Kotlin Notebook에서 지원하는 출력 형식
Kotlin Notebook은 텍스트, HTML, 이미지 등 다양한 출력 유형을 지원합니다. 외부 라이브러리의 도움으로 출력 옵션을 확장하고 차트, 스프레드시트 등으로 데이터를 시각화할 수 있습니다.
각 출력은 Jupiter MIME 타입을 데이터에 매핑하는 JSON 객체입니다. 이 맵에서 Kotlin Notebook은 다른 타입 중에서 가장 높은 우선순위를 가진 지원되는 MIME 타입을 선택하여 다음과 같이 렌더링합니다.
- 텍스트는
text/plainMIME 타입을 사용합니다. - BufferedImage 클래스는 Base64 문자열에 매핑되는
image/pngMIME 타입을 사용합니다. - Image 클래스와 LaTeX 형식은 내부에
img태그가 있는text/htmlMIME 타입을 사용합니다. - Kotlin DataFrame 테이블 및 Kandy 플롯은 정적 HTML 또는 이미지로 지원되는 고유의 내부 MIME 타입을 사용합니다. 이를 통해 GitHub에 표시할 수 있습니다.
수동으로 매핑을 설정할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, 마크다운을 셀 출력으로 사용하려면 다음과 같이 합니다.
MimeTypedResult(
mapOf(
"text/plain" to "123",
"text/markdown" to "# HEADER",
//other mime:value pairs
)
)모든 종류의 출력을 표시하려면 DISPLAY() 함수를 사용합니다. 이 함수는 여러 출력의 조합도 가능하게 합니다.
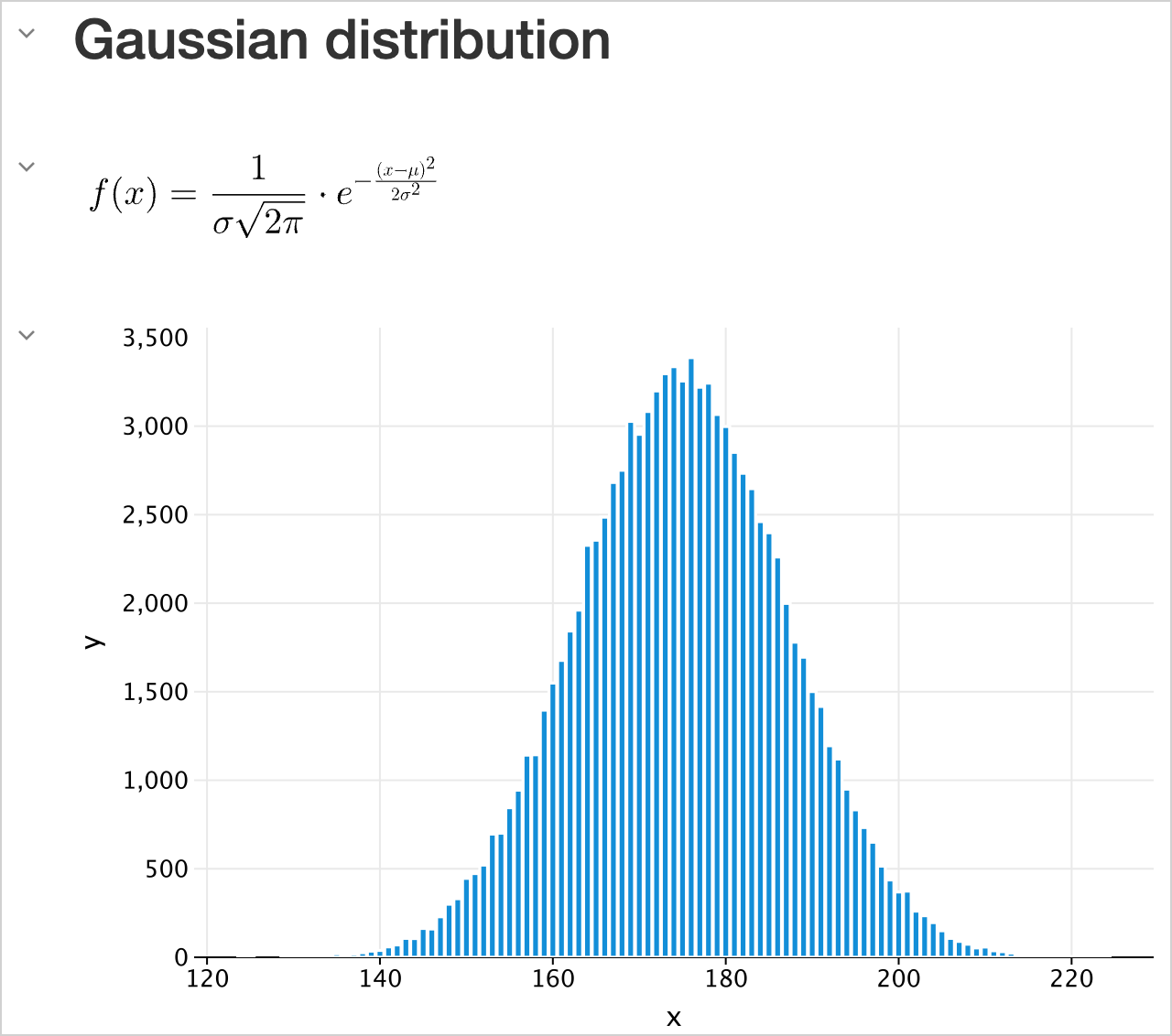
DISPLAY(HTML("<h2>Gaussian distribution</h2>"))
DISPLAY(LATEX("f(x) = \\frac{1}{\\sigma \\sqrt{2\\pi}} \\cdot e^{-\\frac{(x - \\mu)^2}{2\\sigma^2}}"))
val experimentX = experimentData.map { it.key }
val experimentY = experimentData.map { it.value }
DISPLAY(plot {
bars {
x(experimentX)
y(experimentY)
}
})
텍스트
일반 텍스트
가장 간단한 출력 유형은 일반 텍스트입니다. 이 유형은 출력문, 변수 값 또는 코드의 모든 텍스트 기반 출력에 사용됩니다.
val a1: Int = 1
val a2: Int = 2
var a3: Int? = a1 + a2
"My answer is $a3"
- 셀의 결과가 렌더링되어 어떠한 출력 유형으로도 표시될 수 없는 경우,
