為 Spring Boot 專案新增資料庫支援
這是「Spring Boot 與 Kotlin 入門」教學的第三部分。在繼續之前,請確保您已完成先前的步驟:
使用 Kotlin 建立 Spring Boot 專案
將資料類別新增至 Spring Boot 專案
為 Spring Boot 專案新增資料庫支援
使用 Spring Data CrudRepository 進行資料庫存取
在本教學部分中,您將使用 Java 資料庫連接 (JDBC) 為您的專案新增和配置資料庫。 在 JVM 應用程式中,您使用 JDBC 與資料庫互動。 為了方便起見,Spring Framework 提供了 JdbcTemplate 類別,它簡化了 JDBC 的使用並有助於避免常見錯誤。
新增資料庫支援
在基於 Spring Framework 的應用程式中,常見的做法是在所謂的 服務層 中實作資料庫存取邏輯 – 這是業務邏輯所在之處。 在 Spring 中,您應該使用 @Service 註解標記類別,以表示該類別屬於應用程式的服務層。 在此應用程式中,您將為此目的建立 MessageService 類別。
在同一個套件中,建立 MessageService.kt 檔案和 MessageService 類別,如下所示:
// MessageService.kt
package com.example.demo
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate
import java.util.*
@Service
class MessageService(private val db: JdbcTemplate) {
fun findMessages(): List<Message> = db.query("select * from messages") { response, _ ->
Message(response.getString("id"), response.getString("text"))
}
fun save(message: Message): Message {
db.update(
"insert into messages values ( ?, ? )",
message.id, message.text
)
return message
}
}建構子引數與依賴注入 – (private val db: JdbcTemplate)
Kotlin 中的類別有一個主建構子。它也可以有一個或多個 次級建構子。 主建構子 是類別標頭的一部分,位於類別名稱和可選的型別參數之後。在我們的例子中,建構子是 (val db: JdbcTemplate)。
val db: JdbcTemplate 是建構子的引數:
尾隨 Lambda 和 SAM 轉換
findMessages() 函數呼叫 JdbcTemplate 類別的 query() 函數。query() 函數接受兩個引數:一個作為 String 實例的 SQL 查詢,以及一個將每一列映射為一個物件的回呼:
RowMapper 介面只宣告了一個方法,因此可以透過省略介面名稱的 Lambda 表達式來實作它。Kotlin 編譯器知道 Lambda 表達式需要轉換成的介面,因為您將它作為函數呼叫的參數。這在 Kotlin 中被稱為 SAM 轉換:
在 SAM 轉換之後,查詢函數最終有兩個引數:第一個位置是一個 String,最後一個位置是一個 Lambda 表達式。根據 Kotlin 慣例,如果函數的最後一個參數是一個函數,那麼作為相應引數傳遞的 Lambda 表達式可以放在圓括號之外。這種語法也被稱為 尾隨 Lambda:
未使用 Lambda 引數的底線
對於具有多個參數的 Lambda,您可以使用底線 _ 字元來替換您未使用的參數名稱。
因此,查詢函數呼叫的最終語法看起來像這樣:
更新 MessageController 類別
更新 MessageController.kt 以使用新的 MessageService 類別:
