Spring Boot 프로젝트에 데이터베이스 지원 추가
이 튜토리얼은 Spring Boot 및 Kotlin 시작하기의 세 번째 부분입니다. 계속 진행하기 전에 다음 이전 단계를 완료했는지 확인하세요:
Kotlin으로 Spring Boot 프로젝트 생성하기
Spring Boot 프로젝트에 데이터 클래스 추가하기
Spring Boot 프로젝트에 데이터베이스 지원 추가하기
데이터베이스 접근을 위해 Spring Data CrudRepository 사용하기
이 튜토리얼의 이 부분에서는 자바 데이터베이스 연결 (JDBC)을 사용하여 프로젝트에 데이터베이스를 추가하고 구성합니다. JVM 애플리케이션에서는 JDBC를 사용하여 데이터베이스와 상호 작용합니다. 편의를 위해 스프링 프레임워크는 JDBC 사용을 간소화하고 일반적인 오류를 방지하는 데 도움이 되는 JdbcTemplate 클래스를 제공합니다.
데이터베이스 지원 추가
스프링 프레임워크 기반 애플리케이션의 일반적인 관행은 데이터베이스 접근 로직을 소위 서비스 계층에 구현하는 것입니다. 이곳은 비즈니스 로직이 위치하는 곳입니다. 스프링에서 클래스에 @Service 애너테이션을 표시하여 해당 클래스가 애플리케이션의 서비스 계층에 속함을 나타내야 합니다. 이 애플리케이션에서는 이 목적으로 MessageService 클래스를 생성합니다.
동일한 패키지에 다음 내용으로 MessageService.kt 파일과 MessageService 클래스를 생성합니다:
// MessageService.kt
package com.example.demo
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate
import java.util.*
@Service
class MessageService(private val db: JdbcTemplate) {
fun findMessages(): List<Message> = db.query("select * from messages") { response, _ ->
Message(response.getString("id"), response.getString("text"))
}
fun save(message: Message): Message {
db.update(
"insert into messages values ( ?, ? )",
message.id, message.text
)
return message
}
}생성자 인수 및 의존성 주입 – (private val db: JdbcTemplate)
Kotlin의 클래스에는 주 생성자가 있습니다. 또한 하나 이상의 보조 생성자를 가질 수도 있습니다. 주 생성자는 클래스 헤더의 일부이며, 클래스 이름과 선택적 타입 파라미터 뒤에 옵니다. 이 경우 생성자는 (val db: JdbcTemplate)입니다.
val db: JdbcTemplate는 생성자의 인수입니다:
후행 람다 및 SAM 변환
findMessages() 함수는 JdbcTemplate 클래스의 query() 함수를 호출합니다. query() 함수는 두 가지 인수를 받습니다: String 인스턴스로서의 SQL 쿼리와 각 행당 하나의 객체를 매핑할 콜백입니다:
RowMapper 인터페이스는 단 하나의 메서드만 선언하므로, 인터페이스 이름을 생략하고 람다 표현식을 통해 이를 구현할 수 있습니다. Kotlin 컴파일러는 함수 호출의 파라미터로 람다 표현식을 사용하기 때문에 람다 표현식이 변환되어야 할 인터페이스를 알고 있습니다. 이를 Kotlin의 SAM 변환이라고 합니다:
SAM 변환 후, 쿼리 함수는 첫 번째 위치에 String, 마지막 위치에 람다 표현식이라는 두 가지 인수를 갖게 됩니다. Kotlin 컨벤션에 따르면, 함수의 마지막 파라미터가 함수인 경우, 해당 인수로 전달되는 람다 표현식은 괄호 밖에 배치될 수 있습니다. 이러한 구문을 후행 람다라고도 합니다:
사용되지 않는 람다 인수를 위한 밑줄
여러 파라미터를 가진 람다의 경우, 사용하지 않는 파라미터의 이름을 밑줄 _ 문자로 대체할 수 있습니다.
