开始使用 Kotlin 自定义脚本 – 教程
Kotlin 自定义脚本是实验性的。它可能随时被废弃或更改。 仅将其用于求值目的。我们感谢您在 YouTrack 上提供的反馈。
_Kotlin 脚本_是一种技术,可让您将 Kotlin 代码作为脚本执行,无需预先编译或打包为可执行文件。
关于 Kotlin 脚本及其示例的概述,请查看 Rodrigo Oliveira 在 KotlinConf'19 上的演讲 Implementing the Gradle Kotlin DSL。
在本教程中,您将创建一个 Kotlin 脚本项目,该项目使用 Maven 依赖项执行任意 Kotlin 代码。 您将能够像这样执行脚本:
@file:Repository("https://maven.pkg.jetbrains.space/public/p/kotlinx-html/maven")
@file:DependsOn("org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-html-jvm:0.7.3")
import kotlinx.html.*
import kotlinx.html.stream.*
import kotlinx.html.attributes.*
val addressee = "World"
print(
createHTML().html {
body {
h1 { +"Hello, $addressee!" }
}
}
)在执行过程中,指定的 Maven 依赖项(本示例中的 kotlinx-html-jvm)将从指定的 Maven 版本库或本地缓存中解析,并用于脚本的其余部分。
项目结构
一个最小的 Kotlin 自定义脚本项目包含两部分:
- 脚本定义 – 一组参数和配置,定义了如何识别、处理、编译和执行此脚本类型。
- 脚本宿主 – 一个应用程序或组件,处理脚本编译和执行 – 实际运行此类脚本。
考虑到所有这些,最好将项目拆分为两个模块。
开始之前
下载并安装最新版本的 IntelliJ IDEA。
创建项目
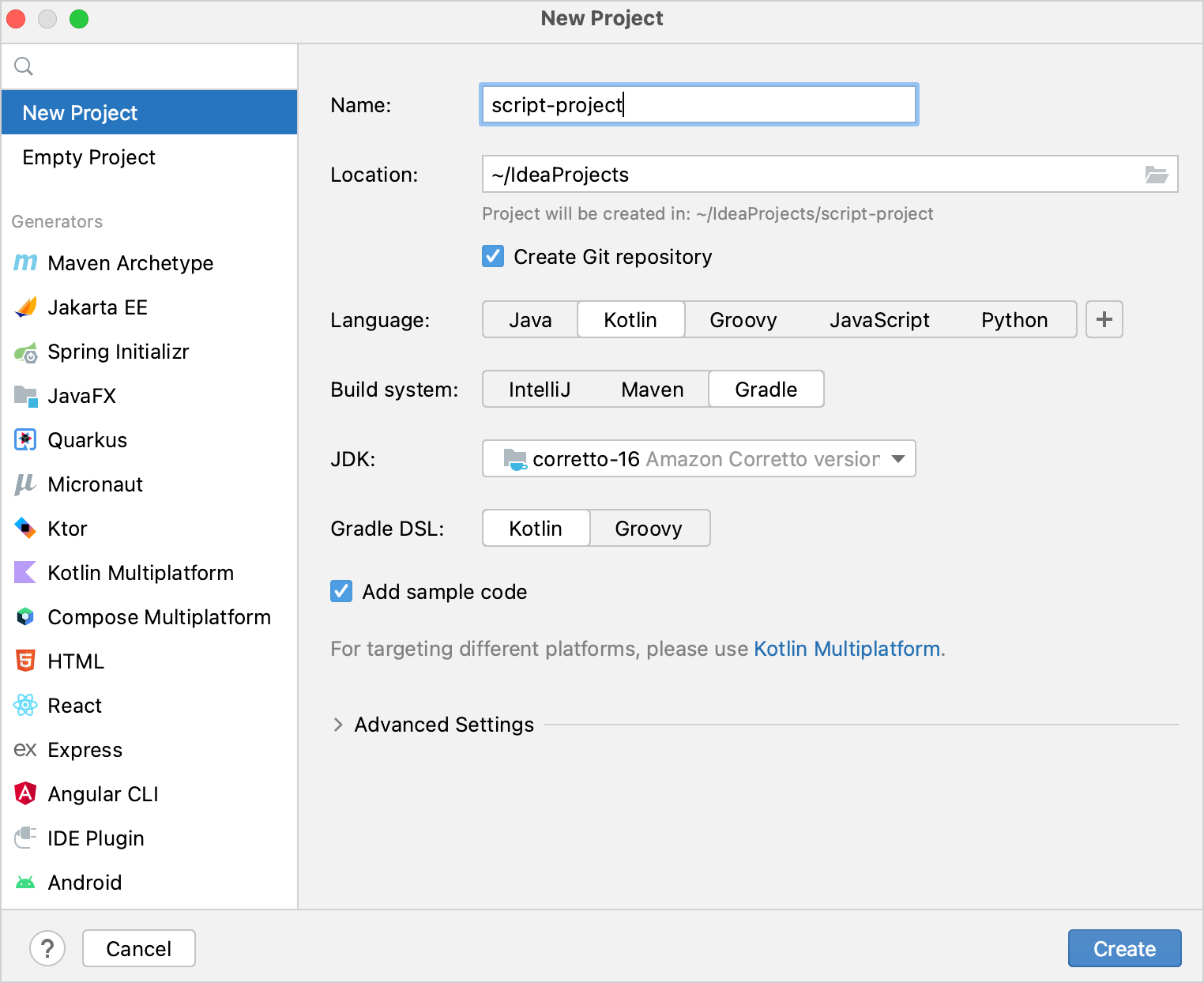
在 IntelliJ IDEA 中,选择 File | New | Project。
在左侧面板中,选择 New Project。
命名新项目并在必要时更改其位置。
勾选 Create Git repository 复选框可将新项目置于版本控制下。您可以在任何时候进行此操作。
从 Language 列表中,选择 Kotlin。
选择 Gradle 构建系统。
从 JDK 列表中,选择要在项目中使用的 JDK。
- 如果 JDK 已安装在您的计算机上,但在 IDE 中未定义,请选择 Add JDK 并指定 JDK 主目录的路径。
- 如果您的计算机上没有必要的 JDK,请选择 Download JDK。
选择 Kotlin 或 Gradle 语言作为 Gradle DSL。
单击 Create。
添加脚本模块