// MessageController.kt
package com.example.demo
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController
import java.net.URI
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/")
class MessageController(private val service: MessageService) {
@GetMapping
fun listMessages() = service.findMessages()
@PostMapping
fun post(@RequestBody message: Message): ResponseEntity<Message> {
val savedMessage = service.save(message)
return ResponseEntity.created(URI("/${savedMessage.id}")).body(savedMessage)
}
}@PostMapping 註解
負責處理 HTTP POST 請求的方法需要使用 @PostMapping 註解進行標記。為了能夠將作為 HTTP Body 內容傳送的 JSON 轉換為物件,您需要對方法引數使用 @RequestBody 註解。由於應用程式的 classpath 中有 Jackson 函式庫,轉換會自動發生。
ResponseEntity
ResponseEntity 代表整個 HTTP 回應:狀態碼、標頭和主體。
使用 created() 方法可以配置回應狀態碼 (201) 並設定 location 標頭,指示所建立資源的上下文路徑。
更新 MessageService 類別
Message 類別的 id 被宣告為可空字串:
data class Message(val id: String?, val text: String)然而,在資料庫中將 null 儲存為 id 值是不正確的:您需要優雅地處理這種情況。
更新您的 MessageService.kt 檔案程式碼,以便在將訊息儲存到資料庫時,如果 id 為 null,則生成一個新值:
// MessageService.kt
package com.example.demo
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.query
import java.util.UUID
@Service
class MessageService(private val db: JdbcTemplate) {
fun findMessages(): List<Message> = db.query("select * from messages") { response, _ ->
Message(response.getString("id"), response.getString("text"))
}
fun save(message: Message): Message {
val id = message.id ?: UUID.randomUUID().toString() // 如果 id 為 null,則產生新 id
db.update(
"insert into messages values ( ?, ? )",
id, message.text
)
return message.copy(id = id) // 傳回帶有新 id 的訊息副本
}
}Elvis 運算子 – ?:
程式碼 message.id ?: UUID.randomUUID().toString() 使用了 Elvis 運算子(非空即取捷徑)?:。如果 ?: 左側的表達式不為 null,Elvis 運算子會傳回它;否則,它會傳回右側的表達式。請注意,只有在左側為 null 時,右側的表達式才會被評估。