따라서 쿼리 함수 호출의 최종 구문은 다음과 같습니다:
MessageController 클래스 업데이트
새 MessageService 클래스를 사용하도록 MessageController.kt를 업데이트합니다:
// MessageController.kt
package com.example.demo
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController
import java.net.URI
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/")
class MessageController(private val service: MessageService) {
@GetMapping
fun listMessages() = service.findMessages()
@PostMapping
fun post(@RequestBody message: Message): ResponseEntity<Message> {
val savedMessage = service.save(message)
return ResponseEntity.created(URI("/${savedMessage.id}")).body(savedMessage)
}
}@PostMapping 애너테이션
HTTP POST 요청을 처리하는 메서드는 @PostMapping 애너테이션으로 주석 처리되어야 합니다. HTTP 본문 내용으로 전송된 JSON을 객체로 변환하려면, 메서드 인수에 @RequestBody 애너테이션을 사용해야 합니다. 애플리케이션의 클래스패스에 Jackson 라이브러리가 있기 때문에 변환이 자동으로 이루어집니다.
ResponseEntity
ResponseEntity는 상태 코드, 헤더, 본문을 포함하여 전체 HTTP 응답을 나타냅니다.
created() 메서드를 사용하면 응답 상태 코드(201)를 구성하고 생성된 리소스의 컨텍스트 경로를 나타내는 location 헤더를 설정할 수 있습니다.
MessageService 클래스 업데이트
Message 클래스의 id는 널러블 문자열로 선언되었습니다:
data class Message(val id: String?, val text: String)하지만 데이터베이스에 null을 id 값으로 저장하는 것은 올바르지 않습니다: 이 상황을 우아하게 처리해야 합니다.
데이터베이스에 메시지를 저장할 때 id가 null인 경우 새 값을 생성하도록 MessageService.kt 파일의 코드를 업데이트합니다:
// MessageService.kt
package com.example.demo
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.query
import java.util.UUID
@Service
class MessageService(private val db: JdbcTemplate) {
fun findMessages(): List<Message> = db.query("select * from messages") { response, _ ->
Message(response.getString("id"), response.getString("text"))
}
fun save(message: Message): Message {
val id = message.id ?: UUID.randomUUID().toString() // Generate new id if it is null
db.update(
"insert into messages values ( ?, ? )",
id, message.text
)
return message.copy(id = id) // Return a copy of the message with the new id
}
}엘비스 연산자 – ?:
코드 message.id ?: UUID.randomUUID().toString()는 엘비스 연산자 (null이 아닐 경우-그 외 경우 단축 구문) ?:를 사용합니다. ?: 왼쪽에 있는 표현식이 null이 아니면 엘비스 연산자는 그 값을 반환하고, 그렇지 않으면 오른쪽에 있는 표현식을 반환합니다. 오른쪽 표현식은 왼쪽이 null인 경우에만 평가된다는 점에 유의하세요.
애플리케이션 코드는 데이터베이스와 함께 작동할 준비가 되었습니다. 이제 데이터 소스를 구성해야 합니다.
데이터베이스 구성
애플리케이션에서 데이터베이스를 구성합니다:
src/main/resources디렉터리에schema.sql파일을 생성합니다. 이 파일은 데이터베이스 객체 정의를 저장합니다:
src/main/resources/schema.sql파일을 다음 코드로 업데이트합니다:sql-- schema.sql CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS messages ( id VARCHAR(60) PRIMARY KEY, text VARCHAR NOT NULL );이것은
id와text두 개의 열을 가진messages테이블을 생성합니다. 테이블 구조는Message클래스의 구조와 일치합니다.src/main/resources폴더에 있는application.properties파일을 열고 다음 애플리케이션 속성을 추가합니다:nonespring.application.name=demo spring.datasource.driver-class-name=org.h2.Driver spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:file:./data/testdb spring.datasource.username=name spring.datasource.password=password spring.sql.init.schema-locations=classpath:schema.sql spring.sql.init.mode=always이 설정은 Spring Boot 애플리케이션에 데이터베이스를 활성화합니다.
스프링 문서에서 일반 애플리케이션 속성의 전체 목록을 확인하세요.