现在您有了一个空的 Kotlin/JVM Gradle 项目。添加所需的模块,脚本定义和脚本宿主:
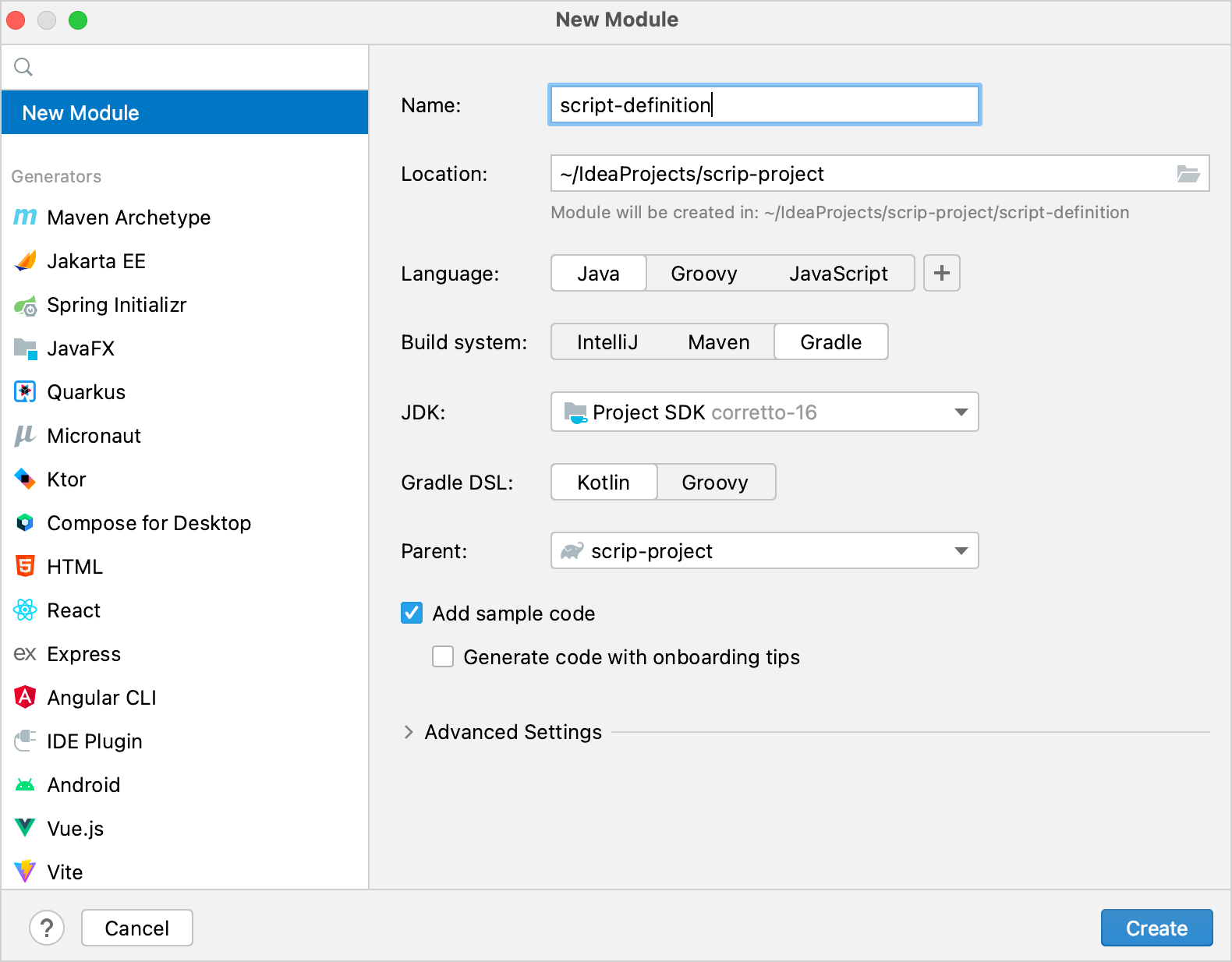
在 IntelliJ IDEA 中,选择 File | New | Module。
在左侧面板中,选择 New Module。此模块将作为脚本定义。
命名新模块并在必要时更改其位置。
从 Language 列表中,选择 Java。
如果您想用 Kotlin 编写构建脚本,请选择 Gradle 构建系统和 Kotlin 作为 Gradle DSL。
选择根模块作为模块的父级。
单击 Create。
在模块的
build.gradle(.kts)文件中,移除 Kotlin Gradle 插件的version。它已在根项目的构建脚本中。再次重复上述步骤,为脚本宿主创建一个模块。
项目应具有以下结构:
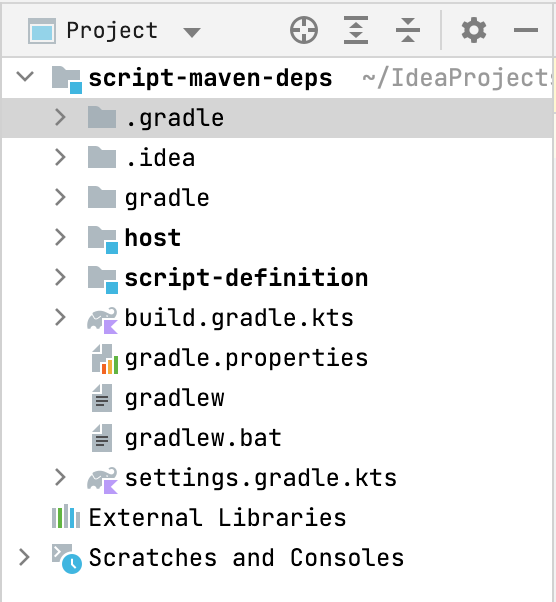
您可以在 kotlin-script-examples GitHub 版本库 中找到此类项目的示例以及更多 Kotlin 脚本示例。
创建脚本定义
首先,定义脚本类型:开发者可在此类脚本中编写的内容以及如何处理它。 在本教程中,这包括对脚本中 @Repository 和 @DependsOn 注解的支持。
在脚本定义模块中,将对 Kotlin 脚本组件的依赖项添加到
build.gradle(.kts)的dependencies代码块中。这些依赖项提供了脚本定义所需的 API:kotlindependencies { implementation("org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-scripting-common") implementation("org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-scripting-jvm") implementation("org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-scripting-dependencies") implementation("org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-scripting-dependencies-maven") // 此特定定义需要 coroutines 依赖项 implementation("org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-coroutines-core:1.10.2") }groovydependencies { implementation 'org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-scripting-common' implementation 