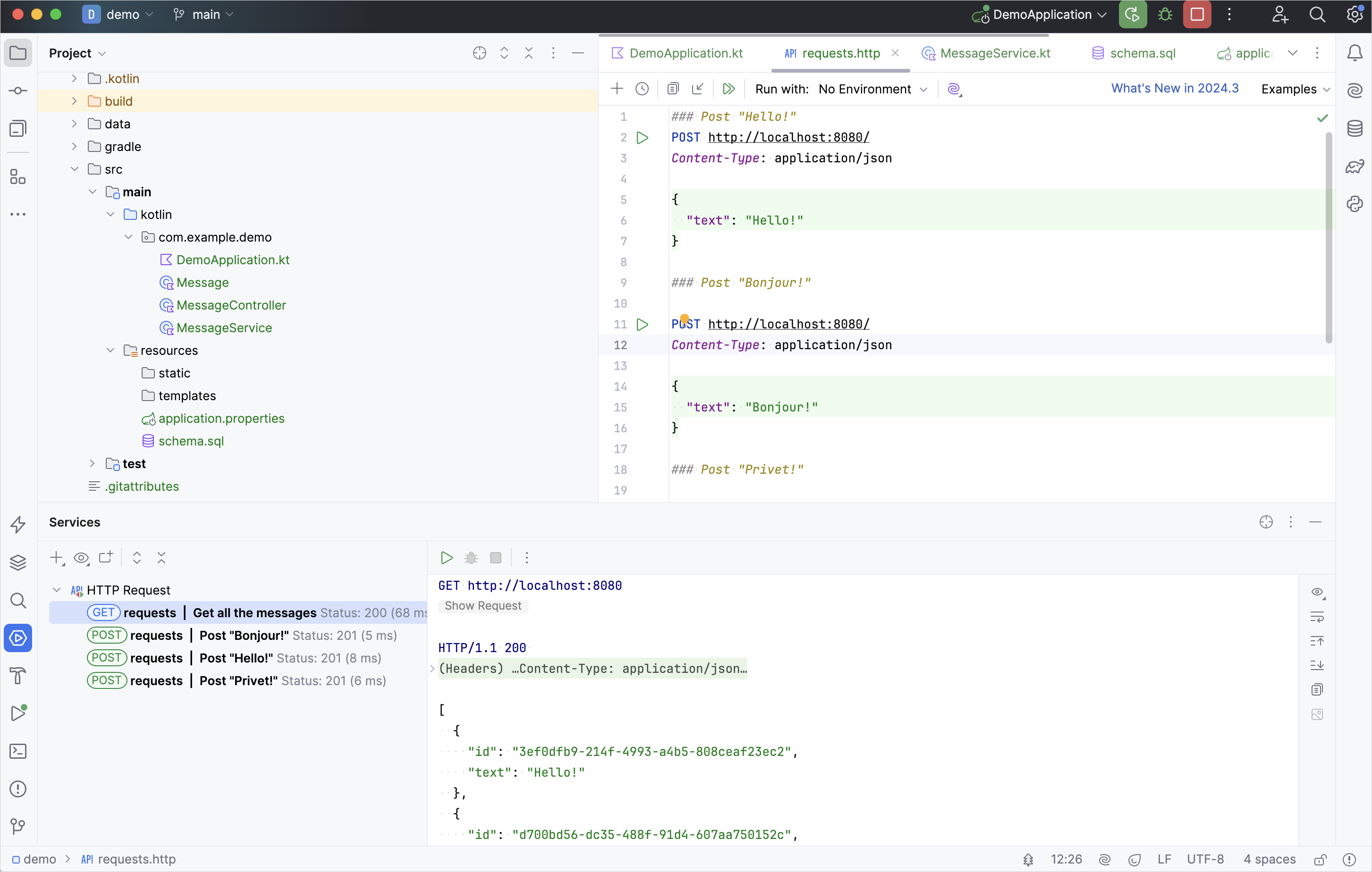
リクエストを実行する別の方法
他のHTTPクライアントやcURLコマンドラインツールを使用することもできます。たとえば、同じ結果を得るには、ターミナルで次のコマンドを実行します。
curl -X POST --location "http://localhost:8080" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d "{ \"text\": \"Hello!\" }"
curl -X POST --location "http://localhost:8080" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d "{ \"text\": \"Bonjour!\" }"
curl -X POST --location "http://localhost:8080" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d "{ \"text\": \"Privet!\" }"
curl -X GET --location "http://localhost:8080"idでメッセージを取得する
idで個別のメッセージを取得する機能のアプリケーションを拡張します。
MessageServiceクラスに、idで個別のメッセージを取得するための新しい関数findMessageById(id: String)を追加します。kotlin// MessageService.kt package com.example.demo import org.springframework.stereotype.Service import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate import org.springframework.jdbc.core.query import java.util.* @Service class MessageService(private val db: JdbcTemplate) { fun findMessages(): List<Message> = db.query("select * from messages") { response, _ -> Message(response.getString("id"), response.getString("text")) } fun findMessageById(id: String): Message? = db.query("select * from messages where id = ?", id) { response, _ -> Message(response.getString("id"), response.getString("text")) }.singleOrNull() fun save(message: Message): Message { val id = message.id ?: UUID.randomUUID().toString() // idがnullの場合に新しいidを生成する db.update( "insert into messages values ( ?, ? )", id, message.text ) return message.copy(id = id) // 新しいidを持つメッセージのコピーを返す } }パラメータリストにおける可変引数 (vararg) の位置
query()関数は3つの引数を取ります。- 実行にパラメータを必要とするSQLクエリ文字列
- String型のパラメータである
id - ラムダ式で実装される
RowMapperインスタンス
query()関数の2番目のパラメータは、可変引数 (vararg) として宣言されています。Kotlinでは、可変引数パラメータの位置はパラメータリストの最後である必要はありません。singleOrNull() 関数