HTTP 요청을 통해 데이터베이스에 메시지 추가
이전에 생성한 엔드포인트와 작업하려면 HTTP 클라이언트를 사용해야 합니다. IntelliJ IDEA에서는 내장 HTTP 클라이언트를 사용하세요:
애플리케이션을 실행합니다. 애플리케이션이 실행되면 POST 요청을 실행하여 메시지를 데이터베이스에 저장할 수 있습니다.
프로젝트 루트 폴더에
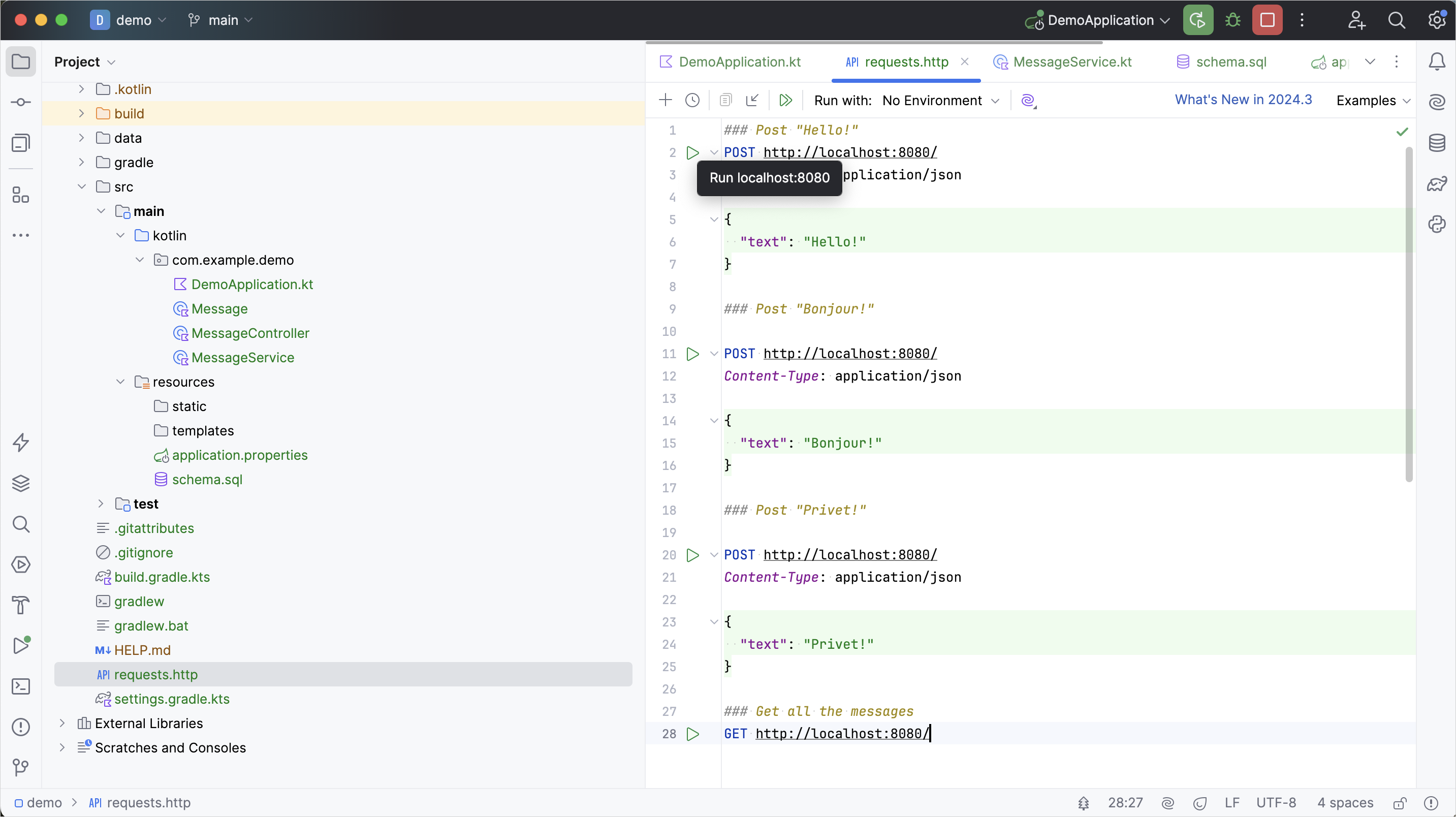
requests.http파일을 생성하고 다음 HTTP 요청을 추가합니다:http### Post "Hello!" POST http://localhost:8080/ Content-Type: application/json { "text": "Hello!" } ### Post "Bonjour!" POST http://localhost:8080/ Content-Type: application/json { "text": "Bonjour!" } ### Post "Privet!" POST http://localhost:8080/ Content-Type: application/json { "text": "Privet!" } ### Get all the messages GET http://localhost:8080/모든 POST 요청을 실행합니다. 요청 선언 옆에 있는 여백의 녹색 실행 아이콘을 사용하세요. 이 요청들은 텍스트 메시지를 데이터베이스에 기록합니다:
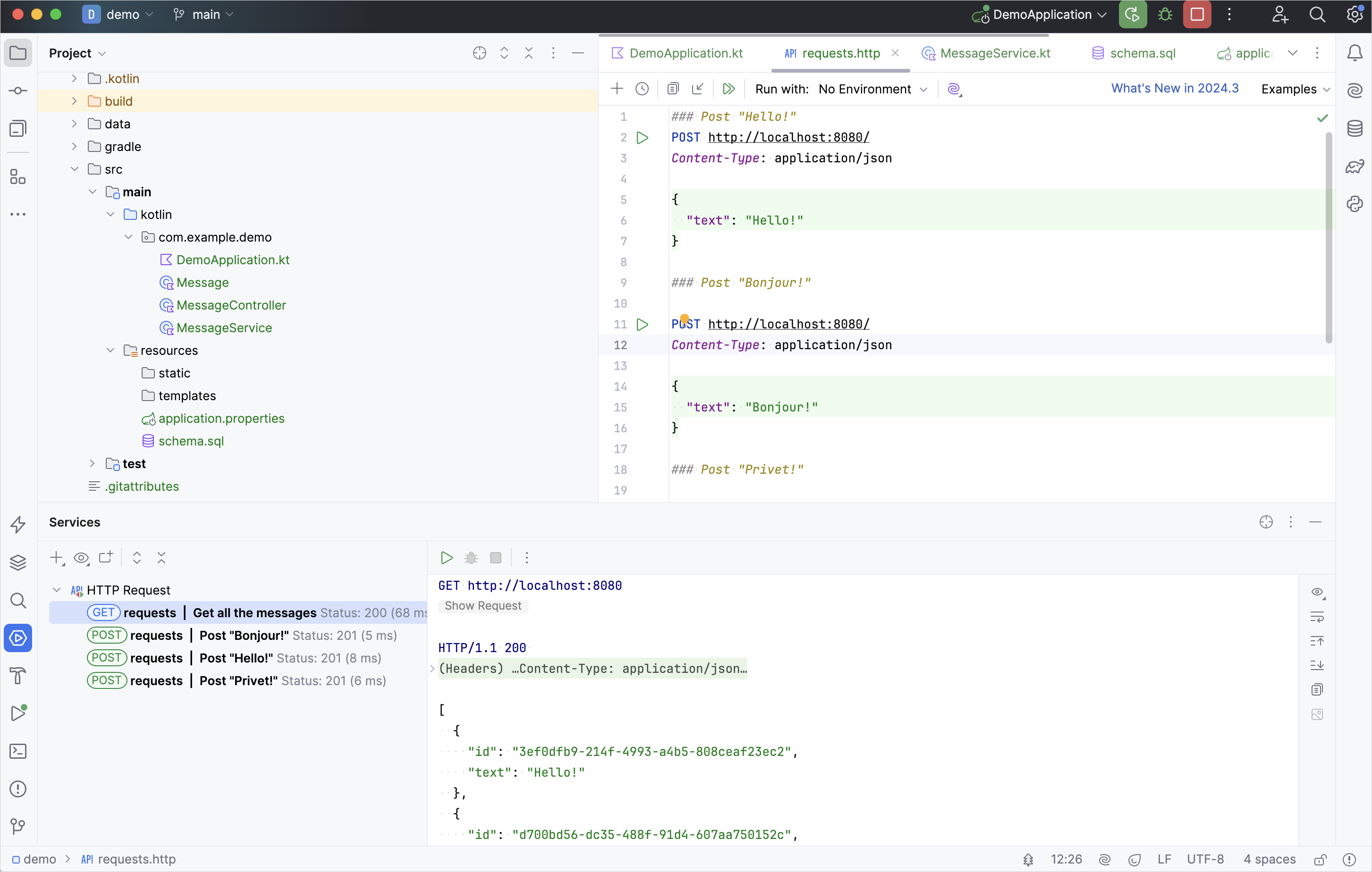
GET 요청을 실행하고 실행 도구 창에서 결과를 확인하세요:
요청을 실행하는 다른 방법
다른 HTTP 클라이언트나 cURL 명령줄 도구를 사용할 수도 있습니다. 예를 들어, 동일한 결과를 얻으려면 터미널에서 다음 명령을 실행합니다:
curl -X POST --location "http://localhost:8080" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d "{ \"text\": \"Hello!\" }"
curl -X POST --location "http://localhost:8080" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d "{ \"text\": \"Bonjour!\" }"
curl -X POST --location "http://localhost:8080" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d "{ \"text\": \"Privet!\" }"
curl -X GET --location "http://localhost:8080"ID별 메시지 검색
ID별로 개별 메시지를 검색하도록 애플리케이션의 기능을 확장합니다.
MessageService클래스에 ID별 개별 메시지를 검색하는 새 함수findMessageById(id: String)를 추가합니다:kotlin// MessageService.kt package com.example.demo import org.springframework.stereotype.Service import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate import org.springframework.jdbc.core.query import java.util.