應用程式程式碼已準備好與資料庫協作。現在需要配置資料來源。
配置資料庫
在應用程式中配置資料庫:
在
src/main/resources目錄中建立schema.sql檔案。它將儲存資料庫物件定義:
使用以下程式碼更新
src/main/resources/schema.sql檔案:sql-- schema.sql CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS messages ( id VARCHAR(60) PRIMARY KEY, text VARCHAR NOT NULL );它建立了
messages表,其中包含兩個欄位:id和text。表結構與Message類別的結構相符。開啟位於
src/main/resources資料夾中的application.properties檔案,並新增以下應用程式屬性:nonespring.application.name=demo spring.datasource.driver-class-name=org.h2.Driver spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:file:./data/testdb spring.datasource.username=name spring.datasource.password=password spring.sql.init.schema-locations=classpath:schema.sql spring.sql.init.mode=always這些設定為 Spring Boot 應用程式啟用資料庫。
請參閱 Spring 文件 中的常用應用程式屬性完整清單。
透過 HTTP 請求將訊息新增至資料庫
您應該使用 HTTP 用戶端來處理先前建立的端點。在 IntelliJ IDEA 中,請使用內嵌的 HTTP 用戶端:
執行應用程式。一旦應用程式啟動並運行,您就可以執行 POST 請求將訊息儲存在資料庫中。
在專案根資料夾中建立
requests.http檔案並新增以下 HTTP 請求:http### Post "Hello!" POST http://localhost:8080/ Content-Type: application/json { "text": "Hello!" } ### Post "Bonjour!" POST http://localhost:8080/ Content-Type: application/json { "text": "Bonjour!" } ### Post "Privet!" POST http://localhost:8080/ Content-Type: application/json { "text": "Privet!" } ### 取得所有訊息 GET http://localhost:8080/執行所有 POST 請求。使用請求宣告旁裝訂線中的綠色 Run 圖示。這些請求會將文字訊息寫入資料庫:
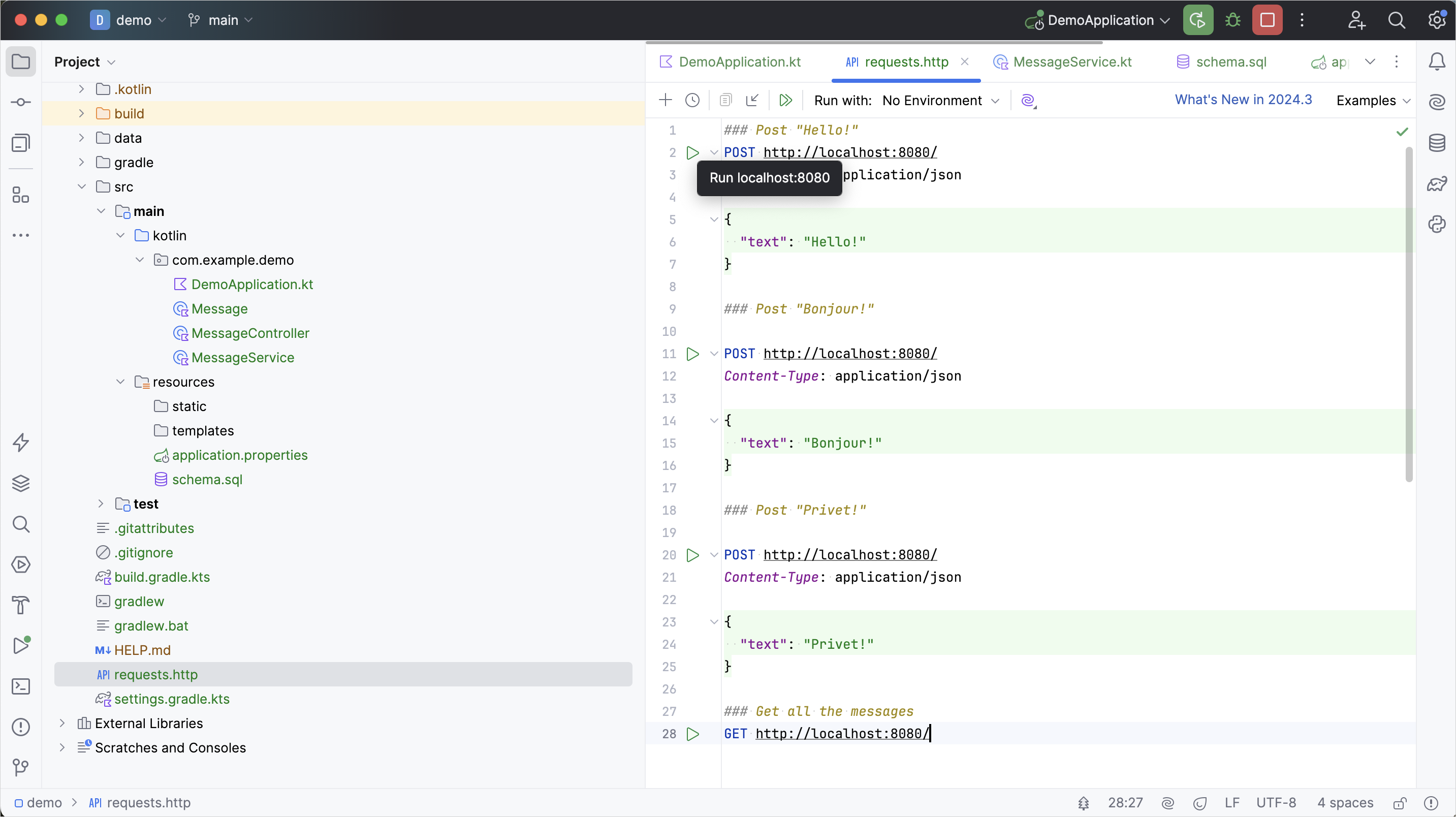
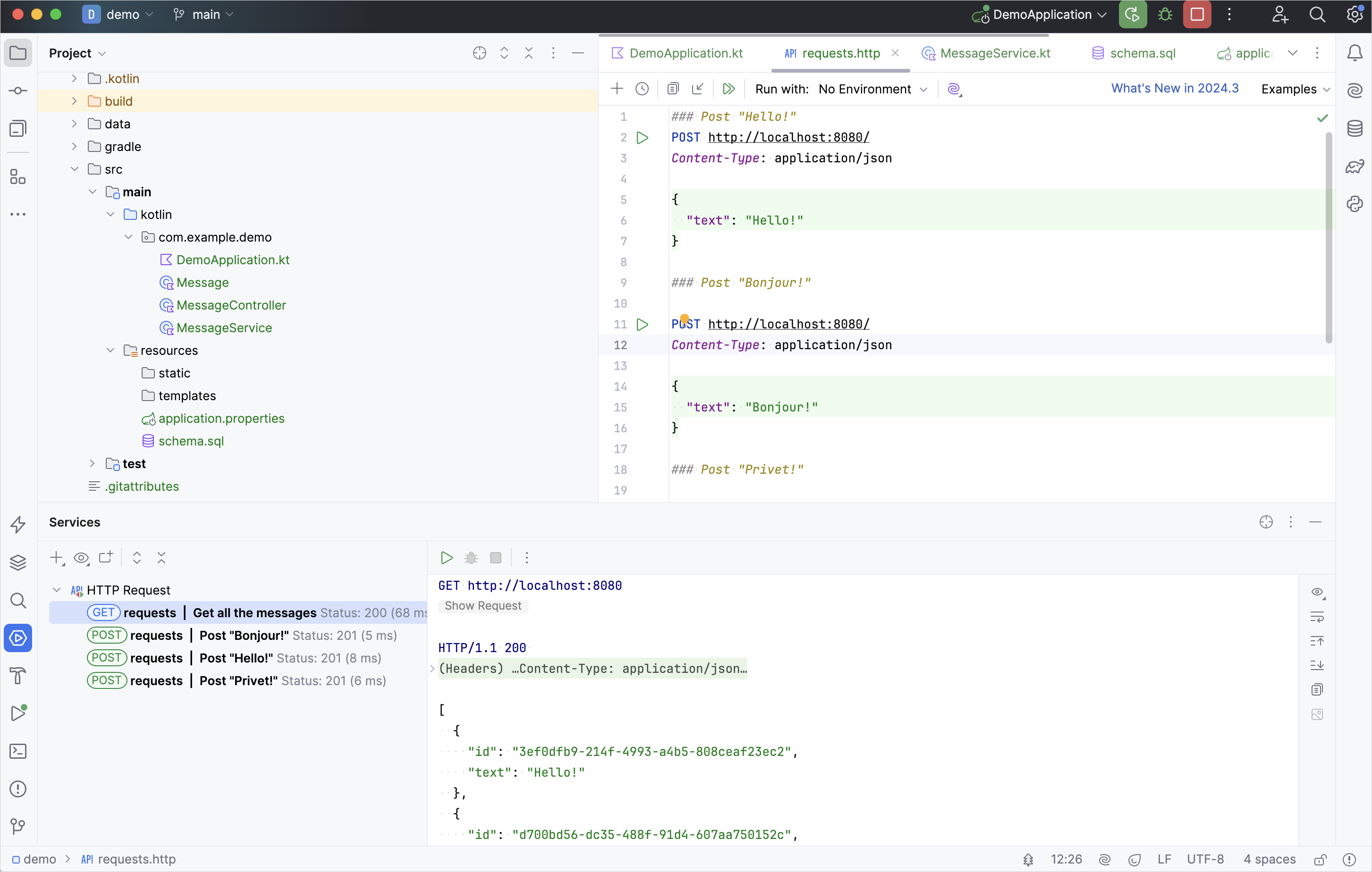
執行 GET 請求並在 Run 工具視窗中查看結果:
執行請求的替代方法
您也可以使用任何其他 HTTP 用戶端或 cURL 命令列工具。例如,在終端機中執行以下命令以取得相同的結果:
curl -X POST --location "http://localhost:8080" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d "{ \"text\": \"Hello!\" }"
curl -X POST --location "http://localhost:8080" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d "{ \"text\": \"Bonjour!\" }"