'org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-scripting-jvm' implementation 'org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-scripting-dependencies' implementation 'org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-scripting-dependencies-maven' // 此特定定义需要 coroutines 依赖项 implementation 'org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-coroutines-core:1.10.2' }在模块中创建
src/main/kotlin/目录并添加一个 Kotlin 源文件,例如scriptDef.kt。在
scriptDef.kt中,创建一个类。它将是此类脚本的超类,因此将其声明为abstract或open。kotlin// 此类脚本的 abstract (或 open) 超类 abstract class ScriptWithMavenDeps此类稍后也将作为脚本定义的引用。
要将该类设为脚本定义,请使用
@KotlinScript注解标记它。向注解传递两个形参:fileExtension– 一个以.kts结尾的字符串,定义了此类脚本的文件扩展名。compilationConfiguration– 一个扩展ScriptCompilationConfiguration的 Kotlin 类,定义了此脚本类型的编译细节。您将在下一步创建它。
kotlin// @KotlinScript 注解标记脚本定义类 @KotlinScript( // 脚本类型的文件扩展名 fileExtension = "scriptwithdeps.kts", // 脚本类型的编译配置 compilationConfiguration = ScriptWithMavenDepsConfiguration::class ) abstract class ScriptWithMavenDeps object ScriptWithMavenDepsConfiguration: ScriptCompilationConfiguration()在本教程中,我们只提供可运行的代码,不解释 Kotlin 脚本 API。 您可以在 GitHub 上找到带有详细解释的相同代码。
如下所示定义脚本编译配置。