toString()함수를 사용하여 일반 텍스트로 출력됩니다. - 코드에 오류가 포함된 경우, Kotlin Notebook은 오류 메시지와 트레이스백을 표시하여 디버깅을 위한 통찰력을 제공합니다.
서식 있는 텍스트
서식 있는 텍스트를 사용하려면 마크다운 유형의 셀을 선택하세요. 이렇게 하면 목록, 테이블, 글꼴 스타일, 코드 블록 등을 사용하여 마크다운 및 HTML 마크업으로 콘텐츠 서식을 지정할 수 있습니다. HTML에는 CSS 스타일 및 JavaScript가 포함될 수 있습니다.
## Line magics
| Spell | Description | Example |
|------------------------------------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| <code>%use</code> | Injects code for supported libraries: artifact resolution, default imports, initialization code, type renderers. | <code>%use klaxon(5.5), lets-plot</code> |
| <code>%trackClasspath</code> | Logs any changes of current classpath. Useful for debugging artifact resolution failures. | <code>%trackClasspath [on |off]</code> |
| <code>%trackExecution</code> | Logs pieces of code that are going to be executed. Useful for debugging of libraries support. | <code>%trackExecution [all|generated|off]</code> |
| <code>%useLatestDescriptors</code> | Use latest versions of library descriptors available. By default, bundled descriptors are used. | <code>%useLatestDescriptors [on|off]</code> |
| <code>%output</code> | Output capturing settings. | <code>%output --max-cell-size=1000 --no-stdout --max-time=100 --max-buffer=400</code> |
| <code>%logLevel</code> | Set logging level. | <code>%logLevel [off|error|warn|info|debug]</code> |
<ul><li><a href="https://github.com/Kotlin/kotlin-jupyter/blob/master/docs/magics.md">Learn more detailes about line magics</a>.</li>