curl -X POST --location "http://localhost:8080" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d "{ \"text\": \"Privet!\" }"
curl -X GET --location "http://localhost:8080"依 ID 擷取訊息
擴展應用程式的功能,以便依 ID 擷取個別訊息。
在
MessageService類別中,新增findMessageById(id: String)函數,以便依 ID 擷取個別訊息:kotlin// MessageService.kt package com.example.demo import org.springframework.stereotype.Service import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate import org.springframework.jdbc.core.query import java.util.* @Service class MessageService(private val db: JdbcTemplate) { fun findMessages(): List<Message> = db.query("select * from messages") { response, _ -> Message(response.getString("id"), response.getString("text")) } fun findMessageById(id: String): Message? = db.query("select * from messages where id = ?", id) { response, _ -> Message(response.getString("id"), response.getString("text")) }.singleOrNull() fun save(message: Message): Message { val id = message.id ?: UUID.randomUUID().toString() // Generate new id if it is null db.update( "insert into messages values ( ?, ? )", id, message.text ) return message.copy(id = id) // Return a copy of the message with the new id } }參數列表中 vararg 引數的位置
query()函數接受三個引數:- 執行時需要參數的 SQL 查詢字串
id,它是 String 型別的參數RowMapper實例,它由 Lambda 表達式實作
query()函數的第二個參數被宣告為 可變引數 (vararg)。在 Kotlin 中,可變引數參數的位置不一定需要在參數列表的最後。singleOrNull() 函數
singleOrNull()函數返回單個元素,如果陣列為空或包含多個相同值的元素,則返回null。用於透過 ID 獲取訊息的
.query()函數是 Spring Framework 提供的 Kotlin 擴充函數。它需要額外的匯入import org.springframework.jdbc.core.query,如上方程式碼所示。將帶有
