Kotlin Notebook 中使用 Kandy 进行数据可视化
Kotlin 提供了一个一站式解决方案,用于强大而灵活的数据可视化,以直观的方式呈现和探索数据,然后再深入复杂的模型。
本教程演示了如何在 IntelliJ IDEA 中使用 Kotlin Notebook 结合 Kandy 和 Kotlin DataFrame 库创建不同类型的图表。
开始之前
Kotlin Notebook 依赖于 Kotlin Notebook 插件,该插件在 IntelliJ IDEA 中默认捆绑并启用。
如果 Kotlin Notebook 特性不可用,请确保插件已启用。有关更多信息,请参见设置环境。
创建新的 Kotlin Notebook:
选择 File | New | Kotlin Notebook。
在你的 Notebook 中,通过运行以下命令导入 Kandy 和 Kotlin DataFrame 库:
kotlin%use kandy %use dataframe
创建 DataFrame
首先创建包含要可视化记录的 DataFrame。此 DataFrame 存储了柏林、马德里和加拉加斯三个城市的月平均温度模拟数据。
使用 Kotlin DataFrame 库中的 dataFrameOf() 函数生成 DataFrame。在 Kotlin Notebook 中运行以下代码片段:
// The months variable stores a list with the 12 months of the year
val months = listOf(
"January", "February",
"March", "April", "May",
"June", "July", "August",
"September", "October", "November",
"December"
)
// The tempBerlin, tempMadrid, and tempCaracas variables store a list with temperature values for each month
val tempBerlin =
listOf(-0.5, 0.0, 4.8, 9.0, 14.3, 17.5, 19.2, 18.9, 14.5, 9.7, 4.7, 1.0)
val tempMadrid =
listOf(6.3, 7.9, 11.2, 12.9, 16.7, 21.1, 24.7, 24.2, 20.3, 15.4, 9.9, 6.6)
val tempCaracas =
listOf(27.5, 28.9, 29.6, 30.9, 31.7, 35.1, 33.8, 32.2, 31.3, 29.4, 28.9, 27.6)
// The df variable stores a DataFrame of three columns, including records of months, temperature, and cities
val df = dataFrameOf(
"Month" to months + months + months,
"Temperature" to tempBerlin + tempMadrid + tempCaracas,
"City" to List(12) { "Berlin" } + List(12) { "Madrid" } + List(12) { "Caracas" }
)通过查看前四行来探查新 DataFrame 的结构:
df.head(4)你可以看到 DataFrame 有三列:Month、Temperature 和 City。DataFrame 的前四行包含柏林从一月到四月的温度记录:
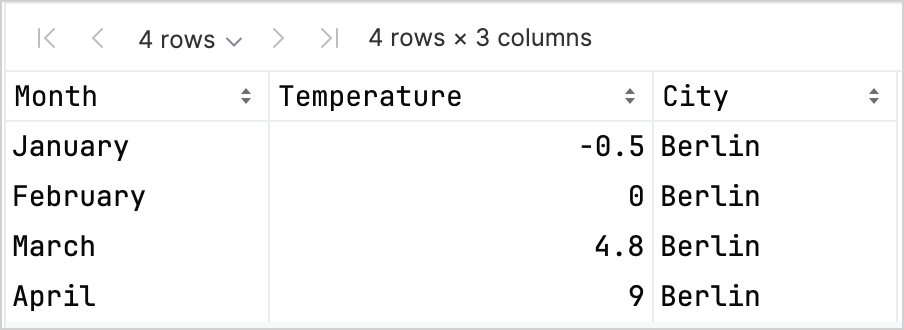
有不同的选项可以访问列的记录,这有助于你在同时使用 Kandy 和 Kotlin DataFrame 库时提高类型安全性。 有关更多信息,请参见 访问 API。
创建折线图
让我们使用上一节中的 df DataFrame 在 Kotlin Notebook 中创建折线图。
使用 Kandy 库中的 plot() 函数。在 plot() 函数中,指定图表类型(在本例中为 line)以及 X 轴和 Y 轴的值。你可以自定义颜色和大小:
df.plot {
line {
// 访问 DataFrame 中用于 X 轴和 Y 轴的列
x(Month)
y(Temperature)
// 访问 DataFrame 中用于分类的列并为这些分类设置颜色
color(City) {
scale = categorical("Berlin" to Color.PURPLE, "Madrid" to Color.ORANGE, "Caracas" to Color.GREEN)
}
// 自定义线的尺寸
width = 1.5
}
// 自定义图表的布局尺寸
layout.size = 1000 to 450
}结果如下:
创建点图
现在,让我们在点图(散点图)中可视化 df DataFrame。
在 plot() 函数中,指定 points 图表类型。添加 X 轴和 Y 轴的值以及 df 列中的分类值。你还可以为图表添加标题:
df.plot {
points {
// 访问 DataFrame 中用于 X 轴和 Y 轴的列
x(Month) { axis.name = "Month" }
y(Temperature) { axis.name = "Temperature" }
// 自定义点的大小
size = 5.5
// 访问 DataFrame 中用于分类的列并为这些分类设置颜色
color(City) {
scale = categorical("Berlin" to Color.LIGHT_GREEN, "Madrid" to Color.BLACK, "Caracas" to Color.YELLOW)
}
}
// 添加图表标题
layout.title = "Temperature per month"
}结果如下:
创建条形图
最后,让我们使用与之前图表相同的数据创建一个按城市分组的条形图。对于颜色,你还可以使用十六进制代码:
// 按城市分组
df.groupBy { City }.plot {
// 添加图表标题
layout.title = "Temperature per month"
bars {
// 访问 DataFrame 中用于 X 轴和 Y 轴的列
x(Month)
y(Temperature)
// 访问 DataFrame 中用于分类的列并为这些分类设置颜色
fillColor(City) {
scale = categorical(
"Berlin" to Color.hex("#6F4E37"),
"Madrid" to Color.hex("#C2D4AB"),
"Caracas" to Color.hex("#B5651D")
)
}
}
}结果如下:
接下来
- 探查 Kandy 库文档中的更多图表示例
- 探查 Lets-Plot 库文档中的更多高级绘图选项
- 在 Kotlin DataFrame 库文档中查找有关创建、探查和管理数据帧的更多信息。
- 在此 YouTube 视频中了解更多有关 Kotlin Notebook 数据可视化的信息。