kotlinobject ScriptWithMavenDepsConfiguration : ScriptCompilationConfiguration( { // 此脚本类型的所有脚本的隐式导入 defaultImports(DependsOn::class, Repository::class) jvm { // 从上下文类加载器提取整个类路径并用作依赖项 dependenciesFromCurrentContext(wholeClasspath = true) } // 回调 refineConfiguration { // 使用提供的处理程序处理指定注解 onAnnotations(DependsOn::class, Repository::class, handler = ::configureMavenDepsOnAnnotations) } } )configureMavenDepsOnAnnotations函数如下:kotlin// 即时重新配置编译的处理程序 fun configureMavenDepsOnAnnotations(context: ScriptConfigurationRefinementContext): ResultWithDiagnostics<ScriptCompilationConfiguration> { val annotations = context.collectedData?.get(ScriptCollectedData.collectedAnnotations)?.takeIf { it.isNotEmpty() } ?: return context.compilationConfiguration.asSuccess() return runBlocking { resolver.resolveFromScriptSourceAnnotations(annotations) }.onSuccess { context.compilationConfiguration.with { dependencies.append(JvmDependency(it)) }.asSuccess() } } private val resolver = CompoundDependenciesResolver(FileSystemDependenciesResolver(), MavenDependenciesResolver())您可以在此处找到完整的代码。
创建脚本宿主
下一步是创建脚本宿主 – 处理脚本执行的组件。
在脚本宿主模块中,将依赖项添加到
build.gradle(.kts)的dependencies代码块中:- 提供脚本宿主所需 API 的 Kotlin 脚本组件
- 您之前创建的脚本定义模块
kotlindependencies { implementation("org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-scripting-common") implementation("org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-scripting-jvm") implementation("org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-scripting-jvm-host") implementation(project(":script-definition")) // 