<li><a href="https://github.com/Kotlin/kotlin-jupyter/blob/master/docs/magics.md">See the full list of supported libraries</a>.</li></ul>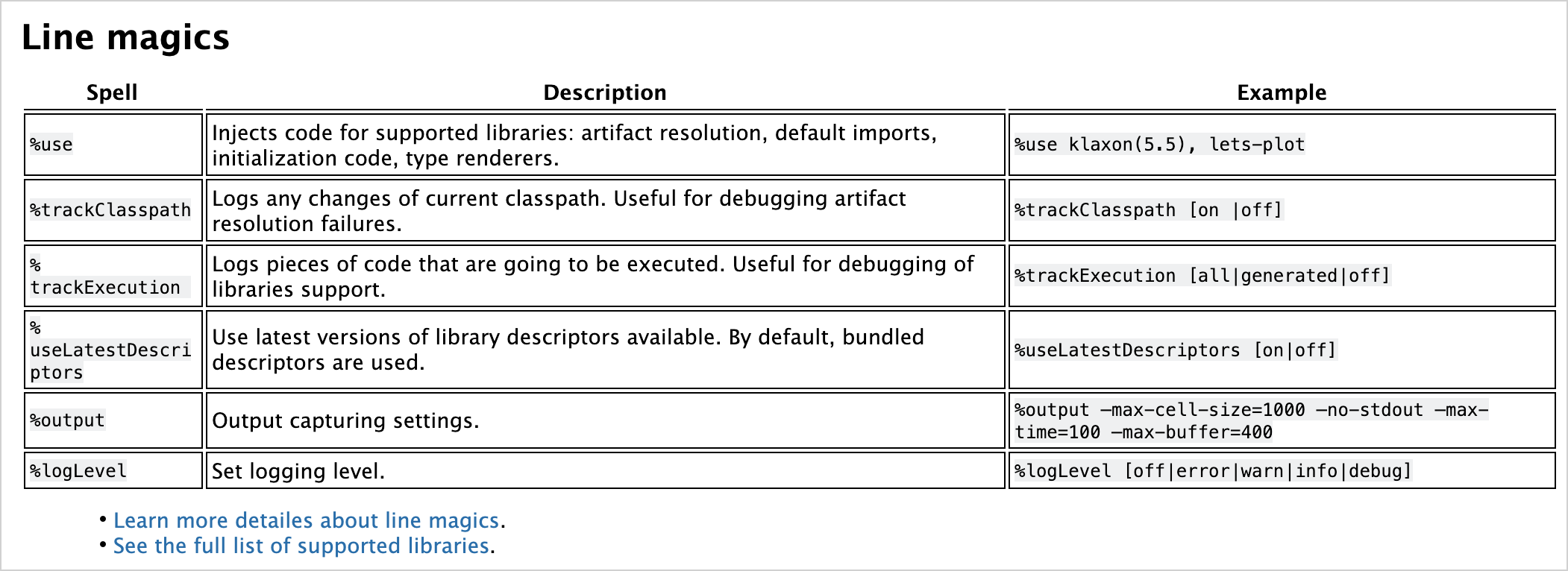
HTML
Kotlin Notebook은 HTML을 직접 렌더링하고, 스크립트를 실행하거나 웹사이트를 임베딩할 수도 있습니다.
HTML("""
<p>Counter: <span id="ctr">0</span> <button onclick="inc()">Increment</button></p>
<script>
function inc() {
let counter = document.getElementById("ctr")
counter.innerHTML = parseInt(counter.innerHTML) + 1;
}
</script>
""")
스크립트를 실행하려면 파일 상단에서 노트북을 신뢰할 수 있는 것으로 표시하세요.
이미지
Kotlin Notebook을 사용하면 파일, 생성된 그래프 또는 기타 시각 미디어에서 이미지를 표시할 수 있습니다. 정적 이미지는 .png, jpeg, .svg와 같은 형식으로 표시될 수 있습니다.
버퍼링된 이미지
기본적으로 BufferedImage 클래스를 사용하여 이미지를 표시할 수 있습니다.
import java.awt.Color
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage
val width = 300
val height = width
val image = BufferedImage(width, height, BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_ARGB)
val graphics = image.createGraphics()
graphics.background = Color.BLACK
graphics.clearRect(0, 0, width, height)
graphics.setRenderingHint(
java.awt.RenderingHints.KEY_ANTIALIASING,
java.awt.RenderingHints.VALUE_ANTIALIAS_ON
)
graphics.color = Color.WHITE
graphics.fillRect(width / 10, height * 8 / 10, width * 10 / 20, height / 10)
graphics.dispose()
로드된 이미지
lib-ext 라이브러리의 도움으로 표준 Jupyter 기능을 확장하고 네트워크에서 로드된 이미지를 표시할 수 있습니다.