id參數的新getMessage(...)函數新增至MessageController類別:kotlin// MessageController.kt package com.example.demo import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController import java.net.URI @RestController @RequestMapping("/") class MessageController(private val service: MessageService) { @GetMapping fun listMessages() = ResponseEntity.ok(service.findMessages()) @PostMapping fun post(@RequestBody message: Message): ResponseEntity<Message> { val savedMessage = service.save(message) return ResponseEntity.created(URI("/${savedMessage.id}")).body(savedMessage) } @GetMapping("/{id}") fun getMessage(@PathVariable id: String): ResponseEntity<Message> = service.findMessageById(id).toResponseEntity() private fun Message?.toResponseEntity(): ResponseEntity<Message> = // 如果訊息為 null(未找到),則將回應碼設為 404 this?.let { ResponseEntity.ok(it) } ?: ResponseEntity.notFound().build() }從上下文路徑擷取值
訊息
id由 Spring Framework 從上下文路徑中擷取,因為您使用@GetMapping("/{id}")註解了新函數。透過使用@PathVariable註解函數引數,您告訴框架將擷取到的值用作函數引數。新函數呼叫MessageService以透過其 ID 擷取個別訊息。具有可空接收者的擴充函數
擴充可以定義為可空接收者類型。如果接收者為
null,則this也為null。所以當定義一個具有可空接收者類型的擴充時,建議在函數主體內執行this == null檢查。您還可以使用空安全呼叫運算子 (
?.) 來執行空檢查,如上方toResponseEntity()函數所示:kotlinResponseEntity
ResponseEntity代表 HTTP 回應,包括狀態碼、標頭和主體。它是一個泛型封裝器,允許您將自訂的 HTTP 回應傳送回用戶端,並對內容有更多的控制。
這是應用程式的完整程式碼:
// DemoApplication.kt
package com.example.demo
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication
import org.springframework.boot.runApplication
@SpringBootApplication
class DemoApplication
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
runApplication<DemoApplication>(*args)
}// Message.kt
package com.example.demo
data class Message(val id: String?, val text: String)// MessageService.kt
package com.example.demo
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.query
import java.util.*
@Service
class MessageService(private val db: JdbcTemplate) {