脚本定义模块 }groovydependencies { implementation 'org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-scripting-common' implementation 'org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-scripting-jvm' implementation 'org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-scripting-jvm-host' implementation project(':script-definition') // 脚本定义模块 }在模块中创建
src/main/kotlin/目录并添加一个 Kotlin 源文件,例如host.kt。定义应用程序的
main函数。在其主体中,检测它是否有一个实参 – 脚本文件的路径 – 然后执行脚本。您将在下一步的单独函数evalFile中定义脚本执行。目前将其声明为空。main函数可以如下所示:kotlinfun main(vararg args: String) { if (args.size != 1) { println("用法:<应用程序> <脚本文件>") } else { val scriptFile = File(args[0]) println("正在执行脚本 $scriptFile") evalFile(scriptFile) } }定义脚本求值函数。这是您将使用脚本定义的地方。通过调用
createJvmCompilationConfigurationFromTemplate并将脚本定义类作为类型形参来获取它。然后调用BasicJvmScriptingHost().eval,向其传递脚本代码及其编译配置。eval返回ResultWithDiagnostics的实例,因此将其设置为函数返回类型。kotlinfun evalFile(scriptFile: File): ResultWithDiagnostics<EvaluationResult> { val compilationConfiguration = createJvmCompilationConfigurationFromTemplate<ScriptWithMavenDeps>() return BasicJvmScriptingHost().eval(scriptFile.toScriptSource(), compilationConfiguration, null) }调整
