Kotlin용 Lets-Plot으로 데이터 시각화
Kotlin용 Lets-Plot (LPK)은 R의 ggplot2 라이브러리를 Kotlin으로 포팅한 다중 플랫폼 플로팅 라이브러리입니다. LPK는 기능이 풍부한 ggplot2 API를 Kotlin 생태계로 가져와 정교한 데이터 시각화 기능이 필요한 과학자와 통계학자에게 적합합니다.
LPK는 Kotlin 노트북, Kotlin/JS, JVM의 Swing, JavaFX, Compose Multiplatform을 포함한 다양한 플랫폼을 대상으로 합니다. 또한 LPK는 IntelliJ, DataGrip, DataSpell, PyCharm과 원활하게 통합됩니다.
이 튜토리얼은 IntelliJ IDEA의 Kotlin Notebook에서 LPK 및 Kotlin DataFrame 라이브러리를 사용하여 다양한 플롯 유형을 생성하는 방법을 보여줍니다.
시작하기 전에
Kotlin Notebook은 Kotlin Notebook 플러그인에 의존하며, 이 플러그인은 기본적으로 IntelliJ IDEA에 번들로 제공되고 활성화되어 있습니다.
Kotlin Notebook 기능이 작동하지 않으면 플러그인이 활성화되어 있는지 확인하십시오. 자세한 내용은 환경 설정을 참조하십시오.
Lets-Plot을 사용하기 위해 새로운 Kotlin Notebook을 생성합니다.
File | New | Kotlin Notebook을 선택합니다.
노트북에서 다음 명령을 실행하여 LPK 및 Kotlin DataFrame 라이브러리를 임포트합니다.
kotlin%use lets-plot %use dataframe
데이터 준비
베를린, 마드리드, 카라카스 세 도시의 월 평균 기온 시뮬레이션 수치를 저장하는 DataFrame을 생성해 보겠습니다.
Kotlin DataFrame 라이브러리의 dataFrameOf() 함수를 사용하여 DataFrame을 생성합니다. 다음 코드 스니펫을 Kotlin Notebook에 붙여넣고 실행하십시오.
// months 변수는 1년 12개월 목록을 저장합니다.
val months = listOf(
"January", "February",
"March", "April", "May",
"June", "July", "August",
"September", "October", "November",
"December"
)
// tempBerlin, tempMadrid, tempCaracas 변수는 각 달의 기온 값을 목록으로 저장합니다.
val tempBerlin =
listOf(-0.5, 0.0, 4.8, 9.0, 14.3, 17.5, 19.2, 18.9, 14.5, 9.7, 4.7, 1.0)
val tempMadrid =
listOf(6.3, 7.9, 11.2, 12.9, 16.7, 21.1, 24.7, 24.2, 20.3, 15.4, 9.9, 6.6)
val tempCaracas =
listOf(27.5, 28.9, 29.6, 30.9, 31.7, 35.1, 33.8, 32.2, 31.3, 29.4, 28.9, 27.6)
// df 변수는 월별 기록, 기온, 도시에 대한 세 개의 열로 구성된 DataFrame을 저장합니다.
val df = dataFrameOf(
"Month" to months + months + months,
"Temperature" to tempBerlin + tempMadrid + tempCaracas,
"City" to List(12) { "Berlin" } + List(12) { "Madrid" } + List(12) { "Caracas" }
)
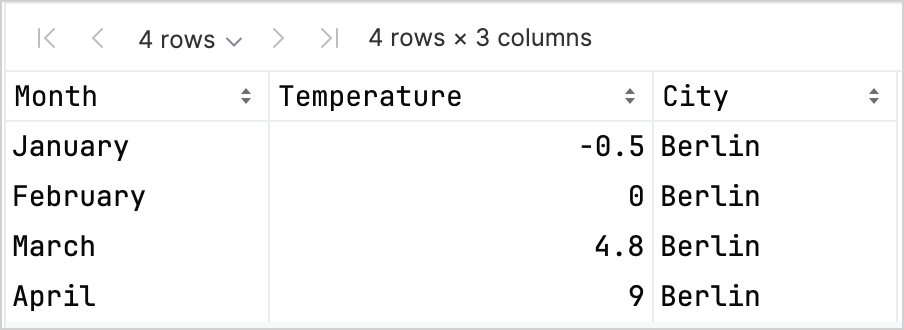
df.head(4)DataFrame에 Month, Temperature, City 세 개의 열이 있음을 알 수 있습니다. DataFrame의 처음 네 행은 1월부터 4월까지 베를린의 기온 기록을 포함합니다.
LPK 라이브러리를 사용하여 플롯을 생성하려면 데이터(df)를 키-값 쌍으로 데이터를 저장하는 Map 타입으로 변환해야 합니다. .toMap() 함수를 사용하여 DataFrame을 Map으로 쉽게 변환할 수 있습니다.
val data = df.toMap()산점도 생성
Kotlin Notebook에서 LPK 라이브러리를 사용하여 산점도를 생성해 보겠습니다.