* @Service class MessageService(private val db: JdbcTemplate) { fun findMessages(): List<Message> = db.query("select * from messages") { response, _ -> Message(response.getString("id"), response.getString("text")) } fun findMessageById(id: String): Message? = db.query("select * from messages where id = ?", id) { response, _ -> Message(response.getString("id"), response.getString("text")) }.singleOrNull() fun save(message: Message): Message { val id = message.id ?: UUID.randomUUID().toString() // Generate new id if it is null db.update( "insert into messages values ( ?, ? )", id, message.text ) return message.copy(id = id) // Return a copy of the message with the new id } }파라미터 목록에서의 vararg 인수 위치
query()함수는 세 가지 인수를 받습니다:- 실행할 매개변수가 필요한 SQL 쿼리 문자열
- String 타입의 매개변수인
id - 람다 표현식으로 구현된
RowMapper인스턴스
query()함수의 두 번째 파라미터는 가변 인수 (vararg)로 선언됩니다. Kotlin에서는 가변 인수 파라미터의 위치가 파라미터 목록의 마지막일 필요는 없습니다.singleOrNull() 함수
singleOrNull()함수는 단일 요소를 반환하거나, 배열이 비어 있거나 동일한 값을 가진 요소가 두 개 이상인 경우null을 반환합니다.ID로 메시지를 가져오는 데 사용되는
.query()함수는 스프링 프레임워크가 제공하는 Kotlin 확장 함수입니다. 위 코드에서 보여지는 것처럼 추가적인import org.springframework.jdbc.core.query임포트가 필요합니다.MessageController클래스에id파라미터가 있는 새index(...)함수를 추가합니다:kotlin// MessageController.kt package com.example.demo import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController import java.net.URI @RestController @RequestMapping("/") class MessageController(private val service: MessageService) { @GetMapping fun listMessages() = ResponseEntity.ok(service.findMessages()) @PostMapping fun post(@RequestBody message: Message): ResponseEntity<Message> { val savedMessage = service.save(message) return ResponseEntity.created(URI("/${savedMessage.id}")).body(savedMessage) } @GetMapping("/{id}") fun getMessage(@PathVariable id: String): ResponseEntity<Message> = service.findMessageById(id).toResponseEntity() private fun Message?.toResponseEntity(): ResponseEntity<Message> = // If the message is null (not found), set response code to 404 this?.let { ResponseEntity.ok(it) } ?: ResponseEntity.notFound().build() }컨텍스트 경로에서 값 검색
새 함수를
@GetMapping("/{id}")로 애너테이션 했으므로 Spring 프레임워크가 컨텍스트 경로에서 메시지id를 검색합니다. 함수 인수에@PathVariable을 애너테이션하여 프레임워크에 검색된 값을 함수 인수로 사용하도록 지시합니다. 새 함수는MessageService를 호출하여 ID별 개별 메시지를 검색합니다.널러블 수신자를 가진 확장 함수
확장은 널러블 수신자 타입으로 정의될 수 있습니다. 수신자가
null이면this도null입니다. 따라서 널러블 수신자 타입을 가진 확장을 정의할 때는 함수 본문 내에서this == null검사를 수행하는 것이 좋습니다.위
toResponseEntity()함수에서와 같이 널 안정성 호출 연산자(?.)를 사용하여 널 검사를 수행할 수도 있습니다:kotlinResponseEntity
ResponseEntity는 상태 코드, 헤더, 본문을 포함하여 HTTP 응답을 나타냅니다. 이는 클라이언트에게 콘텐츠에 대한 더 많은 제어를 통해 사용자 지정 HTTP 응답을 다시 보낼 수 있게 하는 제네릭 래퍼입니다.
다음은 애플리케이션의 전체 코드입니다:
// DemoApplication.kt
package com.example.demo
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication
import org.springframework.boot.runApplication
@SpringBootApplication
class DemoApplication
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
runApplication<DemoApplication>(*args)
}// Message.kt
package com.example.demo
data class Message(val id: String?, val text: String)// MessageService.kt
package com.example.demo
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.query
import java.util.*
@Service
class MessageService(private val db: JdbcTemplate) {
fun findMessages(): List<Message> = db.query("select * from messages") { response, _ ->