%use lib-ext(0.11.0-398)Image("https://kotlinlang.org/docs/images/kotlin-logo.png", embed = false).withWidth(300)
임베디드 이미지
네트워크에서 로드된 이미지의 단점은 링크가 끊어지거나 네트워크 연결이 끊어지는 경우 이미지가 사라진다는 것입니다. 이를 해결하려면 임베디드 이미지를 사용하세요. 예를 들면 다음과 같습니다.
val kotlinMascot = Image("https://blog.jetbrains.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/DSGN-16174-Blog-post-banner-and-promo-materials-for-post-about-Kotlin-mascot_3.png", embed = true).withWidth(400)
kotlinMascot
수학 공식 및 방정식
학계에서 널리 사용되는 조판 시스템인 LaTeX 형식을 사용하여 수학 공식 및 방정식을 렌더링할 수 있습니다.
Jupyter 커널의 기능을 확장하는
lib-ext라이브러리를 노트북에 추가합니다.none%use lib-ext(0.11.0-398)새 셀에서 공식을 실행합니다.
noneLATEX("c^2 = a^2 + b^2 - 2 a b \\cos\\alpha")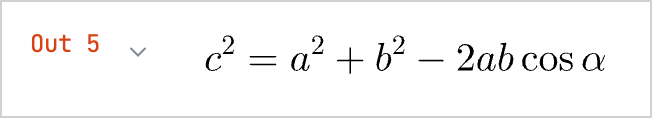
데이터 프레임
Kotlin Notebook을 사용하면 데이터 프레임을 통해 구조화된 데이터를 시각화할 수 있습니다.
Kotlin DataFrame 라이브러리를 노트북에 추가합니다.
none%use dataframe데이터 프레임을 생성하고 새 셀에서 실행합니다.
kotlinval months = listOf( "January", "February", "March", "April", "May", "June", "July", "August", "September", "October", "November", "December" ) // Sales data for different products and months: val salesLaptop = listOf(120, 130, 150, 180, 200, 220, 240, 230, 210, 190, 160, 140) val salesSmartphone = listOf(90, 100, 110, 130, 150, 170, 190, 180, 160, 140, 120, 100) val salesTablet = listOf(60, 70, 80, 90, 100, 110, 120, 110, 100, 90, 80, 70) // A data frame with columns for Month, Sales, and Product val dfSales = dataFrameOf( "Month" to months + months + months, "Sales" to salesLaptop + salesSmartphone + salesTablet, "Product" to List(12) { "Laptop" } + List(12) { "Smartphone" } + List(12) { "Tablet" }, )데이터 프레임은
dataFrameOf()함수를 사용하며 12개월 동안 판매된 제품(랩톱, 스마트폰 및 태블릿)의 수를 포함합니다.프레임의 데이터를 탐색하여, 예를 들어 가장 높은 판매량을 기록한 제품과 월을 찾습니다.
nonedfSales.maxBy("Sales")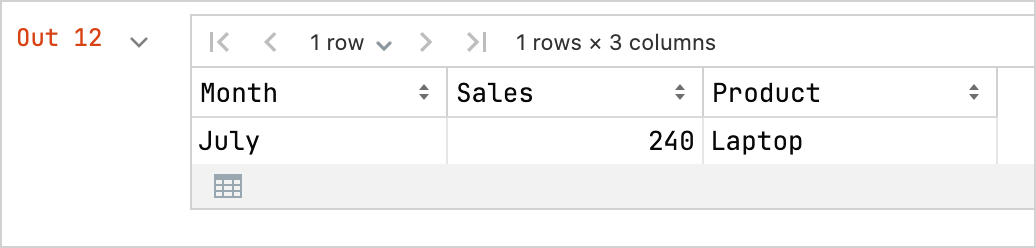
데이터 프레임을 CSV 파일로 내보낼 수도 있습니다.
kotlin// Export your data to CSV format dfSales.writeCSV("sales-stats.csv")
차트
Kotlin Notebook에서 직접 다양한 차트를 생성하여 데이터를 시각화할 수 있습니다.