데이터가 Map 형식으로 준비되면 LPK 라이브러리의 geomPoint() 함수를 사용하여 산점도를 생성합니다. X축과 Y축의 값을 지정하고 범주 및 해당 색상을 정의할 수 있습니다. 또한 필요에 따라 플롯 크기 및 점 모양을 사용자 지정할 수 있습니다.
// X 및 Y 축, 범주와 해당 색상, 플롯 크기 및 플롯 유형을 지정합니다.
val scatterPlot =
letsPlot(data) { x = "Month"; y = "Temperature"; color = "City" } + ggsize(600, 500) + geomPoint(shape = 15)
scatterPlot결과는 다음과 같습니다.
상자 그림 생성
데이터를 상자 그림으로 시각화해 보겠습니다. LPK 라이브러리의 geomBoxplot() 함수를 사용하여 플롯을 생성하고 scaleFillManual() 함수로 색상을 사용자 지정합니다.
// X 및 Y 축, 범주, 플롯 크기 및 플롯 유형을 지정합니다.
val boxPlot = ggplot(data) { x = "City"; y = "Temperature" } + ggsize(700, 500) + geomBoxplot { fill = "City" } +
// 색상 사용자 지정
scaleFillManual(values = listOf("light_yellow", "light_magenta", "light_green"))
boxPlot결과는 다음과 같습니다.
2D 밀도 플롯 생성
이제 일부 무작위 데이터의 분포와 밀도를 시각화하기 위해 2D 밀도 플롯을 생성해 보겠습니다.
2D 밀도 플롯을 위한 데이터 준비
데이터를 처리하고 플롯을 생성하기 위한 종속성을 임포트합니다.
kotlin%use lets-plot @file:DependsOn("org.apache.commons:commons-math3:3.6.1") import org.apache.commons.math3.distribution.MultivariateNormalDistributionKotlin Notebook에 종속성을 임포트하는 방법에 대한 자세한 내용은 Kotlin Notebook 문서를 참조하십시오.
2D 데이터 포인트 세트를 생성하려면 다음 코드 스니펫을 Kotlin Notebook에 붙여넣고 실행하십시오.
kotlin// 세 분포에 대한 공분산 행렬을 정의합니다. val cov0: Array<DoubleArray> = arrayOf( doubleArrayOf(1.0, -.8), doubleArrayOf(-.8, 1.0) ) val cov1: Array<DoubleArray> = arrayOf( doubleArrayOf(1.0, .8), doubleArrayOf(.8, 1.0) ) val cov2: Array<DoubleArray> = arrayOf( doubleArrayOf(10.0, .1), doubleArrayOf(.1, .1) ) // 샘플 수를 정의합니다. val n = 400 // 세 분포에 대한 평균을 정의합니다. val means0: DoubleArray = doubleArrayOf(-2.0, 0.0) val means1: DoubleArray = doubleArrayOf(2.0, 0.0) val means2: DoubleArray = doubleArrayOf(0.0, 1.0) // 세 다변량 정규 분포에서 무작위 샘플을 생성합니다. val xy0 = MultivariateNormalDistribution(means0, cov0).sample(n) val xy1 = MultivariateNormalDistribution(means1, cov1).sample(n) val xy2 = MultivariateNormalDistribution(means2, cov2).sample(n)위 코드에서
xy0,xy1,xy2변수는 2D (x, y) 데이터 포인트를 포함하는 배열을 저장합니다.데이터를
Map타입으로 변환합니다.kotlinval data = mapOf( "x" to (xy0.map { it[0] } + xy1.map { it[0] } + xy2.map { it[0] }).toList(), "y" to (xy0.map { it[1] } + xy1.map { it[1] } + xy2.map { it[1] }).toList() )
2D 밀도 플롯 생성
이전 단계의 Map을 사용하여 데이터 포인트와 이상치를 더 잘 시각화하기 위해 배경에 산점도(geomPoint)와 함께 2D 밀도 플롯(geomDensity2D)을 생성합니다. scaleColorGradient() 함수를 사용하여 색상 스케일을 사용자 지정할 수 있습니다.
val densityPlot = letsPlot(data) { x = "x"; y = "y" } + ggsize(600, 300) + geomPoint(
color = "black",
alpha = .1
) + geomDensity2D { color = "..level.." } +
scaleColorGradient(low = "dark_green", high = "yellow", guide = guideColorbar(barHeight = 10, barWidth = 300)) +
theme().legendPositionBottom()
densityPlot결과는 다음과 같습니다.
다음 단계
- Kotlin용 Lets-Plot 문서에서 더 많은 플롯 예제를 살펴보십시오.
- Kotlin용 Lets-Plot의 API 레퍼런스를 확인하십시오.
- Kotlin DataFrame 및 Kandy 라이브러리 문서에서 Kotlin을 사용하여 데이터를 변환하고 시각화하는 방법을 알아보십시오.
- Kotlin Notebook의 사용법 및 주요 기능에 대한 추가 정보를 찾아보십시오.