singleOrNull()関数は、配列が空の場合、または同じ値を持つ要素が複数ある場合はnullを返し、それ以外の場合は単一の要素を返します。.query()関数は、メッセージをIDで取得するために使用され、Spring Frameworkによって提供されるKotlin拡張関数です。上記のコードで示されているように、追加のインポートimport org.springframework.jdbc.core.queryが必要です。MessageControllerクラスに、idパラメータを持つ新しいindex(...)関数を追加します。kotlin// MessageController.kt package com.example.demo import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController import java.net.URI @RestController @RequestMapping("/") class MessageController(private val service: MessageService) { @GetMapping fun listMessages() = ResponseEntity.ok(service.findMessages()) @PostMapping fun post(@RequestBody message: Message): ResponseEntity<Message> { val savedMessage = service.save(message) return ResponseEntity.created(URI("/${savedMessage.id}")).body(savedMessage) } @GetMapping("/{id}") fun getMessage(@PathVariable id: String): ResponseEntity<Message> = service.findMessageById(id).toResponseEntity() private fun Message?.toResponseEntity(): ResponseEntity<Message> = // メッセージがnull(見つからない)の場合、レスポンスコードを404に設定する this?.let { ResponseEntity.ok(it) } ?: ResponseEntity.notFound().build() }コンテキストパスからの値の取得
メッセージの
idは、新しい関数に@GetMapping("/{id}")アノテーションを付けることで、Spring Frameworkによってコンテキストパスから取得されます。関数引数に@PathVariableアノテーションを付けることで、取得した値を関数引数として使用するようにフレームワークに指示します。新しい関数は、そのidによって個別のメッセージを取得するためにMessageServiceを呼び出します。null許容レシーバーを持つ拡張関数
拡張は、null許容レシーバー型で定義できます。レシーバーが
nullの場合、thisもnullになります。したがって、null許容レシーバー型で拡張を定義する場合、関数本体内でthis == nullチェックを実行することをお勧めします。また、上記の
toResponseEntity()関数のように、null安全な呼び出し演算子 (?.) を使用してnullチェックを実行することもできます。kotlinResponseEntity
ResponseEntityは、ステータスコード、ヘッダー、ボディを含むHTTPレスポンスを表します。これは、コンテンツをより細かく制御して、カスタマイズされたHTTPレスポンスをクライアントに送信できる汎用ラッパーです。
アプリケーションの完全なコードを以下に示します。
// DemoApplication.kt
package com.example.demo
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication
import org.springframework.boot.runApplication
@SpringBootApplication
class DemoApplication
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
runApplication<DemoApplication>(*args)
}// Message.kt
package com.example.demo
data class Message(val id: String?, val text: String)// MessageService.kt
package com.example.demo