Message(response.getString("id"), response.getString("text"))
}
fun findMessageById(id: String): Message? = db.query("select * from messages where id = ?", id) { response, _ ->
Message(response.getString("id"), response.getString("text"))
}.singleOrNull()
fun save(message: Message): Message {
val id = message.id ?: UUID.randomUUID().toString()
db.update(
"insert into messages values ( ?, ? )",
id, message.text
)
return message.copy(id = id)
}
}// MessageController.kt
package com.example.demo
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController
import java.net.URI
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/")
class MessageController(private val service: MessageService) {
@GetMapping
fun listMessages() = ResponseEntity.ok(service.findMessages())
@PostMapping
fun post(@RequestBody message: Message): ResponseEntity<Message> {
val savedMessage = service.save(message)
return ResponseEntity.created(URI("/${savedMessage.id}")).body(savedMessage)
}
@GetMapping("/{id}")
fun getMessage(@PathVariable id: String): ResponseEntity<Message> =
service.findMessageById(id).toResponseEntity()
private fun Message?.toResponseEntity(): ResponseEntity<Message> =
this?.let { ResponseEntity.ok(it) } ?: ResponseEntity.notFound().build()
}애플리케이션 실행
스프링 애플리케이션을 실행할 준비가 되었습니다:
애플리케이션을 다시 실행합니다.
requests.http파일을 열고 새 GET 요청을 추가합니다:http### Get the message by its id GET http://localhost:8080/idGET 요청을 실행하여 데이터베이스에서 모든 메시지를 검색합니다.
실행 도구 창에서 ID 중 하나를 복사하여 다음과 같이 요청에 추가합니다:
http### Get the message by its id GET http://localhost:8080/f910aa7e-11ee-4215-93ed-1aeeac822707위에 언급된 메시지 ID 대신 자신의 메시지 ID를 입력하세요.