fun findMessages(): List<Message> = db.query("select * from messages") { response, _ ->
Message(response.getString("id"), response.getString("text"))
}
fun findMessageById(id: String): Message? = db.query("select * from messages where id = ?", id) { response, _ ->
Message(response.getString("id"), response.getString("text"))
}.singleOrNull()
fun save(message: Message): Message {
val id = message.id ?: UUID.randomUUID().toString()
db.update(
"insert into messages values ( ?, ? )",
id, message.text
)
return message.copy(id = id)
}
}// MessageController.kt
package com.example.demo
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController
import java.net.URI
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/")
class MessageController(private val service: MessageService) {
@GetMapping
fun listMessages() = ResponseEntity.ok(service.findMessages())
@PostMapping
fun post(@RequestBody message: Message): ResponseEntity<Message> {
val savedMessage = service.save(message)
return ResponseEntity.created(URI("/${savedMessage.id}")).body(savedMessage)
}
@GetMapping("/{id}")
fun getMessage(@PathVariable id: String): ResponseEntity<Message> =
service.findMessageById(id).toResponseEntity()
private fun Message?.toResponseEntity(): ResponseEntity<Message> =
this?.let { ResponseEntity.ok(it) } ?: ResponseEntity.notFound().build()
}執行應用程式
Spring 應用程式已準備好執行:
再次執行應用程式。
開啟
requests.http檔案並新增新的 GET 請求:http### 依 ID 取得訊息 GET http://localhost:8080/id執行 GET 請求以從資料庫中擷取所有訊息。
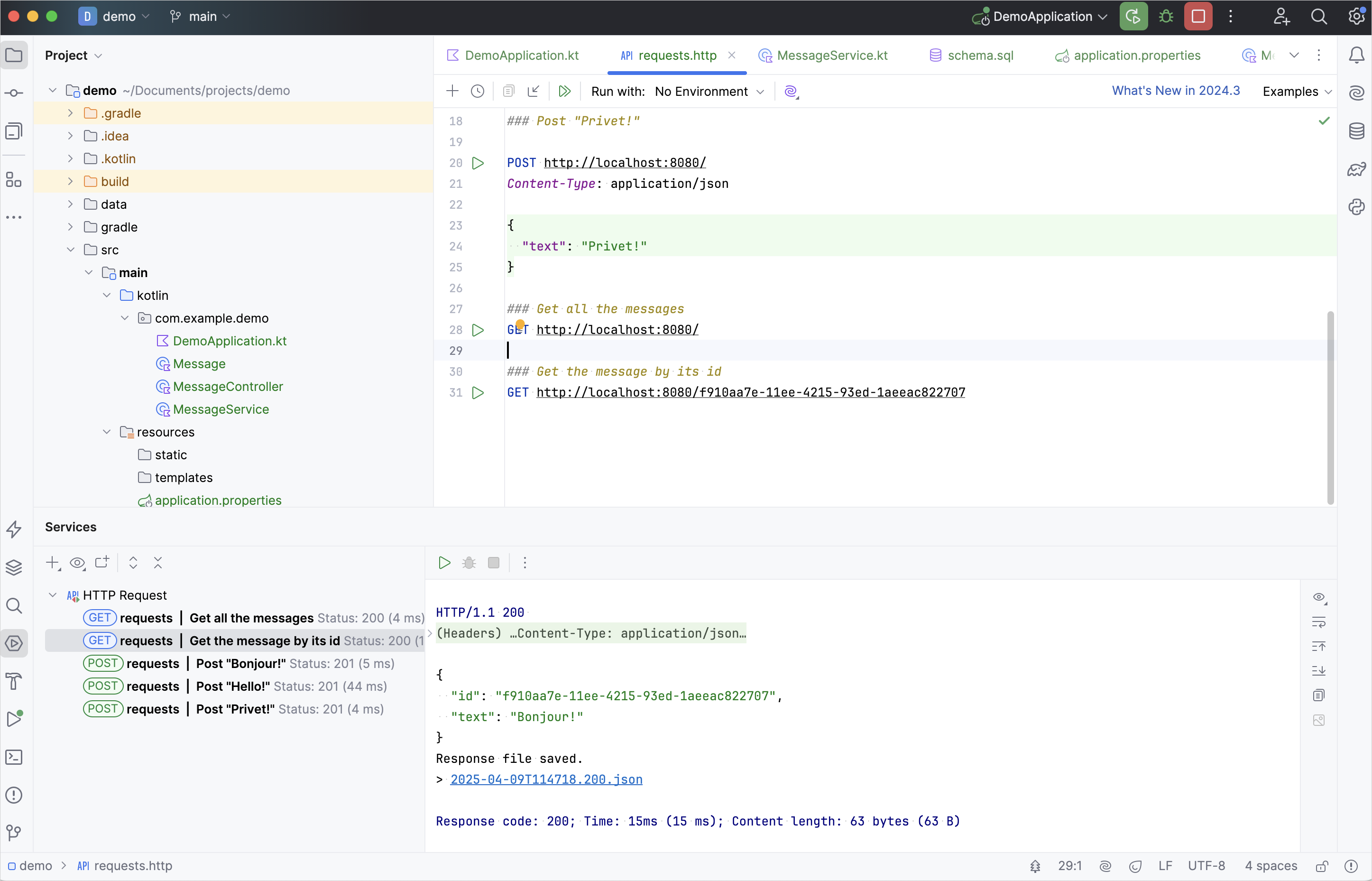
在 Run 工具視窗中,複製其中一個 ID 並將其新增至請求中,如下所示:
http### 依 ID 取得訊息 GET http://localhost:8080/f910aa7e-11ee-4215-93ed-1aeeac822707請將您的訊息 ID 替換為上面提及的 ID。
執行 GET 請求並在 Run 工具視窗中查看結果:
下一步
最後一步將向您展示如何使用 Spring Data 進行更受歡迎的資料庫連接。