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.query
import java.util.*
@Service
class MessageService(private val db: JdbcTemplate) {
fun findMessages(): List<Message> = db.query("select * from messages") { response, _ ->
Message(response.getString("id"), response.getString("text"))
}
fun findMessageById(id: String): Message? = db.query("select * from messages where id = ?", id) { response, _ ->
Message(response.getString("id"), response.getString("text"))
}.singleOrNull()
fun save(message: Message): Message {
val id = message.id ?: UUID.randomUUID().toString()
db.update(
"insert into messages values ( ?, ? )",
id, message.text
)
return message.copy(id = id)
}
}// MessageController.kt
package com.example.demo
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController
import java.net.URI
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/")
class MessageController(private val service: MessageService) {
@GetMapping
fun listMessages() = ResponseEntity.ok(service.findMessages())
@PostMapping
fun post(@RequestBody message: Message): ResponseEntity<Message> {
val savedMessage = service.save(message)
return ResponseEntity.created(URI("/${savedMessage.id}")).body(savedMessage)
}
@GetMapping("/{id}")
fun getMessage(@PathVariable id: String): ResponseEntity<Message> =
service.findMessageById(id).toResponseEntity()
private fun Message?.toResponseEntity(): ResponseEntity<Message> =
this?.let { ResponseEntity.ok(it) } ?: ResponseEntity.notFound().build()
}アプリケーションを実行する
Springアプリケーションを実行する準備ができました。
アプリケーションを再度実行します。
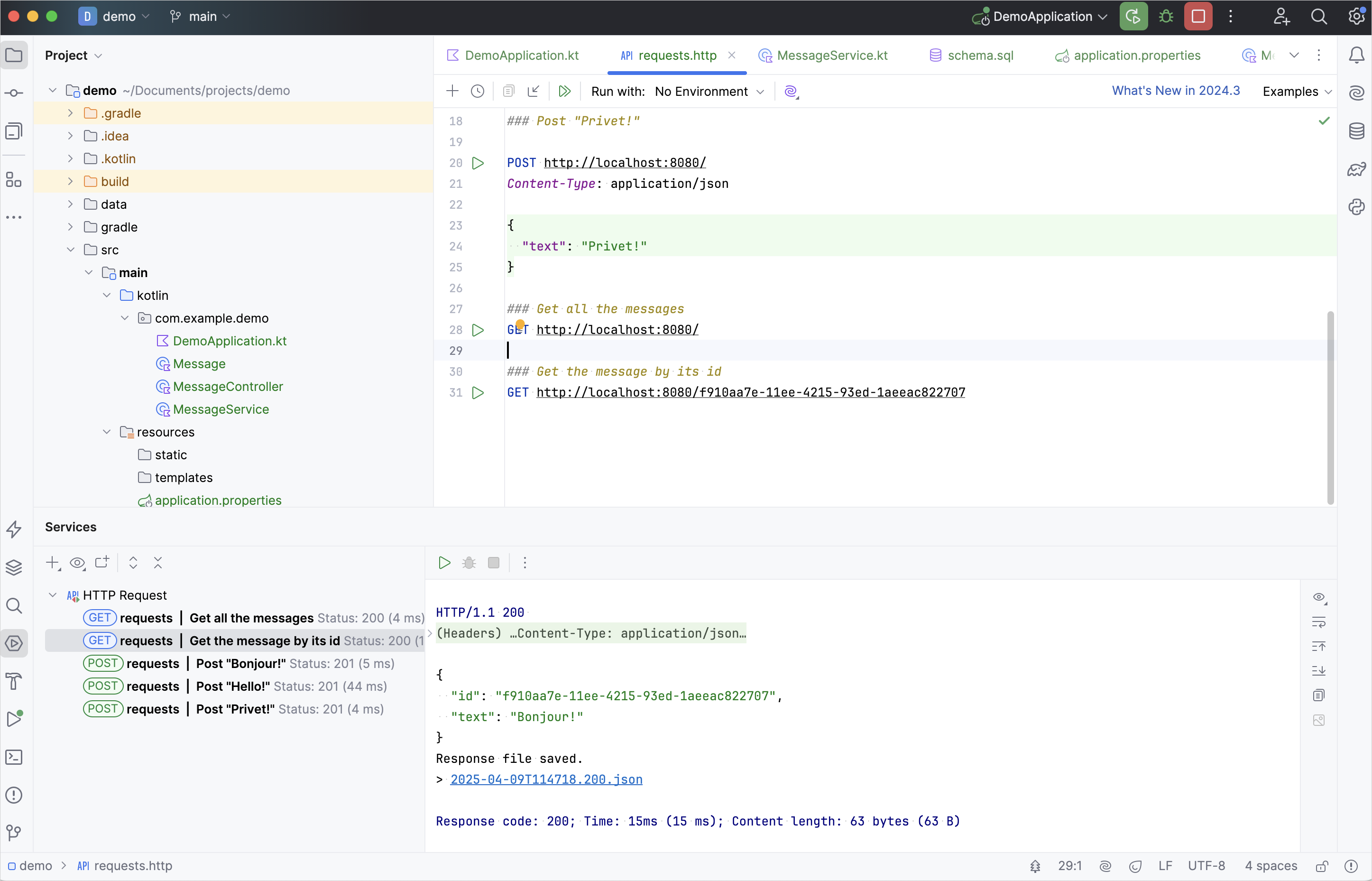
requests.httpファイルを開き、新しいGETリクエストを追加します。http### Get the message by its id GET http://localhost:8080/idGETリクエストを実行して、データベースからすべてのメッセージを取得します。
RunツールウィンドウでいずれかのIDをコピーし、次のようにリクエストに追加します。
http### Get the message by its id GET http://localhost:8080/f910aa7e-11ee-4215-93ed-1aeeac822707上記のメッセージIDの代わりに、あなたのメッセージIDを記述してください。
GETリクエストを実行し、Runツールウィンドウで結果を確認します。
次のステップ
最後のステップでは、Spring Dataを使用してより一般的なデータベース接続を行う方法を示します。