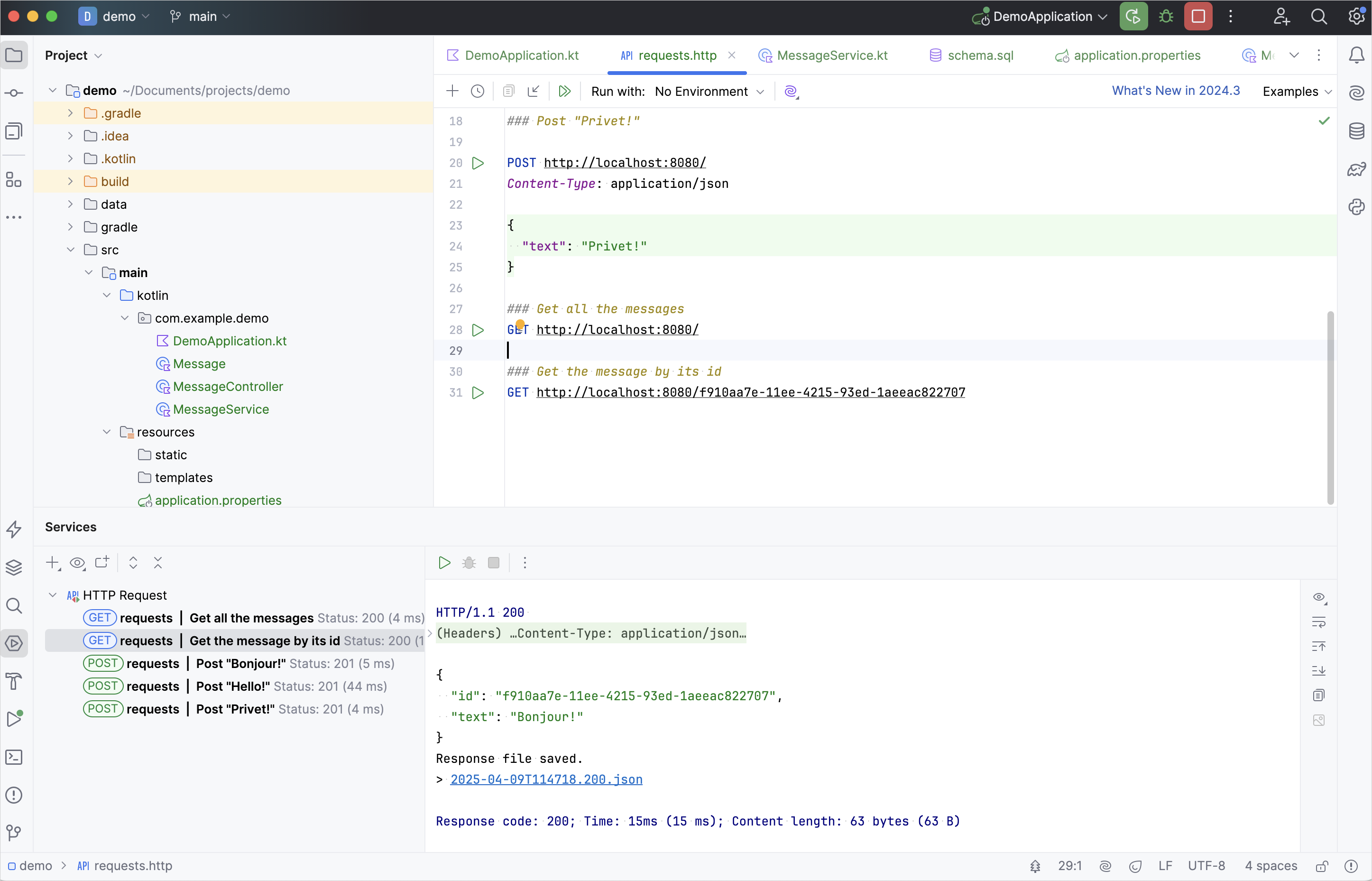
GET 요청을 실행하고 실행 도구 창에서 결과를 확인합니다:
다음 단계
마지막 단계에서는 Spring Data를 사용하여 데이터베이스에 연결하는 더 일반적인 방법을 보여줍니다.