Kandy 플로팅 라이브러리를 노트북에 추가합니다.
none%use kandy동일한 데이터 프레임을 사용하고 새 셀에서
plot()함수를 실행합니다.kotlinval salesPlot = dfSales.groupBy { Product }.plot { bars { // Access the data frame's columns used for the X and Y axes x(Month) y(Sales) // Access the data frame's column used for categories and sets colors for these categories fillColor(Product) { scale = categorical( "Laptop" to Color.PURPLE, "Smartphone" to Color.ORANGE, "Tablet" to Color.GREEN ) legend.name = "Product types" } } // Customize the chart's appearance layout.size = 1000 to 450 layout.title = "Yearly Gadget Sales Results" } salesPlot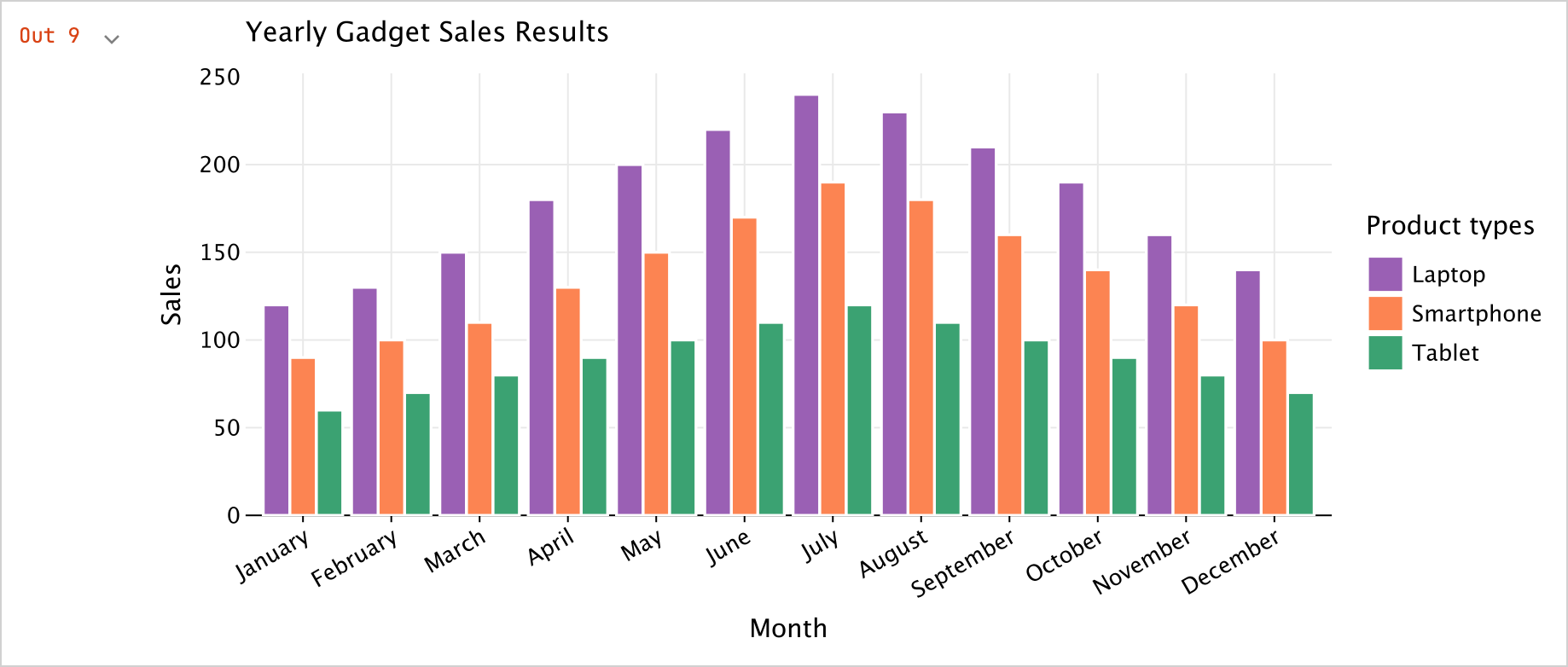
플롯을
.png,jpeg,.html또는.svg형식으로 내보낼 수도 있습니다.kotlin// Specify the output format for the plot file: salesPlot.save("sales-chart.svg")