main函数以打印脚本执行信息:kotlinfun main(vararg args: String) { if (args.size != 1) { println("用法:<应用程序> <脚本文件>") } else { val scriptFile = File(args[0]) println("正在执行脚本 $scriptFile") val res = evalFile(scriptFile) res.reports.forEach { if (it.severity > ScriptDiagnostic.Severity.DEBUG) { println(" : ${it.message}" + if (it.exception == null) "" else ": ${it.exception}") } } } }
您可以在此处找到完整的代码。
运行脚本
要检测脚本宿主的工作方式,请准备要执行的脚本和运行配置。
在项目根目录中创建文件
html.scriptwithdeps.kts,内容如下:kotlin@file:Repository("https://maven.pkg.jetbrains.space/public/p/kotlinx-html/maven") @file:DependsOn("org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-html-jvm:0.7.3") import kotlinx.html.*; import kotlinx.html.stream.*; import kotlinx.html.attributes.* val addressee = "World" print( createHTML().html { body { h1 { +"Hello, $addressee!" } } } )它使用了
kotlinx-html-jvm库中的函数,该库在@DependsOn注解实参中被引用。创建启动脚本宿主并执行此文件的运行配置:
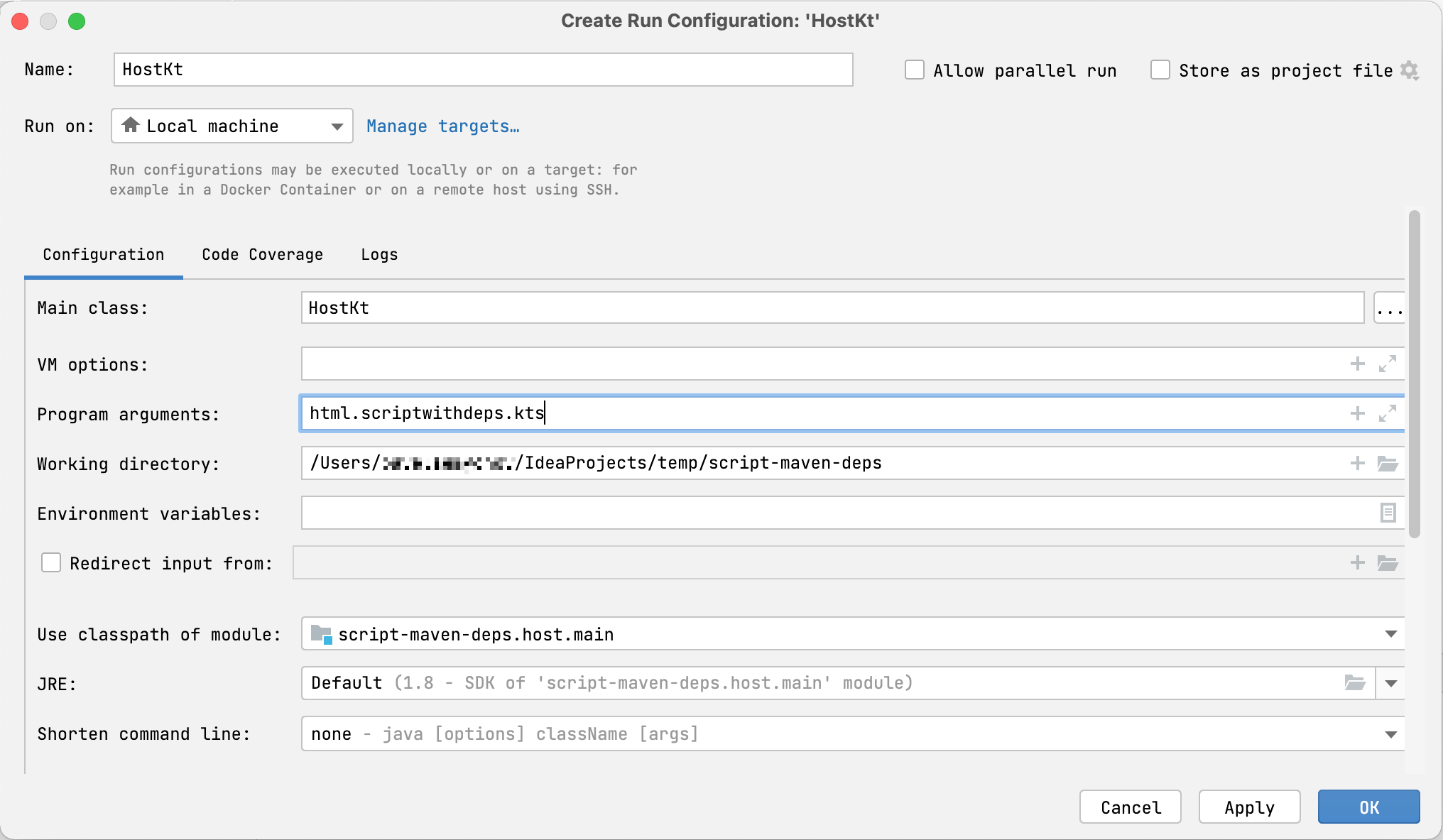
- 打开
host.kt并导航到main函数。它的左侧有一个 Run 边栏图标。 - 右键单击边栏图标并选择 Modify Run Configuration。
- 在 Create Run Configuration 对话框中,将脚本文件名添加到 Program arguments 中,然后单击 OK。
- 打开
运行创建的配置。
您将看到脚本如何执行,解析指定版本库中对 kotlinx-html-jvm 的依赖项,并打印调用其函数的结果:
<html>
<body>
<h1>Hello, World!</h1>
</body>
</html>首次运行时,解析依赖项可能需要一些时间。后续运行将快得多,因为它们使用从本地 Maven 版本库下载的依赖项。
下一步?
创建简单的 Kotlin 脚本项目后,请查找有关此主题的更多信息:
- 阅读 Kotlin 脚本 KEEP
- 浏览更多 Kotlin 脚本示例
- 观看 Rodrigo Oliveira 的演讲 Implementing the Gradle Kotlin DSL
